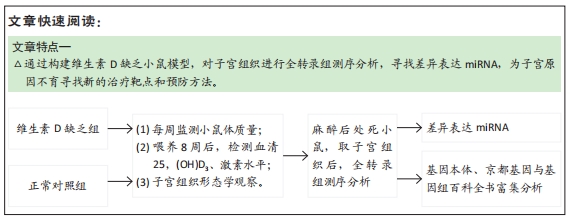
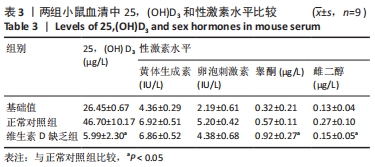
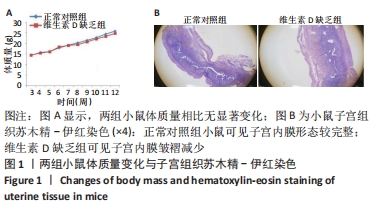
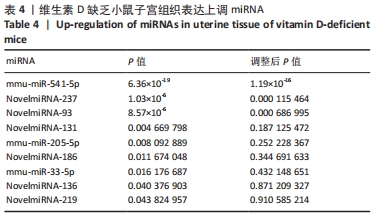
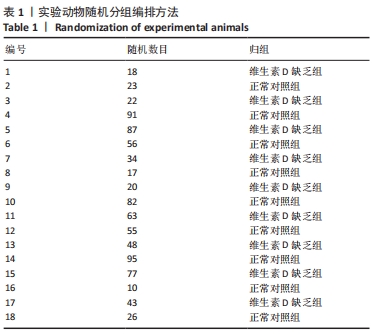
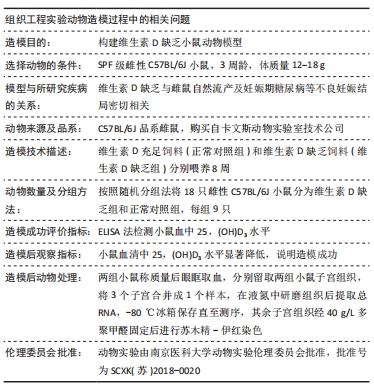
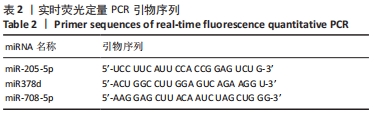
[1] LI G, LIN L, WANG YL, et al. 1,25(OH)2D3 Protects Trophoblasts Against Insulin Resistance and Inflammation Via Suppressing mTOR Signaling. Reprod Sci. 2019; 26(2):223-232.
[2] SUN J. Dietary vitamin D, vitamin D receptor, and microbiome. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2018; 21(6):471-474.
[3] LEI M, LIU Z, GUO J. The Emerging Role of Vitamin D and Vitamin D Receptor in Diabetic Nephropathy. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:4137268.
[4] FOGACCI S, FOGACCI F, BANACH M, et al. Vitamin D supplementation and incident preeclampsia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Clin Nutr. 2020;39(6):1742-1752.
[5] 汤斐, 赵云.子宫动脉介入栓塞合并氨甲喋呤注射在胎盘完全滞留中的应用[J].中华卫生应急电子杂志,2019,5(3):141-146.
[6] AGARWAL S, KOVILAM O, AGRAWAL DK. Vitamin D and its impact on maternal-fetal outcomes in pregnancy: A critical review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2018;58(5): 755-769.
[7] PURSWANI JM, GALA P, DWARKANATH P, et al. The role of vitamin D in pre-eclampsia: a systematic review. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2017;17(1):231.
[8] BENACHI A, BAPTISTE A, TAIEB J, et al. Relationship between vitamin D status in pregnancy and the risk for preeclampsia: A nested case-control study. Clin Nutr. 2020;39(2):440-446.
[9] VAN SCHOOR N, LIPS P. Global Overview of Vitamin D Status. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2017;46(4):845-870.
[10] ZHANG X, JI S, CAI G, et al. H19 Increases IL-17A/IL-23 Releases via Regulating VDR by Interacting with miR675-5p/miR22-5p in Ankylosing Spondylitis. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020;19:393-404.
[11] 袁长深, 容伟明, 卢智贤, 等. 基于生物信息学构建骨肉瘤miRNA-mRNA的调控网络[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021,25(17):2740-2746.
[12] KLIMAN HJ, FRANKFURTER D. Clinical approach to recurrent implantation failure: evidence-based evaluation of the endometrium. Fertil Steril. 2019;111(4):618-628.
[13] MARQUARDT RM, KIM TH, SHIN JH, et al. Progesterone and Estrogen Signaling in the Endometrium: What Goes Wrong in Endometriosis? Int J Mol Sci. 2019; 20(15):3822.
[14] AGIC A, XU H, ALTGASSEN C, et al. Relative expression of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptor, vitamin D 1 alpha-hydroxylase, vitamin D 24-hydroxylase, and vitamin D 25-hydroxylase in endometriosis and gynecologic cancers. Reprod Sci. 2007;14(5):486-497.
[15] MUSCOGIURI G, ALTIERI B, DE ANGELIS C, et al. Shedding new light on female fertility: The role of vitamin D. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2017;18(3):273-283.
[16] 王波, 王雪云. 维生素D缺乏影响受孕及胚胎发育的小鼠动物模型研究[J]. 分子诊断与治疗杂志,2016,8(5):341-345+360.
[17] AUGUSTE A, BESSIÈRE L, TODESCHINI AL, et al. Molecular analyses of juvenile granulosa cell tumors bearing AKT1 mutations provide insights into tumor biology and therapeutic leads. Hum Mol Genet. 2015;24(23):6687-6698.
[18] 黄冬梅, 黄光英, 陆付耳. 胚泡围着床期子宫内膜细胞的增殖分化与凋亡[J]. 生殖医学杂志,2004,13(5):313-316.
[19] NEGAMI AI. Implantation model in vitro. Nihon Sanka Fujinka Gakkai Zasshi. 1992; 44(8):949-959.
[20] FUNG JL, HARTMAN TJ, SCHLEICHER RL, et al. Association of vitamin D intake and serum levels with fertility: results from the Lifestyle and Fertility Study. Fertil Steril. 2017;108(2):302-311.
[21] 张迪, 苏姗, 王强梅, 等. 维生素D 与多囊卵巢综合征关系的研究进展[J]. 徐州医科大学学报,2021,41(1):76-78.
[22] LIANG Y, RIDZON D, WONG L, et al. Characterization of microRNA expression profiles in normal human tissues. BMC Genomics. 2007;8:166.
[23] WANG B, CRUZ ITHIER M, PAROBCHAK N, et al. Vitamin D stimulates multiple microRNAs to inhibit CRH and other pro-labor genes in human placenta. Endocr Connect. 2018;7(12):1380-1388.
[24] QI Y, WANG D, HUANG W, et al. CyclinD1 inhibits dicer and crucial miRNA expression by chromatin modification to promote the progression of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019;38(1):413.
[25] XIN W, LIU X, DING J, et al. Long non-coding RNA derived miR-205-5p modulates human endometrial cancer by targeting PTEN. Am J Transl Res. 2015;7(11):2433-2441.
[26] ABDELGHAFFAR S, SHORA H, ABDELATTY S, et al. MicroRNAs and Risk Factors for Diabetic Nephropathy in Egyptian Children and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2020; 13: 2485-2494.
[27] LAN L, LIANG Z, ZHAO Y, et al. LncRNA MCM3AP-AS1 inhibits cell proliferation in cervical squamous cell carcinoma by down-regulating miRNA-93. Biosci Rep. 2020;40(2):BSR20193794.
[28] LIN L, SUN J, WU D, et al. MicroRNA-186 is associated with hypoxia-inducible factor-1α expression in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2019;7(3):e531.
[29] MOTAWI T, SABRY D, MAURICE NW, et al. Role of mesenchymal stem cells exosomes derived microRNAs; miR-136, miR-494 and miR-495 in pre-eclampsia diagnosis and evaluation. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2018;659:13-21.
[30] CHEN X, HUANG Z, CHEN R. Microrna-136 promotes proliferation and invasion ingastric cancer cells through Pten/Akt/P-Akt signaling pathway. Oncol Lett. 2018; 15(4):4683-4689.
[31] ISHIDA M, SHIMABUKURO M, YAGI S, et al. MicroRNA-378 regulates adiponectin expression in adipose tissue: a new plausible mechanism. PLoS One. 2014;9(11): e111537.
[32] MEERSON A, ELIRAZ Y, YEHUDA H, et al. Obesity impacts the regulation of miR-10b and its targets in primary breast tumors. BMC Cancer. 2019;19(1):86.
[33] GUNGORMEZ C, GUMUSHAN AKTAS H, DILSIZ N, et al. Novel miRNAs as potential biomarkers in stage II colon cancer: microarray analysis. Mol Biol Rep. 2019;46(4): 4175-4183.
[34] ZOU X, WANG J, QU H, et al. Comprehensive analysis of miRNAs, lncRNAs, and mRNAs reveals potential players of sexually dimorphic and left-right asymmetry in chicken gonad during gonadal differentiation. Poult Sci. 2020;99(5):2696-2707.
|