[1] 何万利,黄刚,赵莲萍.认知障碍的海马多模态MRI研究进展[J].磁共振成像,2021,12(4):111-114.
[2] GU X, ZHAO M, HAN X, et al. Presenilin-1 mutation is associated with a hippocampus defect in alzheimer’s disease: meta-analysis for neuroimaging research. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2020;191:105679.
[3] NAZIFI M, ORYAN S, ESFAHANI D, et al. The functional effects of piperine and piperine plus donepezil on hippocampal synaptic plasticity impairment in rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. Life Sci. 2021;265:118802.
[4] WANG Y, FENG L, LIU S, et al. Transcranial magneto-acoustic stimulation improves neuroplasticity in hippocampus of parkinson’s disease model mice. Neurotherapeutics. 2019;16(4):1210-1224.
[5] DYER A, VAHDATPOUR C, SANFELIU A, et al. The role of insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) in brain development,maturation and neuroplasticity. Neuroscience. 2016;325:89-99.
[6] ABBOTT L, NIGUSSIE F. Adult neurogenesis in the mammalian dentate gyrus. Anat Histol Embryol. 2020;49(1):3-16.
[7] SELLES M, FORTUNA J, ZAPPA-VILLAR M, et al. Adenovirus-mediated transduction of insulin-like growth factor 1 protects hippocampal neurons from the toxicity of aβ oligomers and prevents memory loss in an alzheimer mouse model. Mol Neurobiol. 2020;57(3):1473-1483.
[8] TAI F, WANG C, DENG X, et al. Treadmill exercise ameliorates chronic REM sleep deprivation-induced anxiety-like behavior and cognitive impairment in C57BL/6J mice. Brain Res Bull. 2020;164:198-207.
[9] 任瑞瑞,李文艳,王冬梅.胰岛素样生长因子1在病理性疼痛中的作用机制[J].中国生物化学与分子生物学报,2021,37(7):856-862.
[10] SHEARIN S, BRAITSCH M, QUERRY R. The effect of a multi-modal boxing exercise program on cognitive locomotor tasks and gait in persons with Parkinson disease. NeuroRehabilitation. 2021;49(4):619-627.
[11] 翟丽倩,陈晓芬,卢思彤,等.胰岛素样生长因子1(IGF-1)通过激活PI3K/AKT信号通路增强小鼠BV-2小胶质细胞的吞噬功能[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志,2021,37(3):199-204.
[12] 张玥熠,杨青,冯莉娟,等.胰岛素样生长因子1在中枢神经系统疾病发生发展中的作用及机制研究进展[J].山东医药,2022,62(2):100-103.
[13] HELLSTRöM A, LEY D, HANSEN-PUPP I, et al. Insulin-like growth factor 1 has multisystem effects on foetal and preterm infant development. Acta Paediatr. 2016;105(6):576-586.
[14] SONNTAG W, DEAK F, ASHPOLE N, et al. Insulin-like growth factor-1 in CNS and cerebrovascular aging. Front Aging Neurosci. 2013;5:27.
[15] FORBES B. Two years in IGF research. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2016;30-31: 70-74.
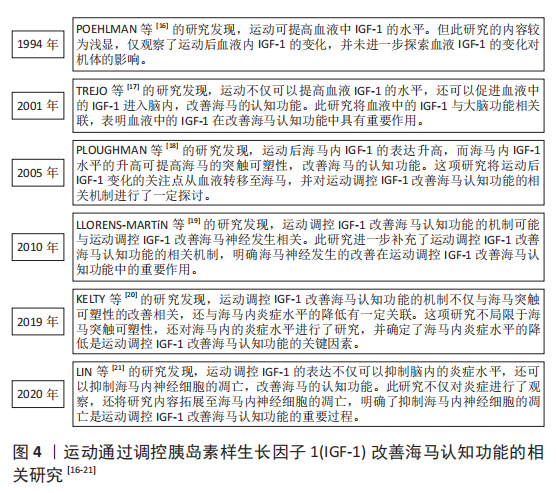
[16] POEHLMAN E, ROSEN C, COPELAND K. The influence of endurance training on insulin-like growth factor-1 in older individuals. Metabolism. 1994; 43(11):1401-1405.
[17] TREJO J, CARRO E, TORRES-ALEMAN I. Circulating insulin-like growth factor I mediates exercise-induced increases in the number of new neurons in the adult hippocampus. J Neurosci. 2001;21(5):1628-1634.
[18] PLOUGHMAN M, GRANTER-BUTTON S, CHERNENKO G, et al. Endurance exercise regimens induce differential effects on brain-derived neurotrophic factor, synapsin-I and insulin-like growth factor I after focal ischemia. Neuroscience. 2005;136(4):991-1001.
[19] LLORENS-MARTíN M, TORRES-ALEMáN I, TREJO J. Exercise modulates insulin-like growth factor 1-dependent and -independent effects on adult hippocampal neurogenesis and behaviour. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2010;44(2): 109-117.
[20] KELTY T, SCHACHTMAN T, MAO X, et al. Resistance-exercise training ameliorates LPS-induced cognitive impairment concurrent with molecular signaling changes in the rat dentate gyrus. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2019; 127(1):254-263.
[21] LIN J, KUO W, BASKARAN R, et al. Swimming exercise stimulates IGF1/ PI3K/Akt and AMPK/SIRT1/PGC1α survival signaling to suppress apoptosis and inflammation in aging hippocampus. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(8): 6852-6864.
[22] LI H, KONG R, WAN B, et al. Initiation of PI3K/AKT pathway by IGF-1 decreases spinal cord injury-induced endothelial apoptosis and microvascular damage. Life Sci. 2020;263:118572.
[23] COSTALES J, KOLEVZON A. The therapeutic potential of insulin-like growth factor-1 in central nervous system disorders. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2016; 63:207-222.
[24] YUAN H, CHEN R, WU L, et al. The regulatory mechanism of neurogenesis by 胰岛素样生长因子1 in adult mice. Mol Neurobiol. 2015;51(2):512-522.
[25] WEN X, JIAO L, TAN H. MAPK/ERK pathway as a central regulator in vertebrate organ regeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(3):1464.
[26] 朱洪竹,朱梅菊.有氧运动联合螺旋藻营养补充对2型糖尿病大鼠学习记忆的影响及其机制[J].天然产物研究与开发,2021,33(11):1845-1853.
[27] CARRO E, TREJO J, BUSIGUINA S, et al. Circulating insulin-like growth factor I mediates the protective effects of physical exercise against brain insults of different etiology and anatomy. J Neurosci. 2001;21(15):5678-5684.
[28] TAMAKOSHI K, HAYAO K, TAKAHASHI H. Early exercise after intracerebral hemorrhage inhibits inflammation and promotes neuroprotection in the sensorimotor cortex in rats. Neuroscience. 2020;438:86-99.
[29] LIU Y, CUI Z, YANG A, et al. Anti-apoptotic and pro-survival effect of exercise training on early aged hypertensive rat cerebral cortex. Aging (Albany NY). 2021;13(16):20495-20510.
[30] YU L, DUAN Y, ZHAO Z, et al. Hydroxysafflor Yellow A (HSYA) improves learning and memory in cerebral ischemia reperfusion-injured rats via recovering synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018;12:371.
[31] ZAPPA VILLAR M, LóPEZ HANOTTE J, CRESPO R, et al. Insulin-like growth factor 1 gene transfer for sporadic Alzheimer’s disease: new evidence for trophic factor mediated hippocampal neuronal and synaptic recovery-based behavior improvement. Hippocampus. 2021;31(10):1137-1153.
[32] HU A, YUAN H, WU L, et al. The effect of constitutive over-expression of insulin-like growth factor 1 on the cognitive function in aged mice. Brain Res. 2016;1631:204-213.
[33] HENDRIKSE J, CHYE Y, THOMPSON S, et al. Regular aerobic exercise is positively associated with hippocampal structure and function in young and middle-aged adults. Hippocampus. 2022;32(3):137-152.
[34] KIM T, BAEK K, YU H, et al. High-intensity exercise improves cognitive function and hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in obese mice maintained on high-fat diet. J Exerc Rehabil. 2020;16(2):124-131.
[35] NIE J, YANG X. Modulation of Synaptic Plasticity by Exercise Training as a Basis for Ischemic Stroke Rehabilitation. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2017;37(1):5-16.
[36] DING Q, VAYNMAN S, AKHAVAN M, et al. Insulin-like growth factor I interfaces with brain-derived neurotrophic factor-mediated synaptic plasticity to modulate aspects of exercise-induced cognitive function. Neuroscience. 2006;140(3):823-833.
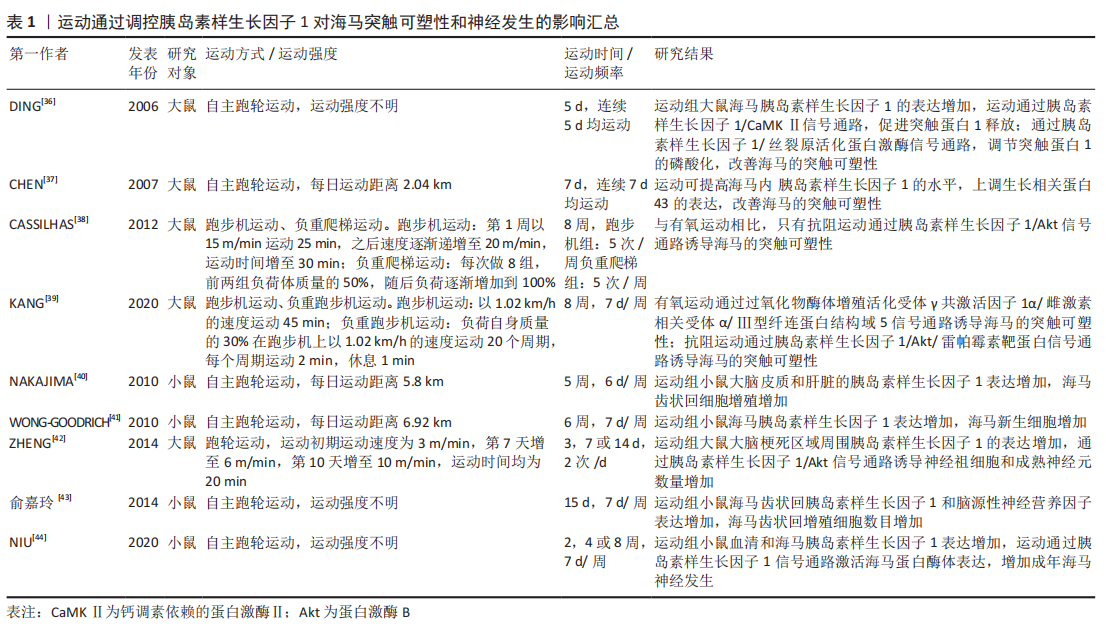
[37] CHEN M, RUSSO-NEUSTADT A. Running exercise-and antidepressant-induced increases in growth and survival-associated signaling molecules are IGF-dependent. Growth Factors. 2007;25(2):118-131.
[38] CASSILHAS R, LEE K, FERNANDES J, et al. Spatial memory is improved by aerobic and resistance exercise through divergent molecular mechanisms. Neuroscience. 2012;202:309-317.
[39] KANG J, WANG Y, WANG D. Endurance and resistance training mitigate the negative consequences of depression on synaptic plasticity through different molecular mechanisms. Int J Neurosci. 2020;130(6):541-550.
[40] NAKAJIMA S, OHSAWA I, OHTA S, et al. Regular voluntary exercise cures stress-induced impairment of cognitive function and cell proliferation accompanied by increases in cerebral IGF-1 and GST activity in mice. Behav Brain Res. 2010;211(2):178-184.
[41] WONG-GOODRICH S, PFAU M, FLORES C, et al. Voluntary running prevents progressive memory decline and increases adult hippocampal neurogenesis and growth factor expression after whole-brain irradiation. Cancer Res. 2010;70(22):9329-9338.
[42] ZHENG H, ZHANG L, LUO J, et al. Physical exercise promotes recovery of neurological function after ischemic stroke in rats. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(6): 10974-10988.
[43] 俞嘉玲,马黎,马兰,等.自主跑轮运动上调成年小鼠海马齿状回区细胞增殖及BDNF、IGF1和WNT4的表达水平[J].生理学报,2014,66(5): 559-568.
[44] NIU X, ZHAO Y, YANG N, et al. Proteasome activation by insulin-like growth factor-1/nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 signaling promotes exercise-induced neurogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;38(2):246-260.
[45] WANG J, ZHANG C, XU P, et al. Phosphoinositide 3‑kinase/protein kinase B regulates inflammation severity via signaling of Toll‑like receptor 4 in severe acute pancreatitis. Mol Med Rep. 2018;17(6):7835-7844.
[46] ZHAO T, ZHU Y, YAO L, et al. IGF-1 alleviates CCL4-induced hepatic cirrhosis and dysfunction of intestinal barrier through inhibition TLR4/NF-κB signaling mediated by down-regulation HMGB1. Ann Hepatol. 2021;26:100560.
[47] BELLINI M, HEREñú C, GOYA R, et al. Insulin-like growth factor-I gene delivery to astrocytes reduces their inflammatory response to lipopolysaccharide. J Neuroinflammation. 2011;8:21.
[48] SCHEFFER D, LATINI A. Exercise-induced immune system response: anti-inflammatory status on peripheral and central organs. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2020;1866(10):165823.
[49] PIAO C, STOICA B, WU J, et al. Late exercise reduces neuroinflammation and cognitive dysfunction after traumatic brain injury. Neurobiol Dis. 2013;54:252-263.
[50] GE L, LIU S, RUBIN L, et al. Research progress on neuroprotection of insulin-like growth factor-1 towards glutamate-induced neurotoxicity. Cells. 2022; 11(4):666.
[51] STANLEY T, FOURMAN L, ZHENG I, et al. Relationship of IGF-1 and IGF-binding proteins to disease severity and glycemia in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021;106(2):e520-e533.
[52] PHARAOH G, OWEN D, YEGANEH A, et al. Disparate central and peripheral effects of circulating IGF-1 deficiency on tissue mitochondrial function. Mol Neurobiol. 2020,57(3):1317-1331.
[53] YAN H, MITSCHELEN M, BIXLER G, et al. Circulating IGF1 regulates hippocampal IGF1 levels and brain gene expression during adolescence. Mol Neurobiol. 2011;211(1):27-37.
[54] ŻEBROWSKA A, SIKORA M, KONARSKA A, et al. Moderate intensity exercise in hypoxia increases IGF-1 bioavailability and serum irisin in individuals with type 1 diabetes. Ther Adv Endocrinol Metab. 2020;11:2042018820925326.
[55] 谢峥,吴永华.运动干预对老年MCI患者认知功能及血清胰岛素样生长因子1水平的影响[J].黑龙江医药,2017,30(3):516-518.
[56] TSAI C, UKROPEC J, UKROPCOVá B, et al. An acute bout of aerobic or strength exercise specifically modifies circulating exerkine levels and neurocognitive functions in elderly individuals with mild cognitive impairment. Neuroimage Clin. 2018;17:272-284.
[57] CHO S, ROH H. Taekwondo enhances cognitive function as a result of increased neurotrophic growth factors in elderly women. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019;16(6):962.
[58] KANG D, BRESSEL E, KIM D. Effects of aquatic exercise on insulin-like growth factor-1,brain-derived neurotrophic factor,vascular endothelial growth factor,and cognitive function in elderly women. Exp Gerontol. 2020;132:110842.
[59] MOLINA-SOTOMAYOR E, CASTILLO-QUEZADA H, MARTíNEZ-SALAZAR C, et al. Effects of progressive resistance training on cognition and IGF-1 levels in elder women who live in areas with high air pollution. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(17):6203.
[60] ARAZI H, BABAEI P, MOGHIMI M, et al. Acute effects of strength and endurance exercise on serum BDNF and IGF-1 levels in older men. BMC Geriatr. 2021;21(1):50.
[61] CARRO E, NUñEZ A, BUSIGUINA S, et al. Circulating insulin-like growth factor I mediates effects of exercise on the brain. J Neurosci. 2000;20(8):2926-2933.
[62] CASSILHAS R, ANTUNES H, TUFIK S, et al. Mood, anxiety,and serum IGF-1 in elderly men given 24 weeks of high resistance exercise. Percept Mot Skills. 2010;110(1):265-276.
[63] TAYLOR L, WILBORN C, KREIDER R, et al. Effects of resistance exercise intensity on extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in men. J Strength Cond Res. 2012;26(3):599-607.
[64] CASSILHAS R, LEE K, VENâNCIO D, et al. Resistance exercise improves hippocampus-dependent memory. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2012;45(12):1215-1220.
[65] FERNANDES J, SOARES J, DO AMARAL BALIEGO L, et al. A single bout of resistance exercise improves memory consolidation and increases the expression of synaptic proteins in the hippocampus. Hippocampus. 2016; 26(8):1096-1103.
[66] ASTILL B, KATSMA M, CAUTHON D, et al. Sex-based difference in Achilles peritendinous levels of matrix metalloproteinases and growth factors after acute resistance exercise. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2017;122(2):361-367.
[67] UYSAL N, AGILKAYA S, SISMAN A, et al. Exercise increases leptin levels correlated with IGF-1 in hippocampus and prefrontal cortex of adolescent male and female rats. J Chem Neuroanat. 2017;81:27-33.
[68] CHEN H, CHUNG Y, CHEN Y, et al. Effects of different types of exercise on body composition,muscle strength, and IGF-1 in the elderly with sarcopenic obesity. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2017;65(4):827-832.
[69] BOYNE P, MEYROSE C, WESTOVER J, et al. Effects of exercise intensity on acute circulating molecular responses poststroke. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2020;34(3):222-234.
[70] STEIN A, DA SILVA T, COELHO F, et al. Acute exercise increases circulating IGF-1 in Alzheimer’s disease patients,but not in older adults without dementia. Behav Brain Res. 2021;396:112903.
[71] NASCIMENTO M, GERAGE A, SILVA D, et al. Effect of resistance training with different frequencies and subsequent detraining on muscle mass and appendicular lean soft tissue, IGF-1, and testosterone in older women. Eur J Sport Sci. 2019;19(2):199-207.
[72] GATTI R, DE PALO E, ANTONELLI G, et al. IGF-I/IGFBP system: metabolism outline and physical exercise. J Endocrinol Invest. 2012;35(7):699-707.
[73] DING Y, CHANG C, XIE L, et al. Intense exercise can cause excessive apoptosis and synapse plasticity damage in rat hippocampus through Ca²⁺ overload and endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis pathway. Chin Med J (Engl). 2014;127(18):3265-3271.
[74] YAU S, GIL-MOHAPEL J, CHRISTIE B, et al. Physical exercise-induced adult neurogenesis:a good strategy to prevent cognitive decline in neurodegenerative diseases? Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:403120.
[75] NISHIDA Y, MATSUBARA T, TOBINA T, et al. Effect of low-intensity aerobic exercise on insulin-like growth factor-I and insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins in healthy men. Int J Endocrinol. 2010;2010:452820.
[76] BAKER L, FRANK L, FOSTER-SCHUBERT K, et al. Effects of aerobic exercise on mild cognitive impairment: a controlled trial. Arch Neurol. 2010;67(1):71-79. |
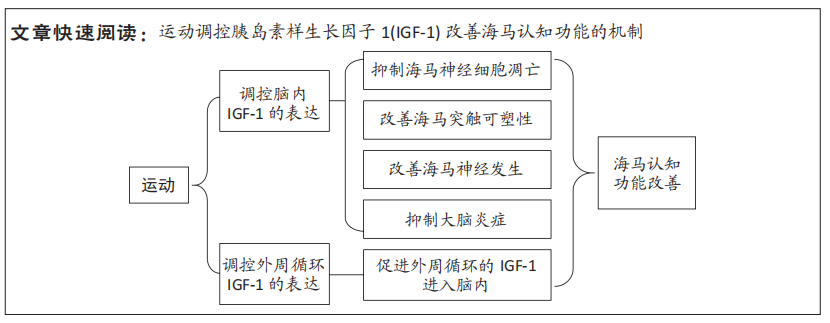
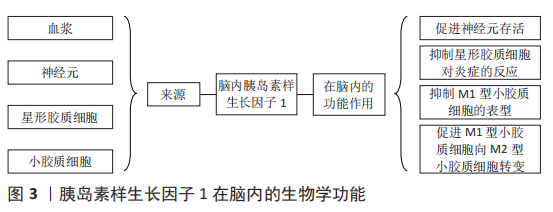
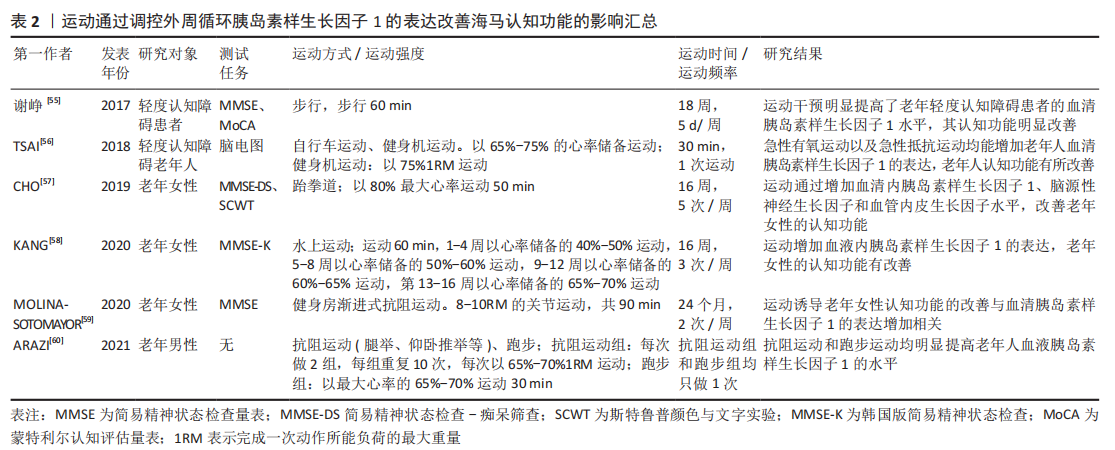
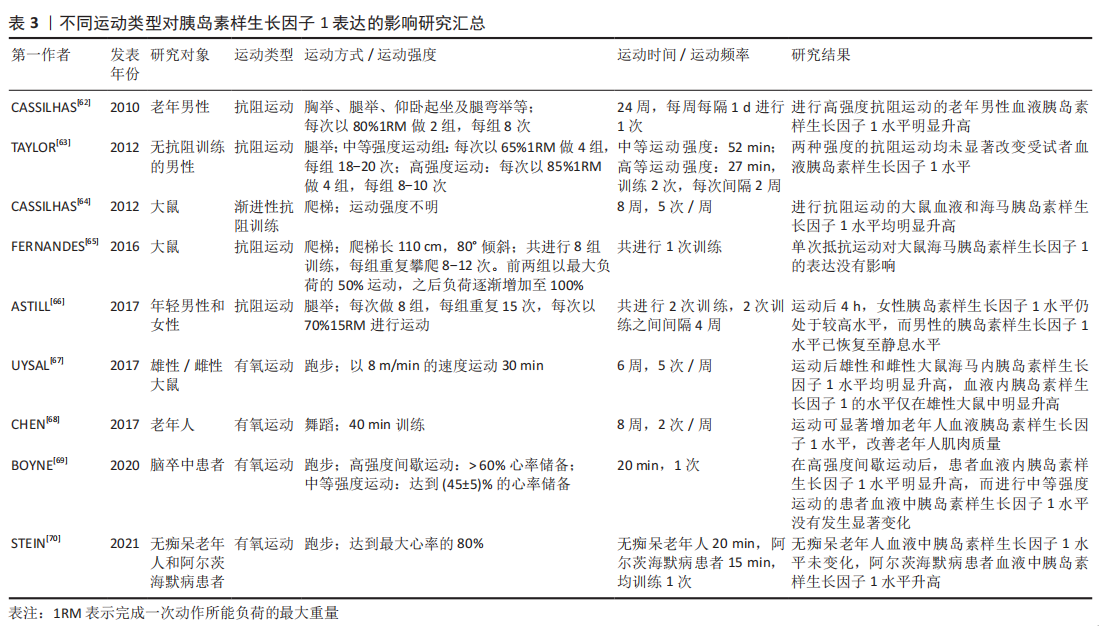
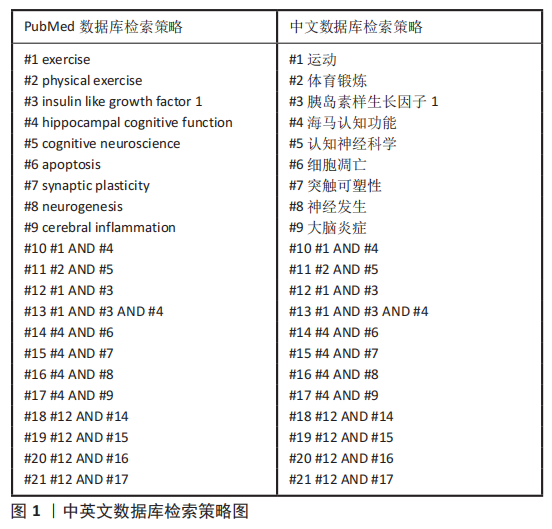
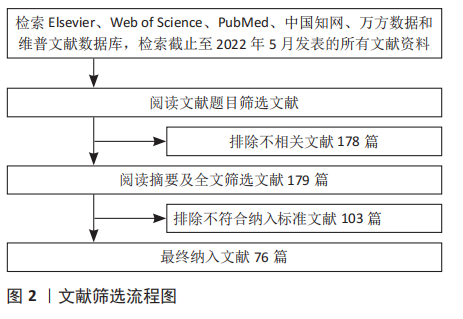
 目前该领域的研究还存在一定的问题:①关于运动干预胰岛素样生长因子1调控海马认知功能及神经退行性疾病的动物实验和临床研究仍然不够充分,应进一步加强运动干预阿尔茨海默病和帕金森病等神经病理动物模型和患者的研究。②在运动干预的方案设计中,不同运动模式、持续时间、运动强度、运动频率以及受试者特征等因素,导致研究结果差异性的原因尚不明确[71-73],例如:相较于抵抗运动,有氧运动对血清及海马胰岛素样生长因子1的影响更为明显。急性体育运动可增加受试者血清胰岛素样生长因子1的水平,而持续的运动训练则会降低受试者血清胰岛素样生长因子1的水平[74]。此外,与久坐男性相比,低强度的运动训练反而会降低运动男性循环胰岛素样生长因子1水平[75]。也有研究表明,每周2次或3次的抗阻运动均未影响血液胰岛素样生长因子1的水平[71],而每周5次的抗阻运动则明显提高血液胰岛素样生长因子1水平[64]。另外,在相同时间内进行同等强度的运动后,轻度认知障碍的男性血浆内胰岛素样生长因子1的升高程度高于女性,但在执行功能的多项测试中其结果却明显不如女性[76]。③运动也可以促进胰岛素样生长因子2的表达,而胰岛素样生长因子2在大脑可塑性、学习和记忆中也发挥着一定作用,在运动改善海马认知功能过程中胰岛素样生长因子1与胰岛素样生长因子2是否存在协同效应,以及其中的机制尚不明确。未来可以针对以上问题继续研究,这将为运动介导胰岛素样生长因子1改善海马认知障碍以及缓解神经退行性病的进展提供更多的理论依据。
目前该领域的研究还存在一定的问题:①关于运动干预胰岛素样生长因子1调控海马认知功能及神经退行性疾病的动物实验和临床研究仍然不够充分,应进一步加强运动干预阿尔茨海默病和帕金森病等神经病理动物模型和患者的研究。②在运动干预的方案设计中,不同运动模式、持续时间、运动强度、运动频率以及受试者特征等因素,导致研究结果差异性的原因尚不明确[71-73],例如:相较于抵抗运动,有氧运动对血清及海马胰岛素样生长因子1的影响更为明显。急性体育运动可增加受试者血清胰岛素样生长因子1的水平,而持续的运动训练则会降低受试者血清胰岛素样生长因子1的水平[74]。此外,与久坐男性相比,低强度的运动训练反而会降低运动男性循环胰岛素样生长因子1水平[75]。也有研究表明,每周2次或3次的抗阻运动均未影响血液胰岛素样生长因子1的水平[71],而每周5次的抗阻运动则明显提高血液胰岛素样生长因子1水平[64]。另外,在相同时间内进行同等强度的运动后,轻度认知障碍的男性血浆内胰岛素样生长因子1的升高程度高于女性,但在执行功能的多项测试中其结果却明显不如女性[76]。③运动也可以促进胰岛素样生长因子2的表达,而胰岛素样生长因子2在大脑可塑性、学习和记忆中也发挥着一定作用,在运动改善海马认知功能过程中胰岛素样生长因子1与胰岛素样生长因子2是否存在协同效应,以及其中的机制尚不明确。未来可以针对以上问题继续研究,这将为运动介导胰岛素样生长因子1改善海马认知障碍以及缓解神经退行性病的进展提供更多的理论依据。