[1] 孟昶,朱磊,田雪文,等. 低氧运动与DNA甲基化的研究进展[J]. 山东体育科技,2019, 41(5): 66-69.
[2] HUANG L, LI T, ZHOU M, et al. Hypoxia Improves Endurance Performance by Enhancing Short Chain Fatty Acids Production via Gut Microbiota Remodeling. Front Microbiol. 2021; 12:820691.
[3] 吴菊花,杨亚南,翁锡全,等. 低氧运动干预营养性肥胖模型大鼠骨骼肌能量代谢的变化[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2022,26(29):4598-4604.
[4] JUNG WS, KIM SW, PARK HY. Interval Hypoxic Training Enhances Athletic Performance and Does Not Adversely Affect Immune Function in Middle- and Long-Distance Runners. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(6):1934.
[5] SLIVKA D, DUMKE C, HAILES W, et al. Impact of Hypoxic Exercise Recovery on Skeletal Muscle Glycogen and Gene Expression. High Alt Med Biol. 2021;22(3):300-307.
[6] PEEK CB. Metabolic Implications of Circadian-HIF Crosstalk. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2020;31(6):459-468.
[7] OELKRUG R, POLYMEROPOULOS ET, JASTROCH M. Brown adipose tissue: physiological function and evolutionary significance. J Comp Physiol B. 2015;185(6):587-606.
[8] RUAS JL, WHITE JP, RAO RR, et al. A PGC-1alpha isoform induced by resistance training regulates skeletal muscle hypertrophy. Cell. 2012;151(6):1319-1331.
[9] MIURA S, KAWANAKA K, KAI Y, et al. An increase in murine skeletal muscle peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator-1alpha (PGC-1alpha) mRNA in response to exercise is mediated by beta-adrenergic receptor activation. Endocrinology. 2007;148(7): 3441-3448.
[10] REINKE H, ASHER G. Crosstalk between metabolism and circadian clocks. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019;20(4):227-241.
[11] SOLT LA, WANG Y, BANERJEE S, et al. Regulation of circadian behaviour and metabolism by synthetic REV-ERB agonists. Nature. 2012;485(7396):62-68.
[12] WOLDT E, SEBTI Y, SOLT LA, et al. Rev-erb-alpha modulates skeletal muscle oxidative capacity by regulating mitochondrial biogenesis and autophagy. Nat Med. 2013;19(8): 1039-1046.
[13] 冯俊鹏,路瑛丽,王雪冰,等. 低氧运动对肥胖大鼠 BAIBA 表达及白色脂肪棕色化的影响[J]. 中国体育科技,2022,58(1):1-8.
[14] 朱磊. 低氧训练诱导miR-27/PPARγ, miR-122/PPARβ调控肥胖大鼠肝脏脂代谢机理的研究[D]. 上海:上海体育学院,2016.
[15] LING J, BREY C, SCHILLING M, et al. Defective lipid metabolism associated with mutation in klf-2 and klf-3: important roles of essential dietary salts in fat storage. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2017;14:22.
[16] SLOT IG, SCHOLS AM, VOSSE BA, et al. Hypoxia differentially regulates muscle oxidative fiber type and metabolism in a HIF-1alpha-dependent manner. Cell Signal. 2014;26(9): 1837-1845.
[17] DE THEIJE CC, LANGEN RC, LAMERS WH, et al. Distinct responses of protein turnover regulatory pathways in hypoxia- and semistarvation-induced muscle atrophy. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2013;305(1):L82-L91.
[18] LAFONTAN M, LANGIN D. Lipolysis and lipid mobilization in human adipose tissue. Prog Lipid Res. 2009;48(5):275-297.
[19] PAGANO ES, SPINEDI E, GAGLIARDINO JJ. White Adipose Tissue and Circadian Rhythm Dysfunctions in Obesity: Pathogenesis and Available Therapies. Neuroendocrinology. 2017;104(4):347-363.
[20] ECKEL-MAHAN KL, PATEL VR, DE MATEO S, et al. Reprogramming of the circadian clock by nutritional challenge. Cell. 2013;155(7):1464-1478.
[21] LI D, IKAGA R, OGAWA H, et al. Different expressions of clock genes in fatty liver induced by high-sucrose and high-fat diets. Chronobiol Int. 2021;38(5):762-778.
[22] MCFADDEN E, JONES ME, SCHOEMAKER MJ, et al. The relationship between obesity and exposure to light at night: cross-sectional analyses of over 100,000 women in the Breakthrough Generations Study. Am J Epidemiol. 2014;180(3):245-250.
[23] TEIJEIRO A, GARRIDO A, FERRE A, et al. Inhibition of the IL-17A axis in adipocytes suppresses diet-induced obesity and metabolic disorders in mice. Nat Metab. 2021;3(4):496-512.
[24] PANG M, YANG J, RAO J, et al. Time-Dependent Changes in Increased Levels of Plasma Irisin and Muscle PGC-1alpha and FNDC5 after Exercise in Mice. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2018;244(2):93-103.
[25] KAYSER B, VERGES S. Hypoxia, energy balance and obesity: from pathophysiological mechanisms to new treatment strategies. Obes Rev. 2013;14(7):579-592.
[26] MONTANARI T, POSCIC N, COLITTI M. Factors involved in white-to-brown adipose tissue conversion and in thermogenesis: a review. Obes Rev. 2017;18(5):495-513.
[27] BOSTROM P, WU J, JEDRYCHOWSKI MP, et al. A PGC1-alpha-dependent myokine that drives brown-fat-like development of white fat and thermogenesis. Nature. 2012;481(7382):463-468.
[28] JAGER S, HANDSCHIN C, ST-PIERRE J, et al. AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) action in skeletal muscle via direct phosphorylation of PGC-1alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007; 104(29):12017-12022.
[29] HARDIE DG, SAKAMOTO K. AMPK: a key sensor of fuel and energy status in skeletal muscle. Physiology (Bethesda). 2006;21:48-60.
[30] FINCK BN, KELLY DP. PGC-1 coactivators: inducible regulators of energy metabolism in health and disease. J Clin Invest. 2006;116(3):615-622.
[31] MU WJ, ZHU JY, CHEN M, et al. Exercise-Mediated Browning of White Adipose Tissue: Its Significance, Mechanism and Effectiveness. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(21):11512.
[32] MARCHEVA B, RAMSEY KM, BUHR ED, et al. Disruption of the clock components CLOCK and BMAL1 leads to hypoinsulinaemia and diabetes. Nature. 2010;466(7306):627-631.
[33] LI X, XU M, WANG F, et al. Interaction of ApoA-IV with NR4A1 and NR1D1 Represses G6Pase and PEPCK Transcription: Nuclear Receptor-Mediated Downregulation of Hepatic Gluconeogenesis in Mice and a Human Hepatocyte Cell Line. PLoS One. 2015;10(11): e0142098.
[34] HASTINGS MH, REDDY AB, MAYWOOD ES. A clockwork web: circadian timing in brain and periphery, in health and disease. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2003;4(8):649-661.
[35] HOGENESCH JB, GU YZ, JAIN S, et al. The basic-helix-loop-helix-PAS orphan MOP3 forms transcriptionally active complexes with circadian and hypoxia factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998;95(10):5474-5479.
[36] TAYLOR BL, ZHULIN IB. PAS domains: internal sensors of oxygen, redox potential, and light. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 1999;63(2):479-506.
[37] ADAMOVICH Y, LADEUIX B, GOLIK M, et al. Rhythmic Oxygen Levels Reset Circadian Clocks through HIF1alpha. Cell Metab. 2017;25(1):93-101.
[38] WU Y, TANG D, LIU N, et al. Reciprocal Regulation between the Circadian Clock and Hypoxia Signaling at the Genome Level in Mammals. Cell Metab. 2017;25(1):73-85.
[39] PEEK CB, LEVINE DC, CEDERNAES J, et al. Circadian Clock Interaction with HIF1alpha Mediates Oxygenic Metabolism and Anaerobic Glycolysis in Skeletal Muscle. Cell Metab. 2017;25(1):86-92.
[40] OK DP, KO K, BAE JY. Exercise without dietary changes alleviates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease without weight loss benefits. Lipids Health Dis. 2018;17(1):207.
[41] DYAR KA, HUBERT MJ, MIR AA, et al. Transcriptional programming of lipid and amino acid metabolism by the skeletal muscle circadian clock. PLoS Biol. 2018;16(8):e2005886.
[42] MA X, ZHOU Z, CHEN Y, et al. RBP4 functions as a hepatokine in the regulation of glucose metabolism by the circadian clock in mice. Diabetologia. 2016;59(2):354-362.
[43] SUZUKI C, USHIJIMA K, ANDO H, et al. Induction of Dbp by a histone deacetylase inhibitor is involved in amelioration of insulin sensitivity via adipocyte differentiation in ob/ob mice. Chronobiol Int. 2019;36(7):955-968.
[44] KOO SH, FLECHNER L, QI L, et al. The CREB coactivator TORC2 is a key regulator of fasting glucose metabolism. Nature. 2005;437(7062):1109-1111.
[45] YOON YS, SEO WY, LEE MW, et al. Salt-inducible kinase regulates hepatic lipogenesis by controlling SREBP-1c phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(16):10446-10452.
[46] LI Y, TONG X, RUMALA C, et al. Thrombospondin1 deficiency reduces obesity-associated inflammation and improves insulin sensitivity in a diet-induced obese mouse model. PLoS One. 2011;6(10):e26656.
[47] ZHANG H, CHEN X, SAIRAM MR. Novel genes of visceral adiposity: identification of mouse and human mesenteric estrogen-dependent adipose (MEDA)-4 gene and its adipogenic function. Endocrinology. 2012;153(6):2665-2676.
[48] WOOLCOTT OO, CASTILLO OA, GUTIERREZ C, et al. Inverse association between diabetes and altitude: a cross-sectional study in the adult population of the United States. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2014;22(9):2080-2090.
[49] SUN Z, JIANG Q, LI J, et al. The potent roles of salt-inducible kinases (SIKs) in metabolic homeostasis and tumorigenesis. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020;5(1):150.
[50] LIU S, HUANG S, WU X, et al. Activation of SIK1 by phanginin A inhibits hepatic gluconeogenesis by increasing PDE4 activity and suppressing the cAMP signaling pathway. Mol Metab. 2020;41:101045.
[51] SONG D, YIN L, WANG C, et al. Adenovirus-mediated expression of SIK1 improves hepatic glucose and lipid metabolism in type 2 diabetes mellitus rats. PLoS One. 2019;14(6): e0210930.
[52] SAKAMOTO K, BULTOT L, GORANSSON O. The Salt-Inducible Kinases: Emerging Metabolic Regulators. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2018;29(12):827-840.
[53] YUAN X, DONG D, LI Z, et al. Rev-erbalpha activation down-regulates hepatic Pck1 enzyme to lower plasma glucose in mice. Pharmacol Res. 2019;141:310-318. |
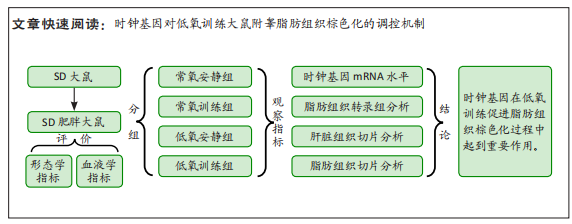
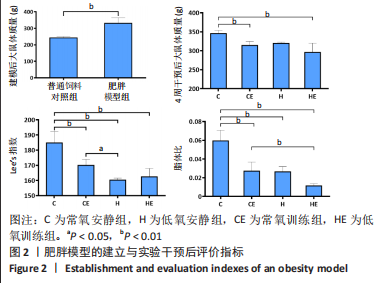
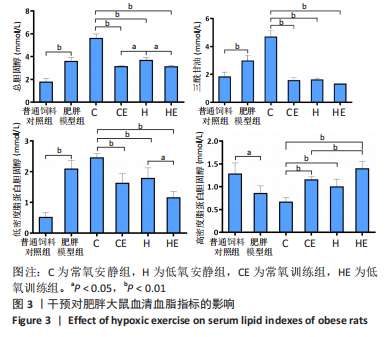
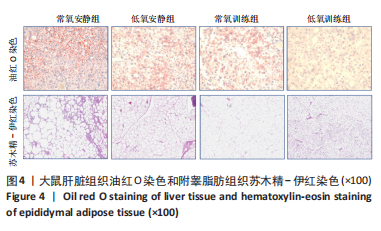
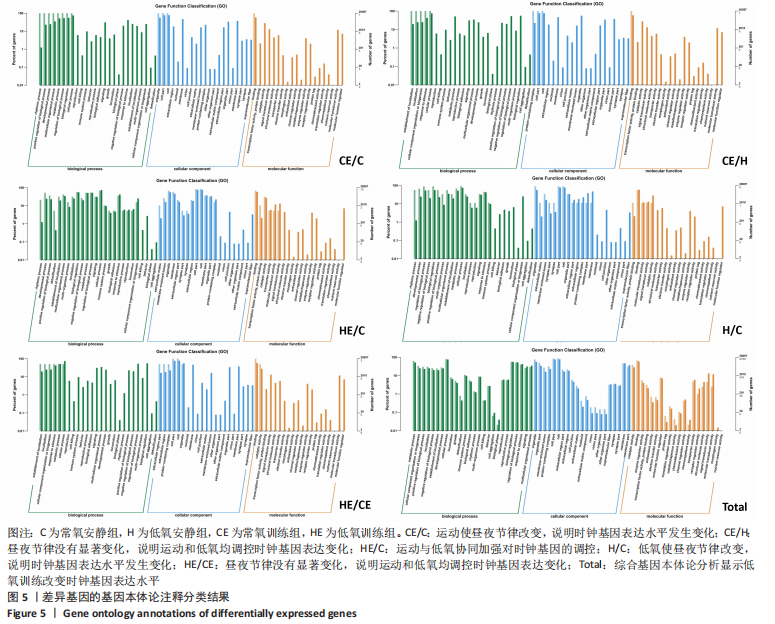
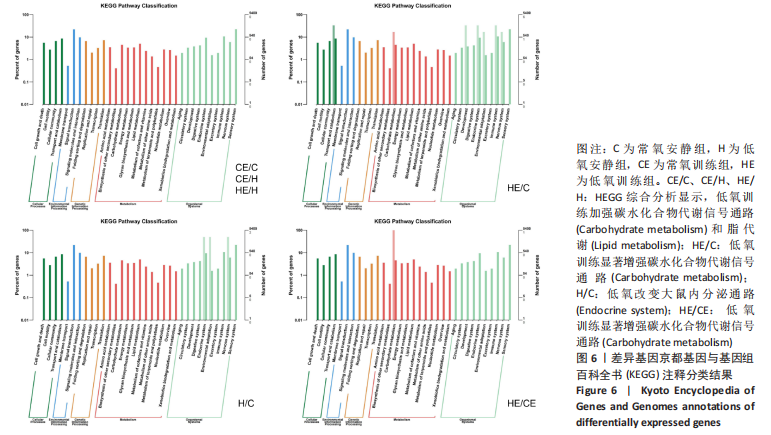
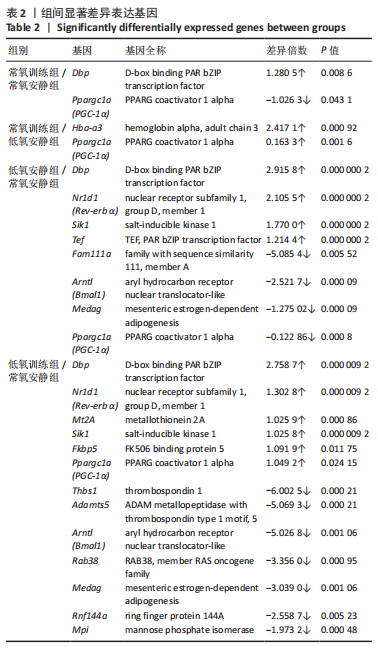
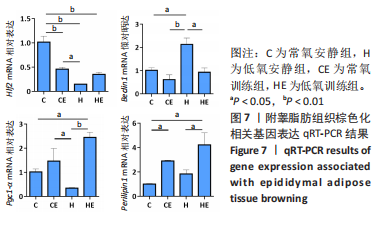

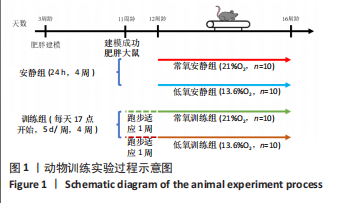
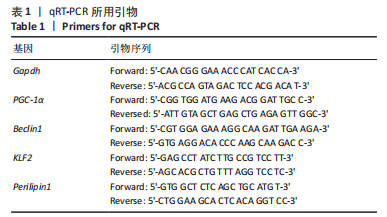
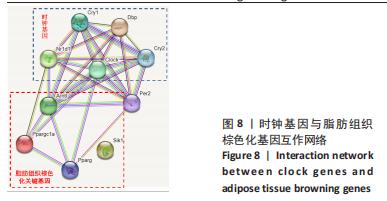 此次研究对脂肪组织棕色化关键基因PGC-1α分析发现,运动干预促进PGC-1α高表达,低氧干预后该基因表达下调;在低氧结合运动干预后,该基因表达可高于常氧安静组,说明缺氧以缺氧诱导因子1α依赖的方式抑制PGC-1α通路,导致该蛋白含量降低[24],运动可刺激该基因表达,促进线粒体生物发生和机体能量维持,加强脂肪棕色化。
此次研究对脂肪组织棕色化关键基因PGC-1α分析发现,运动干预促进PGC-1α高表达,低氧干预后该基因表达下调;在低氧结合运动干预后,该基因表达可高于常氧安静组,说明缺氧以缺氧诱导因子1α依赖的方式抑制PGC-1α通路,导致该蛋白含量降低[24],运动可刺激该基因表达,促进线粒体生物发生和机体能量维持,加强脂肪棕色化。