中国组织工程研究 ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (33): 5404-5412.doi: 10.12307/2023.704
• 干细胞综述 stem cell review • 上一篇
非编码 RNA 调控脊髓损伤后神经元细胞凋亡的作用和机制
许卢春,杨永栋,赵 赫,仲文庆,马昱堃,俞 兴
- 北京中医药大学东直门医院,北京市 100700
-
收稿日期:2022-10-08接受日期:2022-11-16出版日期:2023-11-28发布日期:2023-03-31 -
通讯作者:俞兴,博士,教授,主任医师,博士生导师,北京中医药大学东直门医院,北京市 100700 -
作者简介:许卢春,1995年生,江西省南昌市人,汉族,北京中医药大学东直门医院在读博士,主要从事脊柱外科、脊髓损伤方面的研究。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金面上项目(81973882),项目负责人:俞兴
Effect and mechanism of non-coding RNA in regulating neuronal apoptosis after spinal cord injury
Xu Luchun, Yang Yongdong, Zhao He, Zhong Wenqing, Ma Yukun, Yu Xing
- Dongzhimen Hospital of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100700, China
-
Received:2022-10-08Accepted:2022-11-16Online:2023-11-28Published:2023-03-31 -
Contact:Yu Xing, MD, Professor, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Dongzhimen Hospital of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100700, China -
About author:Xu Luchun, Doctoral candidate, Dongzhimen Hospital of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100700, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Program), No. 81973882 (to YX)
摘要:
文题释义:
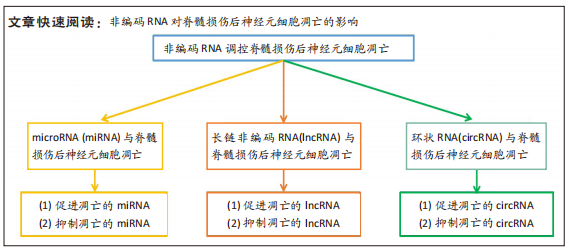
非编码RNA:由microRNA (miRNA)、长链非编码RNA(lncRNA)和环状RNA(circRNA)等组成,是一类不编码蛋白质的RNA。现有研究发现脊髓损伤后,与神经元细胞凋亡相关的非编码RNA出现显著差异性表达,调控特定非编码RNA的表达,可抑制脊髓损伤后神经元细胞凋亡。细胞凋亡:是一种程序性细胞死亡,是继发性脊髓损伤造成脊髓神经元过度死亡的主要方式。神经元大量凋亡常发生于脊髓损伤后24 h之内,因此脊髓损伤后抑制神经元细胞凋亡可减轻继发性脊髓损伤,利于脊髓损伤后脊髓功能的恢复和重建重塑。
背景:脊髓损伤后神经元细胞凋亡是造成脊髓永久性损伤的一个主要原因,探索防止脊髓损伤后神经元凋亡的方法意义重大。现有的动物实验研究表明,非编码RNA能够对脊髓损伤后神经元细胞凋亡进行调控,这或许可以给临床脊髓损伤后神经元保护性治疗提供一定参考。
目的:对非编码RNA调控脊髓损伤后神经元凋亡作用和机制进行综述,为脊髓损伤的保护性治疗提供新的靶点。
方法:以“microRNA,miR,lncRNA,circRNA,noncoding RNA,RNA,SCI,spinal cord injury,spinal cord,apoptosis”为检索词在 PubMed 数据库中进行检索,制定纳排标准,通过阅读文题、摘要和全文进行筛选,最终纳入87篇相关文献。
结果与结论:①神经元细胞凋亡为继发性脊髓损伤中极其重要的病理生理改变,是神经元死亡、脊髓功能障碍的重要致病机制之一。②动物实验研究发现,在脊髓损伤后的脊髓组织中,与神经元细胞凋亡相关的miRNA、长链非编码RNA(lncRNA)与环状RNA(circRNA)可出现差异性表达,一些促进神经元凋亡的miRNA,lncRNA与circRNA过表达,而另一部分抑制神经元凋亡的miRNA、lncRNA与circRNA表达下调。③调控特定miRNA的相应表达,主要通过靶向下调凋亡基因Bax、抑制TLR4/核转录因子κB信号通路、激活PI3K/Akt信号通路等方式可抑制脊髓损伤后神经元细胞过度凋亡。④调控lncRNA和circRNA的表达,主要通过靶向负调控的方式使得特定miRNA出现沉默或过表达,从而发挥其抗神经元细胞凋亡的作用。⑤在miRNA中,miR-125b对Smurf1/KLF2/ATF2轴及JAK1/STAT1信号通路等均可产生调节,而miR-21-5p对程序性细胞死亡因子4(PDCD4)和PI3K/AKT信号通路等可产生调节,具有多途径抗凋亡的作用。⑥在lncRNA和circRNA中,lncRNA-PTENP1,lncRNA-TCTN2和circRNA-HIPK3均对于多种miRNA具有靶向调节作用,这些非编码RNA也许可以成为脊髓损伤后神经元保护性治疗的新靶点。⑦目前对于非编码RNA调控脊髓损伤后神经元细胞凋亡还仅停留在动物及细胞研究层面,未来需要继续探索更加具有靶向作用的非编码RNA药物载体,联合生物组织工程以及其他新兴技术,争取早日向临床转化过渡。
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7736-007X (许卢春)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
许卢春, 杨永栋, 赵 赫, 仲文庆, 马昱堃, 俞 兴. 非编码 RNA 调控脊髓损伤后神经元细胞凋亡的作用和机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(33): 5404-5412.
Xu Luchun, Yang Yongdong, Zhao He, Zhong Wenqing, Ma Yukun, Yu Xing. Effect and mechanism of non-coding RNA in regulating neuronal apoptosis after spinal cord injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(33): 5404-5412.
神经元细胞凋亡是继发性脊髓损伤中极其重要的病理生理改变,是神经元死亡、脊髓功能障碍的重要机制。脊髓损伤后发生的缺血缺氧、氧化应激、炎症刺激及线粒体损伤等因素共同激活神经元细胞凋亡,大量神经元细胞发生凋亡对脊髓造成严重的及不可逆的损伤[14-16]。故研究者们认为抑制神经元细胞凋亡可以对损伤后的脊髓产生保护作用,减少神经元细胞在脊髓损伤后的过量缺失,减轻脊髓损伤的继发的、不可逆的损伤,改善脊髓损伤后的一系列病理生理过程,从而利于脊髓功能的恢复和重建重塑。
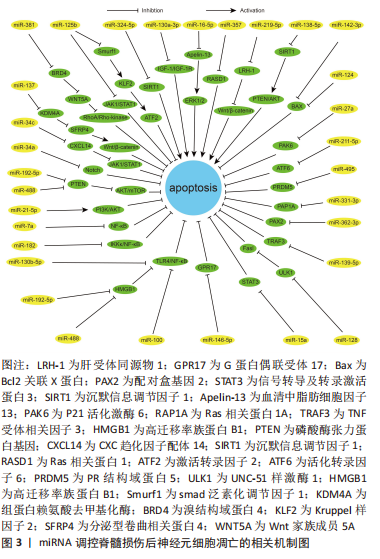
2.2 miRNA 调节脊髓损伤后神经元细胞凋亡的作用机制 microRNA(miR或miRNA)是一类不编码蛋白质的小RNA。其长度短且较整齐,一般为 18-24 个核苷酸的单链片段,在物种之间有较好的保守性[17]。microRNA的形成经过初级 miRNA(pri-miRNA)、前体miRNA(pre-miRNA)、microRNA的成熟体3个过程[18-20]。miRNA可以与一个或多个mRNA互补结合,改变靶基因的表达,靶基因的3’-UTR为miRNA的主要作用位点。人类超过1/3的基因受miRNA调控,可以说miRNA几乎参与所有的细胞过程,细胞凋亡也不例外[21-22]。
脊髓损伤后多种miRNA出现差异性表达[23]。脊髓损伤后细胞凋亡、炎症反应、氧化应激、小胶质细胞活化和神经血管再生等关键病理生理过程均有miRNA参与[24]。现有大量基础研究探索miRNA与脊髓损伤后神经元细胞凋亡的关系,通过对促进和抑制神经元细胞凋亡的miRNA进行相应调节,可以靶向相应的凋亡基因和信号通路起到抗凋亡的作用,相关研究结果或许能为脊髓损伤临床治疗提供一种新思路。
2.2.1 促进神经元凋亡的 miRNA 目前研究已发现脊髓损伤后十余种miRNA的过表达可增加神经元细胞的凋亡,从而加重继发性损伤,对这些miRNA进行表达下调可以减少神经元细胞凋亡,减少继发性脊髓损伤。大鼠脊髓损伤后 miR-324-5p 表达显著升高、 Sirtuin家族的成员沉默信息调节因子1表达下调,通过下调 miR-324-5p直接靶向上调沉默信息调节因子1表达可减少神经元细胞凋亡、减轻脊髓损伤[25]。沉默信息调节因子1亦为 miR-138-5p 的直接靶标,下调此miRNA也可通过靶向沉默其表达从而发挥抗凋亡的保护作用[26]。胰岛素样生长因子1(insulin-like growth factor-1,IGF-1)是一种广谱的生长因子,具有保护神经元、促进神经元的生长发育和抗炎等作用,对miR-130a-3p进行表达沉默可以激活IGF-1/IGF-1R信号通路减少脊髓损伤后神经元细胞凋亡,与此同时,沉默此miRNA还能起到其他的作用,如减少小胶质细胞活化和炎症反应[27]。故研究者们认为miRNA对于脊髓损伤的调控也是一个多机制多靶点的过程,对于多机制相互调控构建相应网络能够有助于更深入地了解脊髓损伤的生理病理进程。miR-16-5p 在脊髓损伤后过表达,下调miR-16-5p表达可靶向上调血清中脂肪细胞因子13激活 ERK1/2 通路,减轻神经元细胞凋亡和炎症反应[28]。甲基转移酶样14是一种介导 m6A 修饰的关键甲基转移酶,m6A 甲基化修饰可抑制 pri-miR-375向miR-375的转化,使其直接靶标Ras相关蛋白1表达上调、减少凋亡[29]。miRNA-219-5p已被确定为多种癌症的肿瘤抑制因子,也可能是治疗脊髓损伤的潜在靶点之一[30],miRNA-219-5p 在损伤的脊髓中高度表达,抑制其表达可靶向上调肝受体同源物1激活Wnt/β-catenin 通路发挥在脊髓损伤中的保护性作用。
2.2.2 抑制神经元凋亡的 miRNA 据报道,脊髓损伤后大量miRNA表达下调,通过对30余种miRNAs 的表达进行上调可以起到保护神经元、减少神经元细胞的凋亡,发挥保护脊髓和减轻脊髓过度损伤的作用。大鼠脊髓损伤后miR-124和 miR-142-3p表达下调[31-32],有研究发现上调此两种miRNA的表达水平均可靶向下调Bcl2关联X蛋白表达、减少促凋亡蛋白的含量及线粒体膜上过渡孔的打开、降低线粒体对细胞色素C的释放,改善脊髓损伤恢复。有研究发现加入组蛋白去乙酰化酶抑制剂后能有效上调miR-27a表达,之后被靶向抑制的P21活化激酶6可发生联级反应导致凋亡减少,促进脊髓损伤恢复[33]。活化转录因子6是一种内质网应激过程中起关键调节作用的转录因子,其在体内的低表达可减弱内质网应激、减少细胞凋亡、改善脊髓损伤后的功能恢复,而过表达的miR-211-5p可对活化转录因子6进行靶向沉默,从而促进脊髓损伤修复[34]。PR结构域蛋白5为PRDM 的家族成员之一,是一种调节神经元细胞凋亡的转录调节因子,急性脊髓损伤后表达增加加剧神经元细胞凋亡。大鼠脊髓损伤后通过过表达 miR-495 可靶向下调此蛋白水平发挥抗凋亡的积极作用[35]。
Ras相关蛋白1A在脊髓损伤后miR-331-3p表达下调,上调其表达可靶向沉默Ras相关蛋白1A 减少神经元细胞凋亡 [36]。配对盒基因2是一种神经元发育所必需的基因,其在体内的高表达与神经元细胞凋亡密切相关。大鼠脊髓损伤后,通过过表达 miR-362-3p可直接靶向负调控配对盒基因2发挥相应作用,同时还可改善脊髓损伤后神经性疼痛[37]。这也给脊髓损伤后常见的神经性疼痛这一难题带来了治疗的新思路。肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子3是TRAF信号蛋白家族的成员,其表达的增加也可促进细胞凋亡,过表达miR-139-5p水平可靶向下调肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子3减少脊髓损伤后神经元细胞凋亡,同时减轻实验动物的异位疼痛和痛觉过敏[38]。UNC-51样激酶1是一种丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶,脊髓损伤后其表达上调导致Fas配体上调,而Fas配体的上调在凋亡和炎症反应中起关键作用。miR-128可以通过对以上分子的逐级调控从而达到对凋亡的抑制作用[39]。信号转导及转录激活蛋白3主要分布于神经元中,脊髓损伤后表达上调可导致神经细胞的凋亡和炎症反应,而过表达miR-15a可靶向下调该蛋白从而通过抑制以上损伤机制改善脊髓损伤[40]。珍宝丸由珍珠、决明子和牛黄等二十九味中药组成,大鼠脊髓损伤后miR-146a-5p表达下调,而珍宝丸可上调其表达、靶向负调控G蛋白偶联受体17,抑制神经元细胞凋亡、促进脊髓功能恢复,这为探索中医药治疗脊髓损伤的内在机制提供一种新的思路[41]。
2.2.3 miRNA通过信号通路抑制神经元细胞凋亡 miRNA还可通过抑制或激活相关信号通路从而发挥抑制凋亡的作用。TLR4/核转录因子κB和PI3K/Akt等信号通路是神经元凋亡的关键通路,一些miRNA可对上述通路进行相应调控从而起到抑制凋亡的作用。Toll样受体4/核转录因子κB信号通路是调节神经元细胞凋亡的关键途径之一,在外源性凋亡激活途径中,Toll样受体4可导致大量肿瘤坏死因子α的分泌,肿瘤坏死因子α通过细胞表面死亡受体参与神经元细胞凋亡的过程,而介导死亡受体1和配体结合的途径由核转录因子κB诱导产生,故抑制Toll样受体4/核转录因子κB通路活性可以减少神经元细胞凋亡。目前研究现已发现miR-100,miR-488,miR-129-5p及miR-130b-5p在脊髓损伤后表达均下调[42-45],而上调这些miR表达后皆可抑制Toll样受体4/核转录因子κB通路激活,从而减少神经元细胞凋亡。其中miR-488和miR-129-5p对于Toll样受体4/核转录因子κB通路的抑制是通过直接靶向下调炎症反应调节因子高迁移率族蛋白B1来实现的。miR-182和miR-7a在大鼠脊髓损伤模型中表达下调,上调其表达可抑制核转录因子κB 通路激活、减少神经元细胞凋亡[46-47]。
PI3K/Akt 通路也是脊髓损伤后调控神经元凋亡的关键通路,蛋白激酶B(Akt)是一种重要的激酶,参与细胞凋亡、增殖等多种生理活动,磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶(PI3K)将磷脂酰肌醇-2-磷酸转化为磷脂酰肌醇-3-磷酸后激活蛋白激酶B,激活的蛋白激酶B通过控制B淋巴细胞瘤2基因、细胞色素C及死亡基因表达水平来调节神经元细胞凋亡。miR-21-5p在脊髓损伤后表达下调,上调miR-21-5p可激活PI3K/AKT通路,从而抑制神经元的凋亡[48]。哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白是蛋白激酶B的下游信号分子,上调其表达可促进脊髓损伤后神经组织的再生和神经元的保护。据报道,上调miR-29b-3p和miR-92a-3p均能通过靶向下调磷酸酶张力蛋白基因(phosphatase and tensin homolog,PTEN)从而激活 Akt/mTOR 通路[49-50],减少神经元细胞凋亡,促进神经功能修复。
除上述两个通路外,miRNA也参与其他调控神经元细胞凋亡的信号通路的激活抑制。JAK2/STAT3信号通路是一种重要的细胞内通路,蛋白酪氨酸激酶2主要调节信号转导和转录活化因子3的磷酸化,此通路在脊髓损伤早期参与调控神经元细胞凋亡和自噬过程。研究发现对脊髓损伤后表达下调的miR-34c进行过表达,可以直接靶向下调CXC趋化因子配体14水平从而抑制JAK2/STAT3通路激活,减少神经元细胞凋亡[51]。脊髓损伤小鼠模型中miR-125b表达显著下调,对其过表达可降低蛋白酪氨酸激酶1和转录活化因子3磷酸化水平,抑制相应通路活性,减少神经元的凋亡[52],同时miR-125b 的过表达还可靶向下调smad泛素化调节因子1水平,通过Smurf1/KLF2/ATF2 轴减少神经元细胞凋亡,促进神经功能恢复[53]。Notch通路在多种生物学过程中起到调节作用,包括细胞的增殖、分化和死亡等,此通路的激活促进细胞凋亡,反之抑制。miR-34a在脊髓损伤后表达下调,上调后可有效抑制 Notch 通路的激活,减少神经元细胞凋亡,保留神经元和轴突的有效数量[54]。
Wnt/β-Catenin 信号通路是一类在生物进化过程中高度保守的信号通路,具有多级调控、级联放大的特点,也参与脊髓损伤后神经元细胞凋亡的调控,而分泌型卷曲相关蛋白4是一种 Wnt 拮抗基因具有协助激活β-Catenin 的功能。研究显示脊髓损伤后通过过表达miR-137可靶向下调组蛋白赖氨酸去甲基化酶直接调控 SFRP4-Wnt/β -Catenin轴抑制神经元细胞凋亡 [55]。Ras同源基因家族成员A为一种小分子G蛋白,Rho激酶是其主要效应底物,在细胞生存、迁移和分化等方面起重要作用。脊髓损伤后RhoA/Rho-激酶通路被异常激活,神经元细胞凋亡增加,内含miR-381的间充质干细胞细胞外囊泡通过靶向下调溴结构域蛋白4来抑制Wnt家族成员5A表达,抑制 RhoA/Rho-激酶通路活性、减少神经元细胞凋亡[56]。
虽然miRNA在脊髓损伤领域的研究报道已经比较丰富,相应的调控机制也有着一定程度的深入探索,但是尚且还需进行临床转化的研究。更加完善miRNA与mRNA分子水平的相互调控网络,丰富miRNA在神经元细胞凋亡的各种调控关系,明确临床患者脊髓损伤后相应miRNA的表达水平,探索更加具有靶向作用的miRNA药物载体,联合生物组织工程以及其他新兴技术,这些对于miRNA的临床转化性研究有着重要意义。
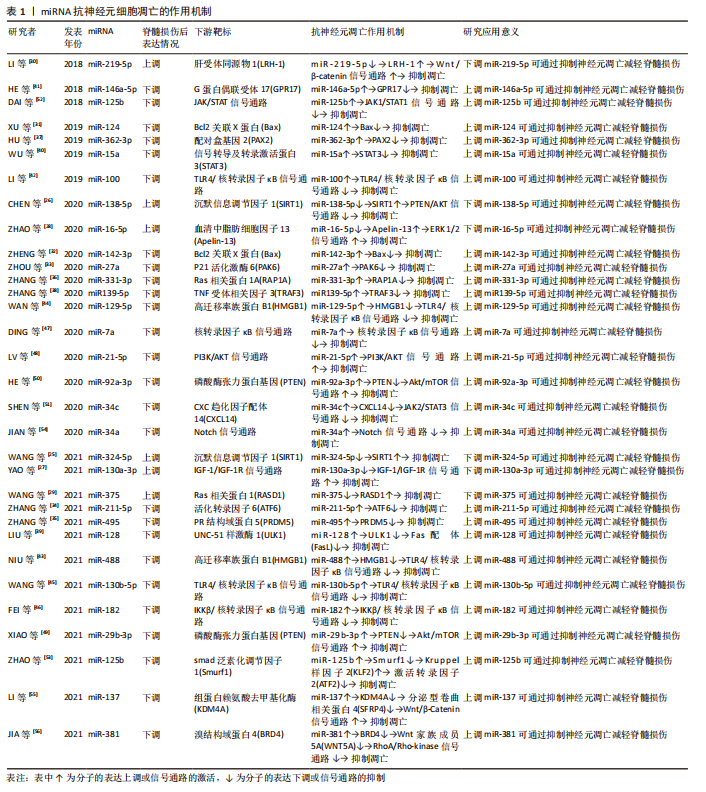
通过整理归纳miRNA调控脊髓损伤后神经元细胞凋亡的相关机制为脊髓损伤后抗神经元细胞凋亡提供了新的策略,对于脊髓损伤后的保护性治疗意义重大,见图3和表1。
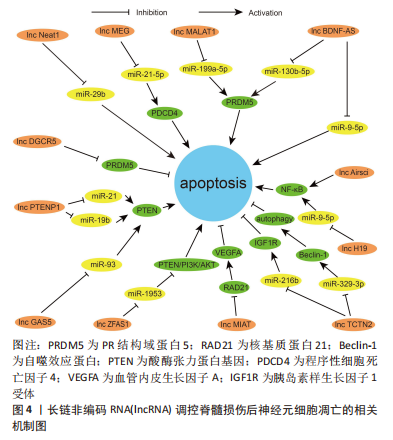
2.3 lncRNA调节脊髓损伤后神经元细胞凋亡的作用机制 lncRNA是另一类不编码蛋白的RNA,与miRNA的短片段不同,其核苷酸长度超过200,分为正义、反义、内含子、双向和基因间lncRNA共5类[57]。lncRNA通过改变自身结构形成分子支架与底物结合,参与表观遗传、转录、翻译、细胞自噬和凋亡等多种生物学过程的调节[58]。大量研究发现,脊髓损伤后lncRNA的表达发生改变,对神经元、小胶质细胞和星形胶质细胞的细胞行为产生影响[59-60]。lncRNA与神经元细胞凋亡有着密切联系,由于其对miRNA的分子海绵作用,其对神经元凋亡的调控大多通过miRNA所介导,调控lncRNA的表达可以通过靶向miRNA来调节脊髓损伤后的神经元细胞的凋亡,故lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA的三维调控网络构建在抑制脊髓损伤后神经元细胞凋亡中尤为重要。
2.3.1 促进神经元凋亡的 lncRNA 一些 lncRNA在脊髓损伤后的表达上调可导致神经元细胞凋亡增加,影响脊髓损伤的预后。脊髓损伤后lncRNA-Neat1表达升高,抑制其表达可以靶向上调miR-29b抑制神经元细胞凋亡,且NEAT1/miR-29b轴对脊髓损伤后的再生也有一定的作用[61]。Wang等[62]发现脊髓损伤后lncRNA-MEG 抑制程序性细胞死亡因子4表达升高、miR-21-5p 表达降低,下调 lncRNA-MEG可靶向负调控miR-21-5p后抑制程序性细胞死亡因子4的表达,抑制神经元细胞凋亡。另外,一些 lncRNA通过靶向调控miRNA抑制PR结构域蛋白5的表达、抑制神经元细胞凋亡,如lncRNA-MALAT1就可通过miR-199a-5p来发挥此作用[63]。BDNF-AS是BDNF的保守反义转录产物,脊髓损伤后lncRNA BDNF-AS表达上调,miR-130b-5p表达下降,通过小干扰RNA转染敲低 BDNF-AS表达也可通过miR-130b-5p来实现抗神经元细胞凋亡的这项功能[64]。
此外,脊髓损伤后锂离子干预也可下调lncRNA BDNF-AS表达、靶向上调miR-9-5p,发挥减少神经元细胞凋亡和改善神经炎症反应的作用[65]。脊髓损伤后部分lncRNA的高表达与核转录因子κB信号通路激活关系密切。脊髓损伤后lncRNA-H19表达上调靶向下调miR-370-3p,激活核转录因子κB通路、增加神经细胞凋亡,降低lncRNA-H19可通过反向调控此条路径来减少神经元细胞凋亡[66]。Zhang等[67]发现脊髓损伤后lncRNA-Airsci表达明显增加,通过下调其表达可显著抑制核转录因子κB通路活性、抑制神经元细胞凋亡和炎症的发生。
近来发现PTEN可通过调控神经元凋亡、炎症免疫反应、突触再生等生物学过程影响脊髓损伤后的修复[68],而一些lncRNA通过调控PTEN表达从而减少神经元细胞凋亡。IncRNA-PTENP1是磷酸酶和张力蛋白同源物基因假基因的一种,大量序列和PTEN同源,因此,PTENP1可以阻止miRNAs介导的PTEN下调。脊髓损伤后IncRNA-PTENP1 表达上调,miR-21和miR-19b表达下调,通过下调IncRNA-PTENP1可靶向上调miR-21与miR-19b,减少PTEN表达,抑制神经元细胞凋亡[69]。脊髓损伤后通过下调LncRNA-GAS5可靶向上调 miR-93也可抑制PTEN表达,减少神经元细胞凋亡和神经炎症反应 [70]。此外,lncRNA-ZFAS1在脊髓损伤后神经元细胞凋亡中也发挥作用,通过下调lncRNA-ZFAS1可靶向过表达 miR-1953从而下调PTEN,激活PI3K/AKT通路,抑制脊髓损伤后神经元细胞凋亡、减轻炎症反应[71]。
2.3.2 抑制神经元凋亡的 lncRNA 脊髓损伤后一些lncRNA表达下降,通过过表达这些lncRNA可减少神经元细胞凋亡,保护脊髓功能。脊髓损伤后lncRNA-MIAT表达下调,通过实验过表达后可靶向抑制核基质蛋白21蛋白降解,促进血管内皮生长因子A转录,抑制神经元细胞凋亡 [72]。ZHANG等[73]发现脊髓损伤后lncRNA-DGCR5表达下调、PR结构域蛋白5表达上调,而过表达lncRNA-DGCR5可靶向下调PR结构域蛋白5抑制神经元细胞凋亡。脊髓损伤后lncRNA-TCTN2 表达下调,若过表达lncRNA-TCTN2可靶向上调 miR-216b、下调自噬效应蛋白从而增强自噬,减少神经元凋亡 [74]。体外细胞实验发现,过表达lncRNA-TCTN2的间充质干细胞外泌体可靶向下调 miR-329-3p,进而负调控其靶标胰岛素样生长因子1受体的表达,减弱脂多糖诱导的神经元凋亡、炎症和氧化应激反应 [75]。
lncRNA在脊髓损伤方面的研究晚于miRNA,但由于其作用较miRNA更加丰富,其在脊髓损伤后能够发挥的功能也许更为重要。由于lncRNA也可以对miRNA起到调控作用,目前对于lncRNA的研究更为重要的是构建并完善lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA的三维调控网络,lncRNA和miRNA的联合抗凋亡治疗可能在未来临床上对于脊髓损伤后的神经继发性损伤保护和损伤后神经修复有着一定的意义。
通过总结lncRNA调控脊髓损伤后神经元细胞凋亡的作用为脊髓损伤后的抗凋亡治疗提供了新的思路,能更好地促进基础研究向临床转化的过渡,见图4和表2。
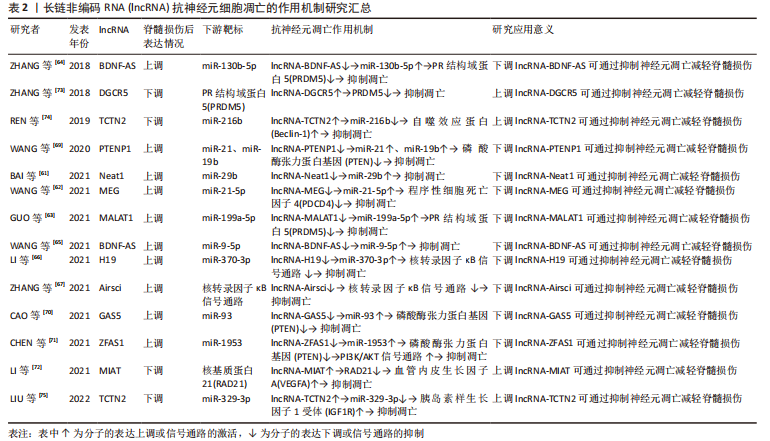
2.4 circRNA调节脊髓损伤后神经元细胞凋亡的作用机制 circRNA是一类呈环状结构的非编码RNA,RNA3’端和5’端相互闭合形成环形,不受外切酶降解,在真核细胞中具有较高的稳定性[76]。circRNA可调节mRNA的稳定性及基因转录,并可作为miRNA海绵靶向控制基因表达[77]。circRNA参与神经细胞的凋亡、增殖、分化和自噬等过程,与多种神经系统疾病密切相关[78-79]。脊髓损伤后circRNA 的表达发生明显变化,由于circRNA对于miRNA同样具有海绵吸附作用,故其对于凋亡的调控同样可以被特定的miRNA所靶向介导。针对性调控circRNA表达能够通过有效抑制神经元细胞凋亡,减少神经元的过量损失,从而起到保护脊髓、减轻继发脊髓损伤的作用。
2.4.1 促进神经元凋亡的 circRNA 一些 circRNA在脊髓损伤后表达上调,促进神经元细胞凋亡,加剧脊髓继发损伤。Chen等[80]发现大鼠脊髓损伤后circRNA-2960表达上调,海绵吸附miRNA-124导致其生物活性被抑制、从而加速神经元细胞凋亡,通过下调circRNA-2960可靶向上调miRNA-124抑制神经元细胞凋亡。血小板反应蛋白1是一种重要的细胞外基质蛋白,脊髓损伤后表达迅速增加,降低其表达可有效减缓包括神经元细胞凋亡在内的继发脊髓损伤系列病理变化。YAO等[81]发现脊髓损伤后Circ-014260表达上调,针对性下调后可靶向上调miR-384、下调血小板反应蛋白1表达,抑制神经元细胞凋亡、抑制氧化应激和内质网应激,减轻脊髓损伤。GUO等[82]发现脊髓损伤后Circ-Ncam2 表达上调,下调其表达能靶向阻断miR-544-3p介导的TLR4/核转录因子κB信号通路激活、抑制小胶质细胞活化,减少神经元细胞凋亡。
2.4.2 抑制神经元凋亡的circRNA 脊髓损伤后对特定circRNA进行表达上调可抑制神经元细胞凋亡,减轻脊髓损伤。YAO等[83]通过表达谱微阵列对脊髓损伤后的circRNA和mRNA进行分析,随后通过生物信息学对潜在的凋亡相关circRNA进行预测及验证,发现小鼠脊髓损伤后circRNA-7079作为抑制神经元细胞凋亡的circRNA表达上调,进一步增加circRNA-7079的表达可通过下调miR-6953-5p提高可溶性半乳糖苷结合凝集素3表达,更为显著的抑制神经元细胞凋亡。成纤维细胞生长因子9广泛存在于中枢神经系统,是miR-380的直接靶标,而ERK1/2是一种调控神经元存活和分化的信号通路,抑制其活性可促进神经元细胞凋亡,成纤维细胞生长因子9表达降低则抑制ERK1/2信号通路活性。Sun等[84]研究发现脊髓损伤后过表达circ-TYW1 可竞争性结合 miR-380通过以上生物学过程抑制神经元细胞凋亡。脊髓损伤后通过增加Circ-HIPK3表达,海绵吸附不同的miRNA,靶向作用于特定的基因,抑制神经元细胞凋亡。双特异性蛋白磷酸酶19和1可抑制脊髓损伤后神经细胞的凋亡,过表达Circ-HIPK3可靶向上调miR-222-3p介导的双特异性蛋白磷酸酶19减少神经元细胞凋亡[85],而过表达Circ-HIPK3可通过miR-382-5p/DUSP1轴减轻神经元凋亡和神经炎症反应[86]。DPYSL5也称为坍塌反应调节蛋白5,在发育中的神经系统中大量表达,介导生长锥引导和轴突伸长,上调Circ-HIPK3 亦可通过调节miR-588/DPYSL5轴减少神经元细胞凋亡 [87]。
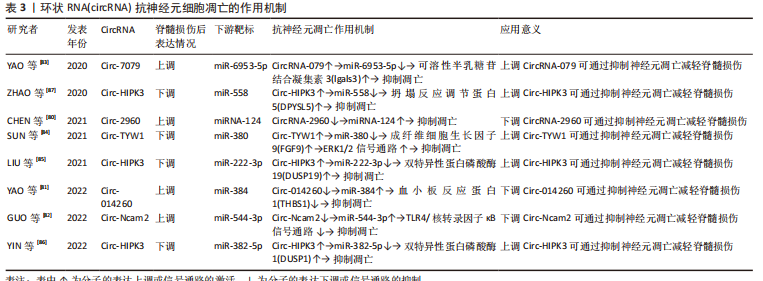
circRNA属于lncRNA的一个类型,由于结构呈环状的特点故单独进行论述。circRNA在非编码RNA的发现过程中出现最晚,故目前相应的研究报道也较少,其在脊髓损伤中的一系列作用,对于神经元细胞凋亡的相应调控机制尚未构成完整体系,未来的重点仍需放在对circRNA在脊髓损伤后的表达水平和调节机制进行探索。了解circRNA在脊髓损伤后对神经元细胞凋亡的调控作用为脊髓损伤的治疗提供了新的靶点,未来需要更多的相关研究来更加深入地探索,见表3。
| [1] SUN P, LIU DZ, JICKLING GC, et al. MicroRNA-based therapeutics in central nervous system injuries. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2018;38(7):1125-1148. [2] WANG F, LIU J, WANG X, et al. The emerging role of lncRNAs in spinal cord injury. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:3467121. [3] BIE F, WANG K, XU T, et al. The potential roles of circular RNAs as modulators in traumatic spinal cord injury. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;141:111826. [4] CUI Y, YIN Y, XIAO Z, et al. LncRNA Neat1 mediates miR-124-induced activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in spinal cord neural progenitor cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):400. [5] DING L, FU WJ, DI HY, et al. Expression of long non-coding RNAs in complete transection spinal cord injury: a transcriptomic analysis. Neural Regen Res. 2020; 15(8):1560-1567. [6] MA K, XU H, ZHANG J, et al. Insulin-like growth factor-1 enhances neuroprotective effects of neural stem cell exosomes after spinal cord injury via an miR-219a-2-3p/YY1 mechanism. Aging (Albany NY). 2019;11(24):12278-12294. [7] YANG R, CAI X, LI J, et al. Protective effects of miR-129-5p on acute spinal cord injury rats. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:8281-8288. [8] LIU J, WU Y. Electro-acupuncture-modulated miR-214 prevents neuronal apoptosis by targeting Bax and inhibits sodium channel Nav1.3 expression in rats after spinal cord injury. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;89:1125-1135. [9] HUANG W, LIN M, YANG C, et al. Rat bone mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes loaded with miR-494 promoting neurofilament regeneration and behavioral function recovery after spinal cord injury. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:1634917. [10] LIU R, WANG W, WANG S, et al. microRNA-21 regulates astrocytic reaction post-acute phase of spinal cord injury through modulating TGF-β signaling. Aging (Albany NY). 2018;10(6):1474-1488. [11] SAKER D, SENCAR L, YILMAZ DM, et al. Relationships between microRNA-20a and microRNA-125b expression and apoptosis and inflammation in experimental spinal cord injury. Neurol Res. 2019; 41(11):991-1000. [12] SOBRIDO-CAMEAN D, BARREIRO-IGLESIAS A. Role of caspase-8 and Fas in cell death after spinal cord injury. Front Mol Neurosci. 2018;11:101. [13] AN Y, LI J, YUAN Q, et al. MicroRNA-466c-3p exerts protective effect on neuronal apoptosis and improves functional recovery post spinal cord injury via mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. AMB Express. 2020;10(1):113. [14] QIAN Z, CHANG J, JIANG F, et al. Excess administration of miR-340-5p ameliorates spinal cord injury-induced neuroinflammation and apoptosis by modulating the P38-MAPK signaling pathway. Brain Behav Immun. 2020;87:531-542. [15] ZHANG XM, ZENG LN, YANG WY, et al. Inhibition of LncRNA Vof-16 expression promotes nerve regeneration and functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2022;17(1):217-227. [16] SHAO Z, LV G, WEN P, et al. Silencing of PHLPP1 promotes neuronal apoptosis and inhibits functional recovery after spinal cord injury in mice. Life Sci. 2018;209:291-299. [17] WANG X, SU X, GONG F, et al. MicroRNA-30c abrogation protects against spinal cord ischemia reperfusion injury through modulating SIRT1. Eur J Pharmacol. 2019;851:80-87. [18] CHEN XB, WANG ZL, YANG QY, et al. Diosgenin glucoside protects against spinal cord injury by regulating autophagy and alleviating apoptosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2018; 19(8):2274. [19] HUANG J, WU C, XU G, et al. The decreased expression of miR-429 in plasma exosomes after spinal cord injury inhibits neuronal apoptosis by mediating the PTEN/PI3K/Akt pathway. Ann Transl Med. 2022;10(1):6. [20] HUANG T, JIA Z, FANG L, et al. Extracellular vesicle-derived miR-511-3p from hypoxia preconditioned adipose mesenchymal stem cells ameliorates spinal cord injury through the TRAF6/S1P axis. Brain Res Bull. 2022;180:73-85. [21] XIAO X, LI W, XU Z, et al. Extracellular vesicles from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells reduce lipopolysaccharide-induced spinal cord injury neuronal apoptosis by mediating miR-29b-3p/PTEN. Connect Tissue Res. 2022; 63(6):634-649. [22] WANG Y, YUAN Y, GAO Y, et al. MicroRNA-31 regulating apoptosis by mediating the phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase/protein kinase B signaling pathway in treatment of spinal cord injury. Brain Dev. 2019;41(8):649-661. [23] ZHOU X, CHEN J, ZHANG H, et al. MicroRNA-23b attenuates the H2O2-induced injury of microglial cells via TAB3/NF-κB signaling pathway. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2018;11(12):5765-5773. [24] WANG F, LI J, ZHAO Y, et al. miR-672-3p promotes functional recovery in rats with contusive spinal cord injury by inhibiting ferroptosis suppressor protein 1. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:6041612. [25] WANG C, GUO X, WANG Y, et al. Silencing of miR-324-5p alleviates rat spinal cord injury by Sirt1. Neurosci Res. 2021;173:34-43. [26] CHEN J, QIN R. MicroRNA‑138‑5p regulates the development of spinal cord injury by targeting SIRT1. Mol Med Rep. 2020;22(1):328-336. [27] YAO L, GUO Y, WANG L, et al. Knockdown of miR-130a-3p alleviates spinal cord injury induced neuropathic pain by activating IGF-1/IGF-1R pathway. J Neuroimmunol. 2021;351:577458. [28] ZHAO QC, XU ZW, PENG QM, et al. Enhancement of miR-16-5p on spinal cord injury-induced neuron apoptosis and inflammatory response through inactivating ERK1/2 pathway. J Neurosurg Sci. 2020. doi: 10.23736/S0390-5616.20.04880-8. [29] WANG H, YUAN J, DANG X, et al. Mettl14-mediated m6A modification modulates neuron apoptosis during the repair of spinal cord injury by regulating the transformation from pri-mir-375 to miR-375. Cell Biosci. 2021;11(1):52. [30] LI J, LI L, SHEN Y. Protective role of microRNA-219-5p inhibitor against spinal cord injury via liver receptor homolog-1/Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway regulation. Exp Ther Med. 2018;15(4):3563-3569. [31] XU Z, ZHANG K, WANG Q, et al. MicroRNA‑124 improves functional recovery and suppresses Bax‑dependent apoptosis in rats following spinal cord injury. Mol Med Rep. 2019;19(4):2551-2560. [32] ZHENG J, KUANG J, ZHANG X, et al. miR-142-3p suppresses apoptosis in spinal cord-injured rats. Transl Neurosci. 2020;11(1):105-115. [33] ZHOU Q, FENG X, YE F, et al. miR-27a promotion resulting from silencing of HDAC3 facilitates the recovery of spinal cord injury by inhibiting PAK6 expression in rats. Life Sci. 2020;260:118098. [34] ZHANG H, PIAO M, GUO M, et al. MicroRNA-211-5p attenuates spinal cord injury via targeting of activating transcription factor 6. Tissue Cell. 2021;68:101459. [35] ZHANG Y, WANG S, LI H, et al. miR-495 reduces neuronal cell apoptosis and relieves acute spinal cord injury through inhibiting PRDM5. J Mol Histol. 2021; 52(2):385-396. [36] ZHANG X, GUO H, XIE A, et al. microRNA-331-3p attenuates neuropathic pain following spinal cord injury via targeting RAP1A. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2020;34(1):25-37. [37] HU Y, LIU Q, ZHANG M, et al. MicroRNA-362-3p attenuates motor deficit following spinal cord injury via targeting paired box gene 2. J Integr Neurosci. 2019;18(1):57-64. [38] ZHANG Z, SHEN L, YAN Y. MiR-139-5p alleviates neural cell apoptosis induced by spinal cord injury through targeting TRAF3. Acta Biochim Pol. 2020;67(3):359-365. [39] LIU R, PENG Z, ZHANG Y, et al. Upregulation of miR-128 inhibits neuronal cell apoptosis following spinal cord injury via FasL downregulation by repressing ULK1. Mol Med Rep. 2021;24(3):667. [40] WU WD, WANG LH, WEI NX, et al. MicroRNA-15a inhibits inflammatory response and apoptosis after spinal cord injury via targeting STAT3. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(21):9189-9198. [41] HE Y, LV B, HUAN Y, et al. Zhenbao pill protects against acute spinal cord injury via miR-146a-5p regulating the expression of GPR17. Biosci Rep. 2018;38(1): BSR20171132. [42] LI XH, FU NS, XING ZM. MiR-100 suppresses inflammatory activation of microglia and neuronal apoptosis following spinal cord injury via TLR4/NF-κB pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(20):8713-8720. [43] NIU F, PAN S. MicroRNA-488 inhibits neural inflammation and apoptosis in spinal cord injury through restraint on the HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Neuroreport. 2021;32(12):1017-1026. [44] WAN G, AN Y, TAO J, et al. MicroRNA-129-5p alleviates spinal cord injury in mice via suppressing the apoptosis and inflammatory response through HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB pathway. Biosci Rep. 2020;40(3):BSR20193315. [45] WANG D, ZHAO S, PAN J, et al. Ginsenoside Rb1 attenuates microglia activation to improve spinal cord injury via microRNA-130b-5p/TLR4/NF-κB axis. J Cell Physiol. 2021;236(3):2144-2155. [46] FEI M, LI Z, CAO Y, et al. MicroRNA-182 improves spinal cord injury in mice by modulating apoptosis and the inflammatory response via IKKβ/NF-κB. Lab Invest. 2021;101(9):1238-1253. [47] DING LZ, XU J, YUAN C, et al. MiR-7a ameliorates spinal cord injury by inhibiting neuronal apoptosis and oxidative stress. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24(1): 11-17. [48] LV X, LIANG J, WANG Z. MiR-21-5p reduces apoptosis and inflammation in rats with spinal cord injury through PI3K/AKT pathway. Panminerva Med. 2020. doi: 10.23736/S0031-0808.20.03974-9. [49] XIAO X, LI W, RONG D, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles facilitate the repair of spinal cord injury via the miR-29b-3p/PTEN/Akt/mTOR axis. Cell Death Discov. 2021;7(1):212. [50] HE S, WANG Z, LI Y, et al. MicroRNA-92a-3p enhances functional recovery and suppresses apoptosis after spinal cord injury via targeting phosphatase and tensin homolog. Biosci Rep. 2020;40(5):BSR20192743. [51] SHEN J, GAO F, ZHAO L, et al. MicroRNA-34c promotes neuronal recovery in rats with spinal cord injury through the C-X-C motif ligand 14/Janus kinase 2/signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 axis. Chin Med J (Engl). 2020; 133(18):2177-2185. [52] DAI J, XU LJ, HAN GD, et al. MicroRNA-125b promotes the regeneration and repair of spinal cord injury through regulation of JAK/STAT pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(3):582-589. [53] ZHAO K, LI R, RUAN Q, et al. microRNA-125b and its downstream Smurf1/KLF2/ATF2 axis as important promoters on neurological function recovery in rats with spinal cord injury. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(13):5924-5939. [54] JIAN YP, DONG SJ, XU SS, et al. MicroRNA-34a suppresses neuronal apoptosis and alleviates microglia inflammation by negatively targeting the Notch pathway in spinal cord injury. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24(3):1420-1427. [55] LI W, ZHANG Y, LV J, et al. MicroRNA-137-mediated lysine demethylase 4A regulates the recovery of spinal cord injury via the SFRP4-Wnt/β-Catenin axis. Int J Neurosci. 2021. doi: 10.1080/00207454.2021.1881093. [56] JIA X, HUANG G, WANG S, et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from mesenchymal stem cells containing microRNA-381 protect against spinal cord injury in a rat model via the BRD4/WNT5A axis. Bone Joint Res. 2021;10(5):328-339. [57] CHEN M, LAI X, WANG X, et al. Long non-coding RNAs and circular RNAs: insights into microglia and astrocyte mediated neurological diseases. Front Mol Neurosci. 2021;14:745066. [58] XIA X, NIU H, MA Y, et al. LncRNA CCAT1 protects astrocytes against OGD/R-induced damage by targeting the miR-218/NFAT5-signaling axis. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2020;40(8):1383-1393. [59] BAN Y, CUI C. Silencing of long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1 (NEAT1) protects PC-12 cells from lps-induced injury via targeting miR-29a. Med Sci Monit. 2020;26:e923914. [60] HE X, ZHANG J, GUO Y, et al. LncRNA MIAT promotes spinal cord injury recovery in rats by regulating RBFOX2-mediated alternative splicing of MCL-1. Mol Neurobiol. 2022;59(8):4854-4868. [61] BAI G, JIANG L, Meng P, et al. LncRNA neat1 promotes regeneration after spinal cord injury by targeting miR-29b. J Mol Neurosci. 2021;71(6):1174-1184. [62] WANG J, ZHAO Y, TANG Y, et al. The role of lncRNA-MEG/miR-21-5p/PDCD4 axis in spinal cord injury. Am J Transl Res. 2021;13(2):646-658. [63] GUO X, CHEN H, LI S, et al. Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 promotes neuronal apoptosis during spinal cord injury through miR-199a-5p/PRDM5 axis. Turk Neurosurg. 2021. doi: 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.36175-21.5. [64] ZHANG H, LI D, ZHANG Y, et al. Knockdown of lncRNA BDNF-AS suppresses neuronal cell apoptosis via downregulating miR-130b-5p target gene PRDM5 in acute spinal cord injury. RNA Biol. 2018;15(8):1071-1080. [65] WANG F, CHANG S, LI J, et al. Lithium alleviated spinal cord injury (SCI)-induced apoptosis and inflammation in rats via BDNF-AS/miR-9-5p axis. Cell Tissue Res. 2021;384(2):301-312. [66] LI X, QIAN Y, TANG K, et al. Inhibition of lncRNA H19/miR-370-3p pathway mitigates neuronal apoptosis in an in vitro model of spinal cord injury (SCI). Transl Neurosci. 2021;12(1):103-113. [67] ZHANG T, LI K, ZHANG ZL, et al. LncRNA Airsci increases the inflammatory response after spinal cord injury in rats through the nuclear factor kappa B signaling pathway. Neural Regen Res. 2021;16(4):772-777. [68] YE K, YU J, LI L, et al. Microvesicles from schwann-like cells as a new biomaterial promote axonal growth. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2021;17(2):291-302. [69] WANG Z, SONG Y, HAN X, et al. Long noncoding RNA PTENP1 affects the recovery of spinal cord injury by regulating the expression of miR-19b and miR-21. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235(4):3634-3645. [70] CAO Y, JIANG C, LIN H, et al. Silencing of long noncoding RNA growth arrest-specific 5 alleviates neuronal cell apoptosis and inflammatory responses through sponging microRNA-93 to repress PTEN expression in spinal cord injury. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021;15:646788. [71] CHEN Y, WEI Z, LIU J, et al. Long noncoding RNA ZFAS1 aggravates spinal cord injury by binding with miR-1953 and regulating the PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathway. Neurochem Int. 2021;147:104977. [72] LI D, YANG T, SHAO C, et al. LncRNA MIAT activates vascular endothelial growth factor A through RAD21 to promote nerve injury repair in acute spinal cord injury. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2021;528:111244. [73] ZHANG H, WANG W, LI N, et al. LncRNA DGCR5 suppresses neuronal apoptosis to improve acute spinal cord injury through targeting PRDM5. Cell Cycle. 2018; 17(16):1992-2000. [74] REN XD, WAN CX, NIU YL. Overexpression of lncRNA TCTN2 protects neurons from apoptosis by enhancing cell autophagy in spinal cord injury. FEBS Open Bio. 2019;9(7):1223-1231. [75] LIU J, LIN M, QIAO F, et al. Exosomes derived from lncRNA TCTN2-modified mesenchymal stem cells improve spinal cord injury by miR-329-3p/IGF1R axis. J Mol Neurosci. 2022;72(3):482-495. [76] QI J, WANG T, ZHANG Z, et al. Circ-ctnnb1 regulates neuronal injury in spinal cord injury through the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Dev Neurosci. 2022; 44(3):131-141. [77] BAN D, XIANG Z, YU P, et al. Circular RNA hecw1 regulates the inflammatory imbalance in spinal cord injury via miR-3551-3p/LRRTM1 axis. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2022;194(11):5151-5166. [78] TIAN F, YANG J, XIA R. Exosomes secreted from circZFHX3-modified mesenchymal stem cells repaired spinal cord injury through mir-16-5p/IGF-1 in mice. Neurochem Res. 2022;47(7):2076-2089. [79] ZHANG L, LI Z, MAO L, et al. Circular RNA in acute central nervous system injuries: a new target for therapeutic intervention. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022;15:816182. [80] CHEN J, FU B, BAO J, et al. Novel circular RNA 2960 contributes to secondary damage of spinal cord injury by sponging miRNA-124. J Comp Neurol. 2021; 529(7):1456-1464. [81] YAO Y, ZHANG X, XU J, et al. circ_014260/miR-384/THBS1 aggravates spinal cord injury in rats by promoting neuronal apoptosis and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Am J Transl Res. 2022;14(1):518-533. [82] GUO K, CHANG Y, JIN Y, et al. circ-Ncam2 (mmu_circ_0006413) Participates in LPS-induced microglia activation and neuronal apoptosis via the TLR4/NF-κB pathway. J Mol Neurosci. 2022;72(8):1738-1748. [83] YAO Y, WANG J, HE T, et al. Microarray assay of circular RNAs reveals cicRNA.7079 as a new anti-apoptotic molecule in spinal cord injury in mice. Brain Res Bull. 2020;164:157-171. [84] SUN Y, ZHOU Y, SHI X, et al. CircTYW1 serves as a sponge for microRNA-380 in accelerating neurological recovery following spinal cord injury via regulating FGF9. Cell Cycle. 2021;20(18):1828-1844. [85] LIU Y, AO S, ZHANG H, et al. Circ_HIPK3 alleviates CoCl2-induced apoptotic injury in neuronal cells by depending on the regulation of the miR-222-3p/DUSP19 axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021;553:126-133. [86] YIN X, ZHENG W, HE L, et al. CircHIPK3 alleviates inflammatory response and neuronal apoptosis via regulating miR-382-5p/DUSP1 axis in spinal cord injury. Transpl Immunol. 2022;73:101612. [87] ZHAO J, QI X, BAI J, et al. A circRNA derived from linear HIPK3 relieves the neuronal cell apoptosis in spinal cord injury via ceRNA pattern. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;528(2):359-367. |
| [1] | 郭淑慧, 杨晔, 江杨洋, 许建文. 神经源性膀胱miRNA-mRNA调控网络的筛选与验证[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(在线): 1-8. |
| [2] | 潘钟杰, 秦志鸿, 郑铁军, 丁晓飞, 廖世杰. 股骨头坏死发病机制中非编码RNA的靶标性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(9): 1441-1447. |
| [3] | 党 祎, 杜成砚, 姚红林, 袁能华, 曹 金, 熊 山, 张顶梅, 王 信. 激素型骨坏死与氧化应激[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
| [4] | 赵 璐, 赵逸菲, 高 达, 刘艳芳, 付婷婷, 徐江雁. Zeste基因抑制子基因12在糖尿病肾脏病模型大鼠肾组织中的表达[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(8): 1179-1186. |
| [5] | 杨九杰, 李 治, 王树杰, 田 野, 赵 伟. 神经电生理监测硬脊膜切开减压治疗急性脊髓损伤过程中脊髓的功能变化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(8): 1232-1236. |
| [6] | 聂晨晨, 苏凯奇, 高 静, 凡勇福, 阮晓迪, 袁 洁, 段昭远, 冯晓东. 环状RNA调控脑缺血发病的作用与机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(8): 1286-1291. |
| [7] | 李欣悦, 李熙恒, 毛天娇, 唐 亮, 李 江. 三维培养人牙周膜干细胞的形态、活性及成骨分化能力[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(6): 846-852. |
| [8] | 袁 维, 刘静东, 徐广辉, 康 健, 李富平, 王英杰, 支中正, 李冠武. 人血管周围干细胞成骨分化及Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的调控[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(6): 866-871. |
| [9] | 廖益东, 明 江, 宋文学, 王梓力, 张 宇, 廖一飞, 徐卡娅, 杨 华. 一种同时培养原代皮质及海马神经元的实验方法[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(6): 897-902. |
| [10] | 郝柳芳, 段红梅, 王子珏, 郝 飞, 郝 鹏, 赵 文, 高钰丹, 杨朝阳, 李晓光. 转基因小鼠脊髓损伤后室管膜细胞的时空动态变化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(6): 883-889. |
| [11] | 李晓寅, 杨晓青, 陈淑莲, 李正超, 王梓琪, 宋 震, 朱达仁, 陈旭义. 胶原/丝素蛋白支架联合神经干细胞治疗创伤性脊髓损伤[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(6): 890-896. |
| [12] | 张岐剑, 徐希明. 外胚层间充质干细胞的获取及应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(6): 928-934. |
| [13] | 袁 博, 谢利德, 付秀美. 许旺细胞源性外泌体促进损伤周围神经的修复与再生[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(6): 935-940. |
| [14] | 张 晴, 高春兰, 于飞飞, 张正皓, 马 芳, 高 源, 李桂忠, 姜怡邓, 马胜超. 同型半胱氨酸致胰岛β细胞凋亡中肝配蛋白A型受体2 DNA甲基化升高[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(5): 714-719. |
| [15] | 李志超, 谭国庆, 苏 辉, 徐展望, 薛海鹏. 非编码RNAs作为潜在治疗靶点在脊髓损伤中的调控效应[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(5): 758-764. |
神经元细胞凋亡是一种神经元程序性细胞死亡,激活细胞凋亡可包括内源和外源两种途径,细胞体积缩小、胞质密度增加、线粒体膜电位消失、染色体DNA降解以及核固缩是其主要特征。神经元细胞凋亡是继发性脊髓损伤造成脊髓神经元过度死亡的主要方式[8]。神经元大量凋亡常发生于脊髓损伤后24 h之内,因此脊髓损伤后抑制神经元细胞凋亡可减轻继发性脊髓损伤,利于脊髓损伤后脊髓功能的恢复和重建重塑[9]。
非编码RNA由microRNA(miRNA)、长链非编码RNA(long non-coding RNA,lncRNA)和环状RNA(circular RNA,circRNA)等组成,是一类不编码蛋白质的RNA。现有研究发现脊髓损伤后,与神经元细胞凋亡相关的非编码RNA出现显著差异性表达,调控特定非编码RNA的表达,可抑制脊髓损伤后神经元细胞凋亡[10-11]。
目前,尚未有报道对非编码RNA调控神经元细胞凋亡的机制进行系统全面的综述,大多报道不能较为完整地反映近年来非编码RNA调控神经元细胞凋亡的研究成果。基于此,文章聚焦于非编码RNA和神经元细胞凋亡,系统整理总结了近年来有关非编码RNA调控脊髓损伤后神经元细胞凋亡的研究进展,对其作用机制进行综述。并对未来探索更加具有靶向作用的非编码RNA药物载体,联合生物组织工程以及其他新兴技术,争取早日从细胞和动物层面的研究向临床转化性研究过渡提出展望,以期为脊髓损伤的保护性治疗提供新的靶点。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
1.1 资料来源
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 由第一作者在2022年8月完成文献检索。
1.1.2 检索数据库 PubMed数据库。
1.1.3 检索词 以“microRNA,miR,lncRNA,circRNA,noncoding RNA,RNA,SCI,spinal cord injury,spinal cord,apoptosis”为检索词进行检索。
1.1.4 检索时间范围 检索时间从PubMed数据库建库至2022年8月。
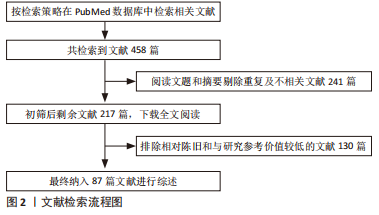
1.1.5 文献检索策略 见图1。

1.1.6 检索文献量 初步检索到458篇相关文献。
1.2 入组标准
1.2.1 纳入标准 ①非编码RNA调控脊髓损伤后神经元细胞凋亡的相关文献;②研究严谨且结论明确的文献;③能反映该领域近几年相关热点的文献。
1.2.2 排除标准 ①重复性文献;②与此综述相关性较差的文
献;③相对陈旧的研究文献;④对该研究参考价值较低的文献。
1.3 文献质量评估和数据的提取 共检索到458篇相关文献,阅读文题摘要后依据纳排标准筛选检索到的文献,剔除重复和不相关文献,最后共纳入文献87篇进行归纳整理与综述,资料提取的方法使用独立提取法。文献检索及筛选流程见图2。
3.2 作者综述区别于他人他篇的特点 目前,尚未有研究报道对非编码RNA调控神经元细胞凋亡的机制进行系统、全面的综述,大多报道仅列出几项凋亡调控机制稍作举例,不能较为完整地反映近年来非编码RNA对于神经元细胞凋亡方面的研究成果。基于此,文章整理总结了近年来有关非编码RNA调控脊髓损伤后神经元细胞凋亡的研究进展,对促进和抑制神经元凋亡的miRNA、lncRNA以及circRNA进行了分类综述,对其保护神经元的靶向机制进行了系统归纳,以期为脊髓损伤的保护性治疗提供新的靶点。
3.3 综述的局限性 该综述重点对非编码RNA调控脊髓损伤后神经元细胞凋亡进行阐述,未对损伤后神经元的其余生理病理过程进行详细描述,对于小胶质细胞、星状胶质细胞等非神经元细胞也未进行重点说明。此外,文章仅对靶向机制明确的非编码RNA进行综述,未纳入全部调控神经元细胞凋亡的非编码RNA。
3.4 综述的重要意义 非编码RNA调控脊髓损伤后神经元细胞凋亡的机制探索研究是近年来脊髓损伤研究领域的热点。动物实验发现脊髓损伤后,与神经元细胞凋亡相关的非编码RNA出现显著差异性表达,调控特定非编码RNA的表达,可靶向调节凋亡相关基因和信号通路,抑制脊髓损伤后神经元细胞过度凋亡,从而减轻继发性脊髓损伤程度,改善相应功能。该综述总结并介绍了非编码RNA调控脊髓损伤后神经元细胞凋亡的作用和机制,可以促进非编码RNA抗神经元细胞凋亡作为脊髓损伤治疗靶点的发展,对于了解脊髓损伤后的神经元抗凋亡保护性治疗有着重要意义。
3.5 课题专家组对未来的建议 脊髓损伤领域中有关非编码RNA的研究方兴未艾,未来的研究中,仍有诸多问题需要解决,如:①非编码RNA与靶基因的不完全互补所致的多靶位点问题,可导致脱靶效应和降低调控的特异性,这也是临床应用前需解决的重点和难点;②完善 mRNA、miRNA、lncRNA和circRNA相互作用的系统调控网络;③明确临床患者脊髓损伤后相应非编码RNA的表达水平,探索更加具有靶向作用的非编码RNA药物载体,联合生物组织工程以及其他新兴技术,争取早日从细胞和动物层面的研究向临床转化性研究过渡。
总之,对脊髓损伤后非编码RNA调控神经元细胞凋亡的机制探索任重而道远,相信随着研究的深入,针对性调控非编码RNA或许可成为临床上脊髓损伤后保护性治疗的一种新方法。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
 #br#
#br#
文题释义:
非编码RNA:由microRNA (miRNA)、长链非编码RNA(lncRNA)和环状RNA(circRNA)等组成,是一类不编码蛋白质的RNA。现有研究发现脊髓损伤后,与神经元细胞凋亡相关的非编码RNA出现显著差异性表达,调控特定非编码RNA的表达,可抑制脊髓损伤后神经元细胞凋亡。细胞凋亡:是一种程序性细胞死亡,是继发性脊髓损伤造成脊髓神经元过度死亡的主要方式。神经元大量凋亡常发生于脊髓损伤后24 h之内,因此脊髓损伤后抑制神经元细胞凋亡可减轻继发性脊髓损伤,利于脊髓损伤后脊髓功能的恢复和重建重塑。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
脊髓损伤是一种高致残性和高死亡率的中枢神经系统疾病,危害严重、发病率不断攀升。脊髓损伤的原因众多,临床多以创伤为主。脊髓损伤分为原发和继发性损伤,外力创伤瞬间直接作用于脊髓导致原发性损伤,原发损伤发生后,以炎症、氧化应激、自噬和凋亡等因素造成广泛而严重的继发性损伤,导致运动和感觉等神经功能不可逆受损。脊髓损伤的治疗一直是临床难题,目前临床常用的治疗方法如手术、糖皮质激素、各种神经营养因子、物理康复治疗等仍未取得突破性进展。脊髓损伤后神经元凋亡缺失是脊髓功能不可逆受损的一个重要因素,因此探索防止脊髓损伤后神经元凋亡的方法意义重大。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||