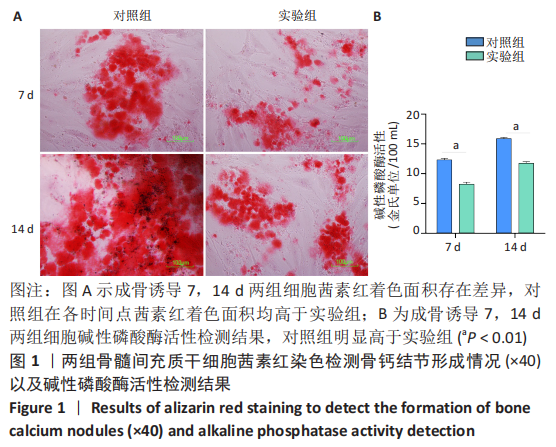
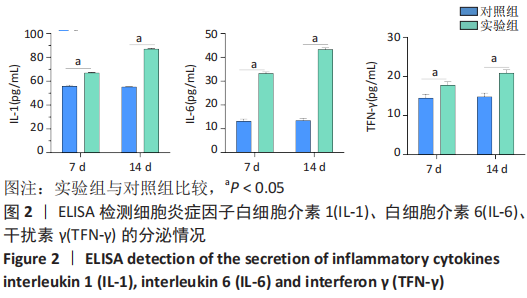
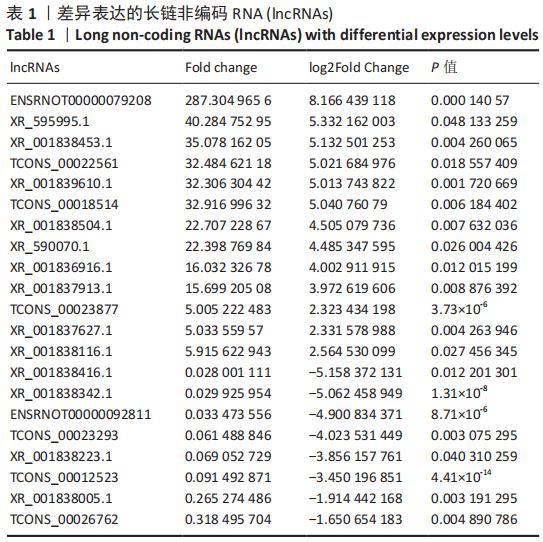
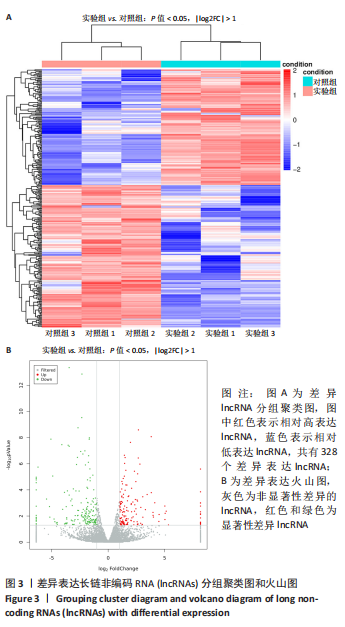
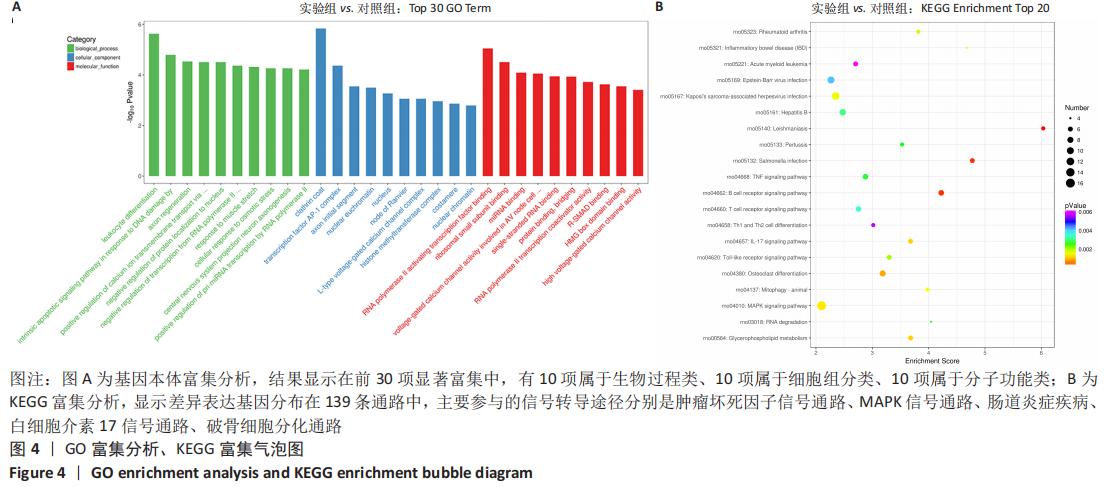
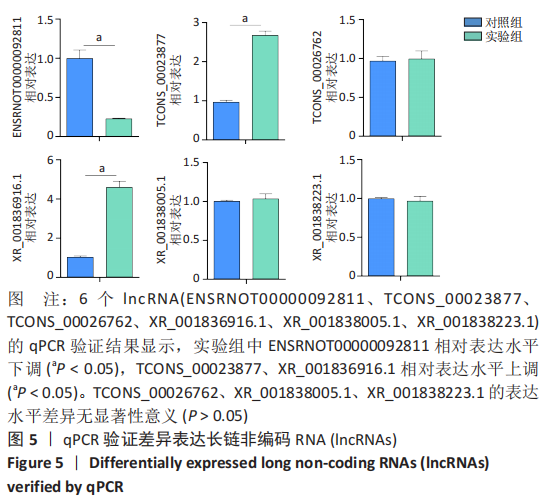
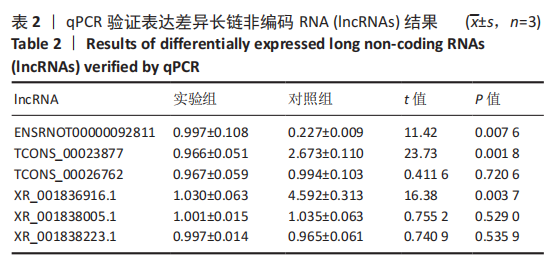
[1] BOFFELI TJ, LUER SA, BRETT KM, et al. A Review of Consecutive Cases to Identify the Rate of Underlying Osteomyelitis in Patients Undergoing Surgical Treatment of Gangrene of the Forefoot and Impact of Acute Infection on Outcome Following Amputation. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2022;61(2):286-292.
[2] CARUSO P, GICCHINO M, LONGO M, et al. When amputation is not the end of the challenge: A successful therapy for osteomyelitis and soft tissue infection in a patient with type 1 diabetes. J Diabetes Investig. 2022;13(1):209-212.
[3] CONCHA S, HERNÁNDEZ-OJEDA A, CONTRERAS O, et al. Chronic nonbacterial osteomyelitis in children: a multicenter case series. Rheumatol Int. 2020;40(1): 115-120.
[4] MORLEY R, ROTHWELL M, STEPHENSON J, et al. Complex Foot Infection Treated With Surgical Debridement and Antibiotic Loaded Calcium Sulfate-A Retrospective Cohort Study of 137 Cases. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2022;61(2):239-247.
[5] 马敬龙,阳富春.成人慢性骨髓炎的临床诊断和治疗进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2020,34(5):651-655.
[6] CROES M, VAN DER WAL BCH, VOGELY HC. Impact of Bacterial Infections on Osteogenesis: Evidence From In Vivo Studies. J Orthop Res. 2019;37(10):2067-2076.
[7] JIN T, LU Y, HE QX, et al. The Role of MicroRNA, miR-24, and Its Target CHI3L1 in Osteomyelitis Caused by Staphylococcus aureus. J Cell Biochem. 2015;116(12): 2804-2813.
[8] WEN H, CHEN Z, CUI Y, et al. LncRNA NONHSAT009968 inhibits the osteogenic differentiation of hBMMSCs in SA-induced inflammation via Wnt3a. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021;577:24-31.
[9] WU H, CAO F, ZHOU W, et al. Long Noncoding RNA FAM83H-AS1 Modulates SpA-Inhibited Osteogenic Differentiation in Human Bone Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Mol Cell Biol. 2020;40(5):e00362-19.
[10] FU W, HE W, REN Y, et al. Distinct expression trend of signature antigens of Staphylococcus aureus osteomyelitis correlated with clinical outcomes. J Orthop Res. 2021;39(2):265-273.
[11] JIN T, ZHU YL, LI J, et al. Staphylococcal protein A, Panton-Valentine leukocidin and coagulase aggravate the bone loss and bone destruction in osteomyelitis. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2013;32(2):322-333.
[12] 宋明瑞,侯毅龙,林艺煌,等.金黄色葡萄球菌感染所致骨量丢失的分子机制研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2021,23(4):349-358.
[13] 文强强,刘岩,苏子龙,等.金黄色葡萄球菌骨髓炎发病机制的研究进展[J].实用骨科杂志,2020,26(10):901-905.
[14] CHEN R, HUANG H, LIANG L, et al. Improving the repair mechanism and miRNA expression profile of tibial defect in rats based on silent information regulator 7 protein analysis of mesenchymal stem cells. Bioengineered. 2022;13(3):4674-4687.
[15] LIU Z, DENG Y, LI T, et al. The opposite functions of miR-24 in the osteogenesis and adipogenesis of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells are mediated by the HOXB7/β-catenin complex. FASEB J. 2020;34(7):9034-9050.
[16] TENG Z, ZHU Y, HAO Q, et al. Long non-coding RNA taurine upregulated gene 1 is downregulated in osteoporosis and influences the osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. PeerJ. 2021;9:e11251.
[17] TENG ZW, ZHU Y, NA Q, et al. Regulatory effect of miRNA on multi-directional differentiation ability of mesenchymal stem cell in treatment of osteoporosis. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2016;30(2):345-352.
[18] CUI Y, LU S, TAN H, et al. Silencing of Long Non-Coding RNA NONHSAT009968 Ameliorates the Staphylococcal Protein A-Inhibited Osteogenic Differentiation in Human Bone Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;39(4):1347-1359.
[19] YU G, WANG LG, HAN Y, et al. clusterProfiler: an R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. OMICS. 2012;16(5):284-287.
[20] JIN QY, ZHU QH, DENG W, et al. Follistatin-like 1 suppresses osteoblast differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal cells during inflammation. Arch Oral Biol. 2022;135:105345.
[21] KUANG W, ZHENG L, XU X, et al. Dysregulation of the miR-146a-Smad4 axis impairs osteogenesis of bone mesenchymal stem cells under inflammation. Bone Res. 2017;5:17037.
[22] ZHU K, YANG C, DAI H, et al. Crocin inhibits titanium particle-induced inflammation and promotes osteogenesis by regulating macrophage polarization. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;76:105865.
[23] GUO Y, SONG G, SUN M, et al. Prevalence and Therapies of Antibiotic-Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020;10:107.
[24] BASKAR K, ANUSUYA T, DEVANAND VENKATASUBBU G. Mechanistic investigation on microbial toxicity of nano hydroxyapatite on implant associated pathogens. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;73:8-14.
[25] DING R, WEI S, HUANG M. Long non-coding RNA KCNQ1OT1 overexpression promotes osteogenic differentiation of staphylococcus aureus-infected human bone mesenchymal stem cells by sponging microRNA miR-29b-3p. Bioengineered. 2022;13(3):5855-5867.
[26] KAVANAGH N, O’BRIEN FJ, KERRIGAN SW. Staphylococcus aureus protein A causes osteoblasts to hyper-mineralise in a 3D extra-cellular matrix environment. PLoS One. 2018;13(6):e0198837.
[27] REN LR, WANG H, HE XQ, et al. Staphylococcus aureus Protein A induces osteoclastogenesis via the NF‑κB signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16(5): 6020-6028.
[28] FAN Q, LI Y, SUN Q, et al. miR-532-3p inhibits osteogenic differentiation in MC3T3-E1 cells by downregulating ETS1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020; 525(2):498-504.
[29] JI Y, FANG QY, WANG SN, et al. Lnc-RNA BLACAT1 regulates differentiation of bone marrow stromal stem cells by targeting miR-142-5p in osteoarthritis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24(6):2893-2901.
[30] BEHERA J, KUMAR A, VOOR MJ, et al. Exosomal lncRNA-H19 promotes osteogenesis and angiogenesis through mediating Angpt1/Tie2-NO signaling in CBS-heterozygous mice. Theranostics. 2021;11(16):7715-7734.
[31] BAI Y, GONG X, DONG R, et al. Long non-coding RNA HCAR promotes endochondral bone repair by up regulating VEGF and MMP13 in hypertrophic chondrocyte through sponging miR-15b-5p. Genes Dis. 2020;9(2):456-465. |