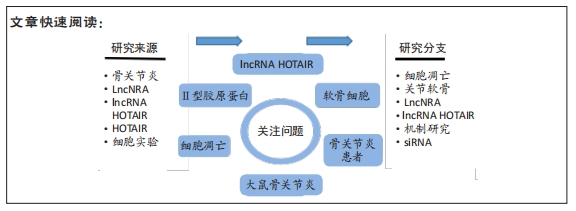
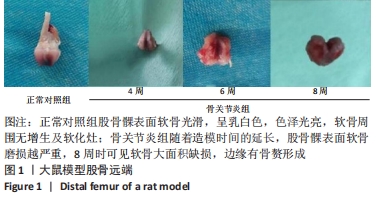
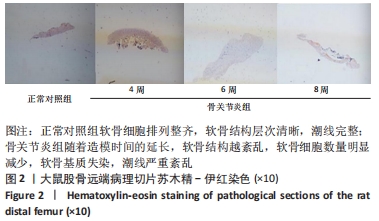
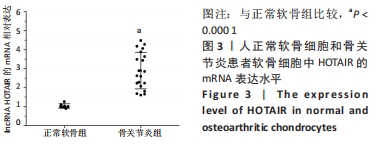
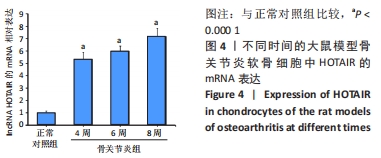
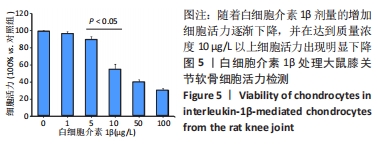
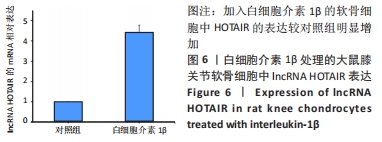
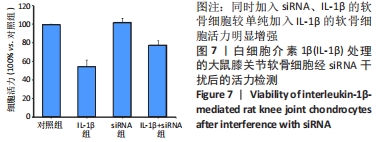
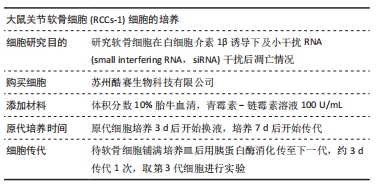
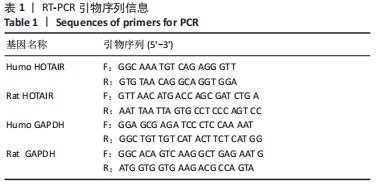
[1] HAWKER GA. Osteoarthritis is a serious disease. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2019;37 Suppl 12(5):3-6.
[2] JOHNSON VL, HUNTER DJ. The epidemiology of osteoarthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2014;28(1):5-15.
[3] CHARLIER E, DEROYER C, CIREGIA F, et al. Chondrocyte dedifferentia tion and osteoarthritis(OA). Biochem Pharmacol. 2019;165:49-65.
[4] CORREA D, LIETMAN SA. Articular cartilage repair: Current needs, methods and research directions. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017;62:67-77.
[5] ARMIENTO AR, STODDART MJ, ALINI M, et al. Biomaterials for articular cartilage tissue engineering: Learning from biology. Acta Biomater. 2018;65:1-20.
[6] 张洪美.膝骨关节炎的规范诊治与阶梯治疗[J].中国骨伤,2019, 32(5):1391-1395.
[7] HENROTIN Y, CLUTTERBUCK AL, ALLAWAY D, et al. Biological actions of curcumin on articular chondrocytes.Oetenarthritis Cartilage. 2010;18(2):141-149.
[8] SHAKIBAEI M, JOHN T, SCHULZE-TANZIL G, et al.Suppression of NF-kappaB activation by curcumin leads to inhibition of expression of cyclo-oxygenase-2 and matrix metalloproteinase-9 in human articular chondrocytes: Implications for the treatment of osteoarthritis. Biochem Pharmacol. 2007;73(9):1434-1445.
[9] 张玉昌,赵萍,慕向前,等.SOX2基因对骨关节炎软骨细胞凋亡的影响研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2019,25(12):1773-1777.
[10] TANG L, DING J, ZHOU G, et al. LncRNA p21 promotes chondrocyte apoptosis in osteoarthritis by acting as a sponge for miR451. Mol Med Rep. 2018;18(6):5295-5301.
[11] MUSUMECI G, CASTROGIOVANNI P, TROVATO FM, et al. Biomarkers of chondrocyte apoptosis and autophagy in osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(9):20560-20575.
[12] POULSEN E, GONCALVES GH, BRICCA A, et al. Knee osteoarthritis risk is increased 4-6 fold after knee injury - a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Sports Med. 2019;53(23):1454-1463.
[13] XING D, LIANG JQ, LI Y, et al. Identification of Long Noncoding RNA Associated with Osteoarthritis in Humans. Orthop Surg. 2014;6(4):288-293.
[14] ZHANG CP, WANG P, JIANG PF, et al. Upregulation of lncRNA HOTAIR contributes to IL-1β-induced MMP overexpression and chondrocytes apoptosis in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis. Gene. 2016; 586(2):248-253.
[15] WEI B, WEI W, ZHAO B, et al.Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR inhibits miR-17-5p to regulate osteogenic differentiation and proliferation in non-traumatic osteonecrosis of femoral head. PLoS One. 2017;12(2): e0169097.
[16] WEIMER A, MADRY H, VENKATESAN JK, et al. Benefits of recombinant adeno–associated virus(rAAV)–mediated insulinlike growth factor I(IGF–I) overexpression for the long–term reconstruction of human osteoarthritic cartilage by modulation of the IGF–I axis. Mol Med. 2012; 18:346-358.
[17] LANE NE, SHIDARA K, WISE BL. Osteoarthritis year in review 2016: clinical. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2017;25(2):209-215.
[18] CHEN WK, YU XH, YANG W, et al. IncRNAs: novel players in intervertebral discdegeneration and osteoarthritis. Cell Prolif. 2017;50(1):e12313.
[19] TANO K, AKIMITSU N. Long non-coding RNAs in cancer progression. Frontiers in Genetics. 2012;3:219.
[20] YU X, LI Z. Long non-coding RNA growth arrest-specific transcript 5 in tumor biology. Oncol Lett. 2015;10(4):1953-1958.
[21] KHALIL AM, GUTTMAN M, HUARTE M, et al. Many human large intergenic noncoding RNAs associate with chromatin-modifying complexes and affect gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009; 106(28):11667-11672.
[22] FU M, HUANG G, ZHANG Z, et al. Expression profile of long noncoding RNAs in cartilage from knee osteoarthritis patients. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015;23(3):423-432.
[23] YANG Z, ZHOU L, WU LM, et al. Overexpression of long non-coding RNA HOTAIR predicts tumor recurrence in hepatocellular carcinoma patients following liver transplantation. Ann Surg Oncol. 2011;18:1243-1250.
[24] EGEBLAD M, RASCH MG, WEAVER VM. Dynamic interplay between the collagen scaffold and tumor evolution. Curr Opinion cCell Biol. 2010;22:697-706.
[25] XU ZY, YU QM, DU YA, et al. Knockdown of long non-coding RNA HOTAIR suppresses tumor invasion and reverses epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer. Int J Biol Sci. 2013;9(6):587-597.
[26] KOGO R, SHIMAMURA T, MIMORI K, et al. Long noncoding RNA HOTAIR regulates polycomb-dependent chromatin modification and is associated with poor prognosis in colorectal cancers. Cancer Res. 2011;71:6320-6326.
[27] GUPTA RA, SHAH N, WANG KC, et al. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR reprograms chromatin state to promote cancer metastasis. Nature. 2010;464:1071-1076.
[28] JING L, YUAN W, RUOFAN D, et al. HOTAIR enhanced aggressive biological behaviors and induced radio-resistance via inhibiting p21 in cervical cancer. Tumour Biology. 2015;36:3611-3619.
[29] ZHAO W, GENG D, LI S, et al. LncRNA HOTAIR influences cell growth, migration,invasion, and apoptosis via the miR-20a-5p/HMGA2 axis in breast cancer. Cancer Med. 2018;7(3):842-855.
[30] ZHANG HJ, WEI QF, WANG SJ, et al. LncRNA HOTAIR alleviates rheumatoid arthritis by targeting miR-138 and inactivating NF-kappaB pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2017;50:283-290.
[31] LIETMAN C, WU B, LECHNER S, et al. Inhibition of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling ameliorates osteoarthritis in a murine model of experimental osteoarthritis. JCI Insight. 2018;3(3):e96308.
[32] BOUAZIZ W, SIGAUX J, MODROWSKI D, et al. nteraction of HIF1alpha and beta-catenin inhibits matrix metalloproteinase 13 expression and prevents cartilage damage in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016; 113(19):5453-5458.
[33] 孙强,赵轶男,王远瑞,等. LncRNA HOTAIR调控miR-130a-3p对骨关节炎软骨细胞增殖和分化的影响[J]. 中国骨与关节杂志,2019, 8(12):931-937.
[34] CHEN H, QI J, BI Q, et al. Expression profile of long noncoding RNA (HOTAIR) and its predicted target miR-17-3p in LPS-induced inflammatory injury in human articular chondrocyte C28/I2 cells.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2017;10(9):9146-9157.
[35] ZHANG HJ, WEI QF, WANG SJ, et al. LncRNA HOTAIR alleviates rheumatoid arthritis by targeting miR-138 and inactivating NF-kappaB pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2017;50:283-290.
|