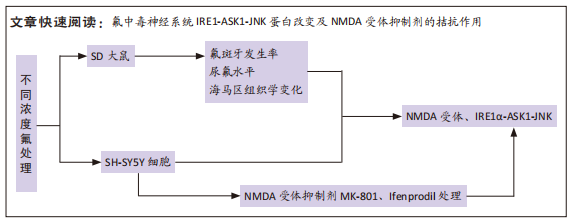
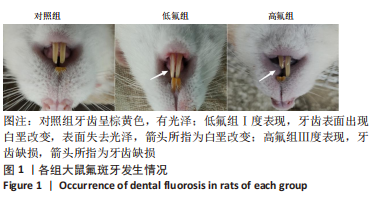
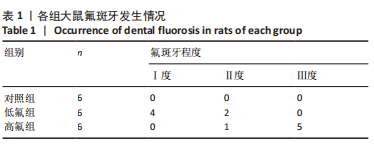
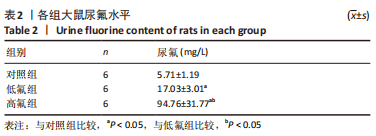
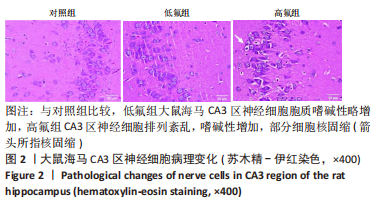
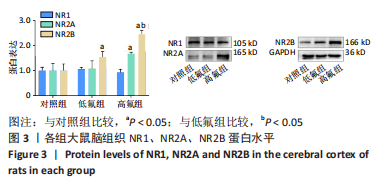
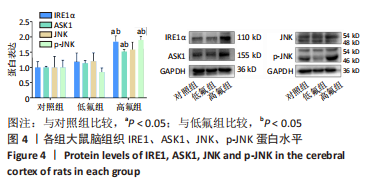
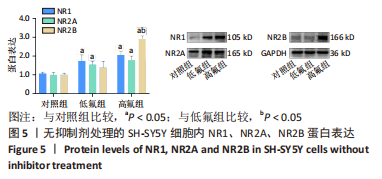
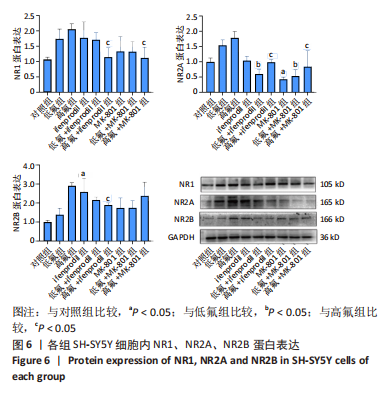
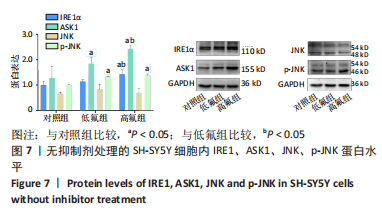
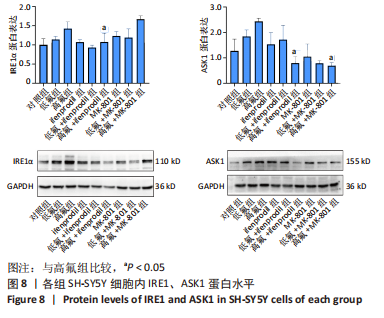
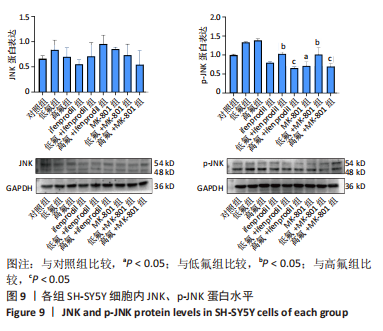
[1] JOHNSTON NR, STROBEL SA. Principles of fluoride toxicity and the cellular response: a review. Arch Toxicol. 2020;94(4):1051-1069.
[2] VALDEZ-JIMÉNEZ L, SORIA FREGOZO C, MIRANDA BELTRÁN ML, et al. Effects of the fluoride on the central nervous system. Neurologia. 2011;26(5):297-300.
[3] GRANDJEAN P. Developmental fluoride neurotoxicity: an updated review. Environ Health. 2019;18(1):110.
[4] ŻWIEREŁŁO W, MARUSZEWSKA A, SKÓRKA-MAJEWICZ M, et al. Fluoride in the Central Nervous System and Its Potential Influence on the Development and Invasiveness of Brain Tumours-A Research Hypothesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(2): 1558.
[5] NAGENDRA AH, BOSE B, SHENOY PS. Recent advances in cellular effects of fluoride: an update on its signalling pathway and targeted therapeutic approaches. Mol Biol Rep. 2021;48(7):5661-5673.
[6] DEC K, ŁUKOMSKA A, SKONIECZNA-ŻYDECKA K, et al. Chronic Exposure to Fluoride Affects GSH Level and NOX4 Expression in Rat Model of This Element of Neurotoxicity. Biomolecules. 2020;10(3):422.
[7] BOOKER SA, WYLLIE DJA. NMDA receptor function in inhibitory neurons. Neuropharmacology. 2021;196:108609.
[8] CHENG F, DU L, KIM JJ, et al. NMDA and AMPA receptor physiology and role in visceral hypersensitivity: a review. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;34(5):471-477.
[9] ALKADHI KA. NMDA receptor-independent LTP in mammalian nervous system. Prog Neurobiol. 2021;200:101986.
[10] PHILLIPS BP, GOMEZ-NAVARRO N, MILLER EA. Protein quality control in the endoplasmic reticulum. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2020;65:96-102.
[11] PARK SJ, LI C, CHEN YM. Endoplasmic Reticulum Calcium Homeostasis in Kidney Disease: Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Targets. Am J Pathol. 2021;191(2):256-265.
[12] ZHANG IX, RAGHAVAN M, SATIN LS. The Endoplasmic Reticulum and Calcium Homeostasis in Pancreatic Beta Cells. Endocrinology. 2020;161(2):bqz028.
[13] SUN F, LI X, YANG C, et al. A role for PERK in the mechanism underlying fluoride-induced bone turnover. Toxicology. 2014;325:52-66.
[14] QIU LL, PAN W, LUO D, et al. Dysregulation of BDNF/TrkB signaling mediated by NMDAR/Ca2+/calpain might contribute to postoperative cognitive dysfunction in aging mice. J Neuroinflammation. 2020;17(1):23.
[15] ZHOU L, DUAN J. The NMDAR GluN1-1a C-terminus binds to CaM and regulates synaptic function. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021;534:323-329.
[16] WEGEHAUPT F, MENGHINI G. Fluoride Update. Swiss Dent J. 2020;130(9):677-683.
[17] SRIVASTAVA S, FLORA SJS. Fluoride in Drinking Water and Skeletal Fluorosis: a Review of the Global Impact. Curr Environ Health Rep. 2020;7(2):140-146.
[18] AGALAKOVA NI, NADEI OV. Inorganic fluoride and functions of brain. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2020;50(1):28-46.
[19] REN C, LI HH, ZHANG CY, et al. Effects of chronic fluorosis on the brain. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2022;244:114021.
[20] WANG J, YUE B, ZHANG X, et al. Effect of exercise on microglial activation and transcriptome of hippocampus in fluorosis mice. Sci Total Environ. 2021;760:143376.
[21] WEI W, PANG S, SUN D. The pathogenesis of endemic fluorosis: Research progress in the last 5 years. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(4):2333-2342.
[22] GU LS, WEI X, LING JQ. Etiology, diagnosis, prevention and treatment of dental fluorosis. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2020;55(5):296-301.
[23] DA SILVA JAC, SCHRÖDER N. The Role of Ca2+ Permeable AMPA Receptors in Neurodegeneration, Neurotoxicity, and Neuroinflammation. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2023;22(5):624-633.
[24] 孙丽丛, 张丹参, 景永帅. NMDA受体对中枢神经系统的影响[J]. 中国药理学与毒理学杂志,2021,35(9):641.
[25] CERCATO MC, COLETTIS N, SNITCOFSKY M, et al. Hippocampal NMDA receptors and the previous experience effect on memory. J Physiol Paris. 2014;108(4-6): 263-269.
[26] GROENENDYK J, AGELLON LB, MICHALAK M. Calcium signaling and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2021;363:1-20.
[27] WANG X, ENO CO, ALTMAN BJ, et al. ER stress modulates cellular metabolism. Biochem J. 2011;435(1):285-296.
[28] HETZ C, ZHANG K, KAUFMAN RJ. Mechanisms, regulation and functions of the unfolded protein response. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020;21(8):421-438.
[29] AJOOLABADY A, LINDHOLM D, REN J, et al. ER stress and UPR in Alzheimer’s disease: mechanisms, pathogenesis, treatments. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13(8):706.
[30] GONG J, WANG XZ, WANG T, et al. Molecular signal networks and regulating mechanisms of the unfolded protein response. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2017;18(1): 1-14.
[31] DI CONZA G, HO PC. ER Stress Responses: An Emerging Modulator for Innate Immunity. Cells. 2020;9(3):695.
[32] 李林江,万生芳,李荣科,等.基于ATF6/CHOP通路的红芪多糖对糖尿病胃轻瘫大鼠胃窦组织平滑肌的影响[J].中国中医药信息杂志,2022,29(11):67-72.
[33] 曹洁,姚隆 .PERK/ATF4/CHOP信号通路在饱和脂肪酸诱导肝细胞脂毒性凋亡中的作用[J].中国生物制品学杂志,2017,30(8):811-818.
[34] 温建霞,何丽,冯江龙,等.不同剂量氟对大鼠肾皮质IRE1α-ASK1-JNK蛋白表达的影响[J].中华地方病学杂志,2022,41(2):100-104.
[35] XU F, TONG M, TONG CSW, et al. A Combinatorial CRISPR-Cas9 Screen Identifies Ifenprodil as an Adjunct to Sorafenib for Liver Cancer Treatment. Cancer Res. 2021;81(24):6219-6232.
[36] DANNENHOFFER CA, WERNER DF, VARLINSKAYA EI, et al. Adolescent intermittent ethanol exposure does not alter responsiveness to ifenprodil or expression of vesicular GABA and glutamate transporters. Dev Psychobiol. 2021;63(5):903-914.
[37] ZHANG C, ZHANG Y, QIN Y, et al. Ifenprodil and Flavopiridol Identified by Genomewide RNA Interference Screening as Effective Drugs To Ameliorate Murine Acute Lung Injury after Influenza A H5N1 Virus Infection. mSystems. 2019;4(6):e00431.
[38] SONG X, JENSEN MØ, JOGINI V, et al. Mechanism of NMDA receptor channel block by MK-801 and memantine. Nature. 2018;556(7702):515-519.
[39] KRUK-SLOMKA M, BIALA G. Cannabidiol Attenuates MK-801-Induced Cognitive Symptoms of Schizophrenia in the Passive Avoidance Test in Mice. Molecules. 2021;26(19):5977.
[40] SAOUD H, KERESELIDZE E, EYBRARD S, et al. MK-801-induced behavioral and dopaminergic responses in the shell part of the nucleus accumbens in adult male rats are disrupted after neonatal blockade of the ventral subiculum. Neurochem Int. 2021;150:105195.
|