[1] GBD 2016 Traumatic Brain Injury and Spinal Cord Injury Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of traumatic brain injury and spinal cord injury, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18(1):56-87.
[2] BADHIWALA JH, WILSON JR, FEHLINGS MG. Global burden of traumatic brain and spinal cord injury. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18(1):24-25.
[3] SUZUKI H, IMAJO Y, FUNABA M, et al. Current Concepts of Biomaterial Scaffolds and Regenerative Therapy for Spinal Cord Injury. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(3):2528.
[4] FIANI B, ARSHAD MA, SHAIKH ES, et al. Current updates on various treatment approaches in the early management of acute spinal cord injury. Rev Neurosci. 2021;32(5):513-530.
[5] CHAUDHARI LR, KAWALE AA, DESAI SS, et al. Pathophysiology of Spinal Cord Injury and Tissue Engineering Approach for Its Neuronal Regeneration: Current Status and Future Prospects. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023;1409:51-81.
[6] ANJUM A, YAZID MD, FAUZI DAUD M, et al. Spinal Cord Injury: Pathophysiology, Multimolecular Interactions, and Underlying Recovery Mechanisms. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(20):7533.
[7] HELLENBRAND DJ, QUINN CM, PIPER ZJ, et al. Inflammation after spinal cord injury: a review of the critical timeline of signaling cues and cellular infiltration. J Neuroinflammation. 2021;18(1):284.
[8] LI S, DINH HTP, MATSUYAMA Y, et al. Molecular Mechanisms in the Vascular and Nervous Systems following Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury. Life (Basel). 2022;13(1):9.
[9] JIN LY, LI J, WANG KF, et al. Blood-Spinal Cord Barrier in Spinal Cord Injury: A Review. J Neurotrauma. 2021;38(9):1203-1224.
[10] PFYFFER D, FREUND P. Spinal cord pathology revealed by MRI in traumatic spinal cord injury. Curr Opin Neurol. 2021;34(6):789-795.
[11] ALIZADEH A, DYCK SM, KARIMI-ABDOLREZAEE S. Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury: An Overview of Pathophysiology, Models and Acute Injury Mechanisms. Front Neurol. 2019;10:282.
[12] MOMENI HR, JARAHZADEH M, FARJAD E. Glutamate excitotoxicity; a possible mechanism for apoptosis of motoneurons in adult mouse spinal cord slices. Neurophysiology. 2020; 52(6): 408-414.
[13] ELI I, LERNER DP, GHOGAWALA Z. Acute Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury. Neurol Clin. 2021;39(2):471-488.
[14] DE FARIA O JR, PIVONKOVA H, VARGA B, et al. Periods of synchronized myelin changes shape brain function and plasticity. Nat Neurosci. 2021;24(11):1508-1521.
[15] DUNCAN GJ, SIMKINS TJ, EMERY B. Neuron-Oligodendrocyte Interactions in the Structure and Integrity of Axons. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:653101.
[16] FAN B, WEI Z, FENG S. Progression in translational research on spinal cord injury based on microenvironment imbalance. Bone Res. 2022;10(1):35.
[17] RAFFAELE S, BOCCAZZI M, FUMAGALLI M. Oligodendrocyte Dysfunction in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Perspectives. Cells. 2021;10(3):565.
[18] XIN W, CHAN JR. Myelin plasticity: sculpting circuits in learning and memory. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2020;21(12):682-694.
[19] SPAAS J, VAN VEGGEL L, SCHEPERS M, et al. Oxidative stress and impaired oligodendrocyte precursor cell differentiation in neurological disorders. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021;78(10):4615-4637.
[20] HUNTEMER-SILVEIRA A, PATIL N, BRICKNER MA, et al. Strategies for Oligodendrocyte and Myelin Repair in Traumatic CNS Injury. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021;14:619707.
[21] DUNCAN GJ, MANESH SB, HILTON BJ, et al. The fate and function of oligodendrocyte progenitor cells after traumatic spinal cord injury. Glia. 2020;68(2):227-245.
[22] YANG T, DAI Y, CHEN G, et al. Dissecting the Dual Role of the Glial Scar and Scar-Forming Astrocytes in Spinal Cord Injury. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020;14:78.
[23] ZHANG Y, YANG S, LIU C, et al. Deciphering glial scar after spinal cord injury. Burns Trauma. 2021;9:tkab035.
[24] YANG B, ZHANG F, CHENG F, et al. Strategies and prospects of effective neural circuits reconstruction after spinal cord injury. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(6):439.
[25] LINNERBAUER M, ROTHHAMMER V. Protective Functions of Reactive Astrocytes Following Central Nervous System Insult. Front Immunol. 2020;11:573256.
[26] HE Y, LIU X, CHEN Z. Glial Scar-a Promising Target for Improving Outcomes After CNS Injury. J Mol Neurosci. 2020;70(3):340-352.
[27] WU Y, TANG Z, ZHANG J, et al. Restoration of spinal cord injury: From endogenous repairing process to cellular therapy. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022;16:1077441.
[28] YIU G, HE Z. Glial inhibition of CNS axon regeneration. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006;7(8):617-627.
[29] VARADARAJAN SG, HUNYARA JL, HAMILTON NR, et al. Central nervous system regeneration. Cell. 2022;185(1):77-94.
[30] TRAN AP, WARREN PM, SILVER J. New insights into glial scar formation after spinal cord injury. Cell Tissue Res. 2022;387(3):319-336.
[31] LI C, WU Z, ZHOU L, et al. Temporal and spatial cellular and molecular pathological alterations with single-cell resolution in the adult spinal cord after injury. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022;7(1):65.
[32] ZAKRZEWSKI W, DOBRZYŃSKI M, SZYMONOWICZ M, et al. Stem cells: past, present, and future. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):68.
[33] ASSINCK P, DUNCAN GJ, HILTON BJ, et al. Cell transplantation therapy for spinal cord injury. Nat Neurosci. 2017;20(5):637-647.
[34] YAMAZAKI K, KAWABORI M, SEKI T, et al. Clinical Trials of Stem Cell Treatment for Spinal Cord Injury. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(11):3994.
[35] SUN X, HUANG LY, PAN HX, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and exercise restore motor function following spinal cord injury by activating PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Neural Regen Res. 2023;18(5):1067-1075.
[36] PANG QM, CHEN SY, FU SP, et al. Regulatory Role of Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Secondary Inflammation in Spinal Cord Injury. J Inflamm Res. 2022;15:573-593.
[37] ABDOLMOHAMMADI K, MAHMOUDI T, ALIMOHAMMADI M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy as a new therapeutic approach for acute inflammation. Life Sci. 2023;312:121206.
[38] LV B, ZHANG X, YUAN J, et al. Biomaterial-supported MSC transplantation enhances cell-cell communication for spinal cord injury. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):36.
[39] PANG QM, DENG KQ, ZHANG M, et al. Multiple strategies enhance the efficacy of MSCs transplantation for spinal cord injury. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;157:114011.
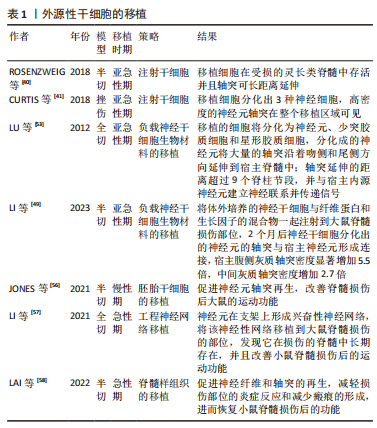
[40] ROSENZWEIG ES, BROCK JH, LU P, et al. Restorative effects of human neural stem cell grafts on the primate spinal cord. Nat Med. 2018;24(4):484-490.
[41] CURTIS E, MARTIN JR, GABEL B, et al. A First-in-Human, Phase I Study of Neural Stem Cell Transplantation for Chronic Spinal Cord Injury. Cell Stem Cell. 2018;22(6):941-950.e6.
[42] OH SK, JEON SR. Current Concept of Stem Cell Therapy for Spinal Cord Injury: A Review. Korean J Neurotrauma. 2016;12(2):40-46.
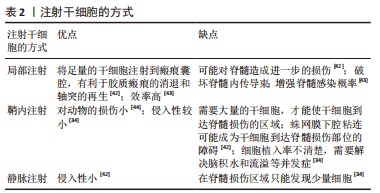
[43] 张达,屠冠军. 骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗脊髓损伤的途径及联合方式[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2012,16(49): 9265-9270.
[44] BAKSHI A, HUNTER C, SWANGER S, et al. Minimally invasive delivery of stem cells for spinal cord injury: advantages of the lumbar puncture technique. J Neurosurg Spine. 2004;1(3):330-337.
[45] TAHMASEBI F, BARATI S. Effects of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on spinal cord injury patients. Cell Tissue Res. 2022;389(3):373-384.
[46] SHU J, CHENG F, GONG Z, et al. Transplantation Strategies for Spinal Cord Injury Based on Microenvironment Modulation. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;15(6):522-530.
[47] LI Z, ZHAO T, DING J, et al. A reactive oxygen species-responsive hydrogel encapsulated with bone marrow derived stem cells promotes repair and regeneration of spinal cord injury. Bioact Mater. 2022;19:550-568.
[48] YING Y, HUANG Z, TU Y, et al. A shear-thinning, ROS-scavenging hydrogel combined with dental pulp stem cells promotes spinal cord repair by inhibiting ferroptosis. Bioact Mater. 2022;22:274-290.
[49] LI Y, TRAN A, GRAHAM L, et al. BDNF guides neural stem cell-derived axons to ventral interneurons and motor neurons after spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol. 2023;359:114259.
[50] WANG Z, DUAN H, HAO F, et al. Circuit reconstruction of newborn neurons after spinal cord injury in adult rats via an NT3-chitosan scaffold. Prog Neurobiol. 2023;220:102375.
[51] NEW LE, YANAGAWA Y, MCCONKEY GA, et al. GABAergic regulation of cell proliferation within the adult mouse spinal cord. Neuropharmacology. 2023;223:109326.
[52] GAO X, YOU Z, LI Y, et al. Multifunctional hydrogel modulates the immune microenvironment to improve allogeneic spinal cord tissue survival for complete spinal cord injury repair. Acta Biomater. 2023;155:235-246.
[53] LU P, WANG Y, GRAHAM L, et al. Long-distance growth and connectivity of neural stem cells after severe spinal cord injury. Cell. 2012;150(6):1264-1273.
[54] ZAREPOUR A, BAL ÖZTÜRK A, KOYUNCU IRMAK D, et al. Combination therapy using nanomaterials and stem cells to treat spinal cord injuries. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2022;177:224-240.
[55] JAKEMAN LB, REIER PJ. Fetal spinal cord transplantation after spinal cord injury: around and back again[C]. Oxford: Academic Press, 2015: 351-365.
[56] JONES I, NOVIKOVA LN, WIBERG M, et al. Human Embryonic Stem Cell-derived Neural Crest Cells Promote Sprouting and Motor Recovery Following Spinal Cord Injury in Adult Rats. Cell Transplant. 2021;30:963689720988245.
[57] LI G, ZHANG B, SUN JH, et al. An NT-3-releasing bioscaffold supports the formation of TrkC-modified neural stem cell-derived neural network tissue with efficacy in repairing spinal cord injury. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(11):3766-3781.
[58] LAI BQ, BAI YR, HAN WT, et al. Construction of a niche-specific spinal white matter-like tissue to promote directional axon regeneration and myelination for rat spinal cord injury repair. Bioact Mater. 2021;11:15-31.
[59] LIU S, CHEN Z. Employing Endogenous NSCs to Promote Recovery of Spinal Cord Injury. Stem Cells Int. 2019;2019:1958631.
[60] 张浩,肖世宁,张钰,等. 内源性神经干细胞在脊髓损伤修复的研究进展[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2022, 30(24): 2250-2254.
[61] MYCKATYN TM, MACKINNON SE, MCDONALD JW. Stem cell transplantation and other novel techniques for promoting recovery from spinal cord injury. Transpl Immunol. 2004;12(3-4):343-358.
[62] 张正丰. 内源性神经干细胞与脊髓损伤的研究进展[J].中国康复理论与实践,2010,16(4):344-346.
[63] 范一鸣,刘方煜,张洪宇,等.脊髓损伤后室管膜区内源性神经干细胞反应的系列问题[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(7):1137-1142.
[64] LI X, FLORIDDIA EM, TOSKAS K, et al. Regenerative Potential of Ependymal Cells for Spinal Cord Injuries Over Time. EBioMedicine. 2016;13:55-65.
[65] QIN Y, ZHANG W, YANG P. Current states of endogenous stem cells in adult spinal cord. J Neurosci Res. 2015;93(3):391-398.
[66] MORENO-MANZANO V, RODRÍGUEZ-JIMÉNEZ FJ, GARCÍA-ROSELLÓ M, et al. Activated spinal cord ependymal stem cells rescue neurological function. Stem Cells. 2009;27(3):733-743.
[67] BACOVA M, BIMBOVA K, KISUCKA A, et al. Epidural oscillating field stimulation increases axonal regenerative capacity and myelination after spinal cord trauma. Neural Regen Res. 2022;17(12):2730-2736.
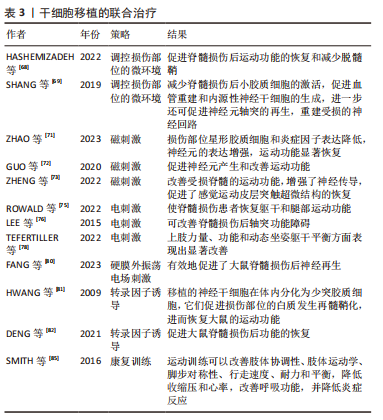
[68] HASHEMIZADEH S, HOSSEINDOOST S, OMIDI A, et al. Novel therapeutic approach to slow down the inflammatory cascade in acute/subacute spinal cord injury: Early immune therapy with lipopolysaccharide enhanced neuroprotective effect of combinational therapy of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor and bone-marrow mesenchymal stem cell in spinal cord injury. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022;16:993019.
[69] SHANG J, QIAO H, HAO P, et al. bFGF-Sodium Hyaluronate Collagen Scaffolds Enable the Formation of Nascent Neural Networks After Adult Spinal Cord Injury. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2019;15(4):703-716.
[70] HALLETT M. Transcranial magnetic stimulation: a primer. Neuron. 2007;55(2):187-199.
[71] ZHAO D, ZHANG Y, ZHENG Y, et al. Double-target neural circuit-magnetic stimulation improves motor function in spinal cord injury by attenuating astrocyte activation. Neural Regen Res. 2023;18(5):1062-1066.
[72] GUO M, WU L, SONG Z, et al. Enhancement of Neural Stem Cell Proliferation in Rats with Spinal Cord Injury by a Combination of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (rTMS) and Human Umbilical Cord Blood Mesenchymal Stem Cells (hUCB-MSCs). Med Sci Monit. 2020;26:e924445.
[73] ZHENG Y, ZHAO D, XUE DD, et al. Nerve root magnetic stimulation improves locomotor function following spinal cord injury with electrophysiological improvements and cortical synaptic reconstruction. Neural Regen Res. 2022;17(9):2036-2042.
[74] DORRIAN RM, BERRYMAN CF, LAUTO A, et al. Electrical stimulation for the treatment of spinal cord injuries: A review of the cellular and molecular mechanisms that drive functional improvements. Front Cell Neurosci. 2023;17:1095259.
[75] ROWALD A, KOMI S, DEMESMAEKER R, et al. Activity-dependent spinal cord neuromodulation rapidly restores trunk and leg motor functions after complete paralysis. Nat Med. 2022;28(2):260-271.
[76] LEE M, KIERNAN MC, MACEFIELD VG, et al. Short-term peripheral nerve stimulation ameliorates axonal dysfunction after spinal cord injury. J Neurophysiol. 2015;113(9):3209-3218.
[77] MARQUEZ-CHIN C, POPOVIC MR. Functional electrical stimulation therapy for restoration of motor function after spinal cord injury and stroke: a review. Biomed Eng Online. 2020;19(1):34.
[78] TEFERTILLER C, BARTELT P, STOBELAAR M, et al. Improving Upper Extremity Strength, Function, and Trunk Stability Using Wide-Pulse Functional Electrical Stimulation in Combination With Functional Task-Specific Practice. Top Spinal Cord Inj Rehabil. 2022;28(2):139-152.
[79] 黄先甲,张坤坤,钱军,等. 振荡电场刺激治疗脊髓损伤的研究进展[J]. 安徽医科大学学报,2016,51(11):1710-1712.
[80] FANG C, SUN J, QIAN J, et al. Oscillating field stimulation promotes neurogenesis of neural stem cells through miR-124/Tal1 axis to repair spinal cord injury in rats. Neural Regen Res. 2023;18(4):895-900.
[81] HWANG DH, KIM BG, KIM EJ, et al. Transplantation of human neural stem cells transduced with Olig2 transcription factor improves locomotor recovery and enhances myelination in the white matter of rat spinal cord following contusive injury. BMC Neurosci. 2009;10:117.
[82] DENG M, XIE P, CHEN Z, et al. Mash-1 modified neural stem cells transplantation promotes neural stem cells differentiation into neurons to further improve locomotor functional recovery in spinal cord injury rats. Gene. 2021;781:145528.
[83] ZHAO B, ZHOU X, LIU C, et al. The effects of walking training onset on motor evoked potentials after acute spinal cord injury. Neurosci Lett. 2020;739:135338.
[84] MARQUES MR, NICOLA FC, SANCHES EF, et al. Locomotor Training Promotes Time-dependent Functional Recovery after Experimental Spinal Cord Contusion. Neuroscience. 2018;392:258-269.
[85] SMITH AC, KNIKOU M. A Review on Locomotor Training after Spinal Cord Injury: Reorganization of Spinal Neuronal Circuits and Recovery of Motor Function. Neural Plast. 2016;2016:1216258.
[86] XU B, YIN M, YANG Y, et al. Transplantation of neural stem progenitor cells from different sources for severe spinal cord injury repair in rat. Bioact Mater. 2022;23:300-313.
[87] ZIPSER CM, CRAGG JJ, GUEST JD, et al. Cell-based and stem-cell-based treatments for spinal cord injury: evidence from clinical trials. Lancet Neurol. 2022;21(7):659-670.
[88] GUO W, ZHANG X, ZHAI J, et al. The roles and applications of neural stem cells in spinal cord injury repair. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:966866.
[89] PAREDES-ESPINOSA MB, PALUH JL. Human stem cell-derived neurons and neural circuitry therapeutics: Next frontier in spinal cord injury repair. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2022;247(23):2142-2151.
[90] SZYMONIUK M, LITAK J, SAKWA L, et al. Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Application of Multipotent Stem Cells for Spinal Cord Injury. Cells. 2022;12(1):120.
[91] 吕谨南, 谭伟,杨磊落,等. 干细胞移植治疗脊髓损伤的研究进展[J]. 当代医药论丛,2018,16(9):45-47. |