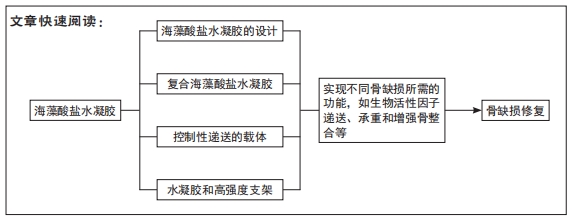
[1] HO-SHUI-LING A, BOLANDER J, RUSTOM LE, et al. Bone regeneration strategies: engineered scaffolds, bioactive molecules and stem cells current stage and future perspectives. Biomaterials. 2018;180:143-162.
[2] SHAKYA AK, KANDALAM U. Three-dimensional macroporous materials for tissue engineering of craniofacial bone. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2017;55(9):875-891.
[3] TOURNIER P, GUICHEUX J, PARE A, et al. A partially demineralized allogeneic bone graft: in vitro osteogenic potential and preclinical evaluation in two different intramembranous bone healing models. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):4907.
[4] DIMITRIOU R, MATALIOTAKIS GI, ANGOULES AG, et al. Complications following autologous bone graft harvesting from the iliac crest and using the RIA:A systematic review. Injury-Int J Care Inj. 2011;42:S3-S15.
[5] 谢程欣,余城墙,王维,等.骨形态发生蛋白与自体骨移植治疗四肢长骨骨不连的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(5): 803-810.
[6] YUAN HP, FERNANDES H, HABIBOVIC P, et al. Osteoinductive ceramics as a synthetic alternative to autologous bone grafting. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(31):13614-13619.
[7] HAUGEN HJ, LYNGSTADAAS SP, ROSSI F, et al. Bone grafts:which is the ideal biomaterial? J Clin Periodontol. 2019;46:92-102.
[8] ZHENG Y, WANG J, CHANG B, et al. Clinical study on repair of metacarpal bone defects using titanium alloy implantation and autologous bone grafting. Exp Ther Med. 2020;20(6):233.
[9] AGARWAL R, GARCIA AJ. Biomaterial strategies for engineering implants for enhanced osseointegration and bone repair. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015;94:53-62.
[10] BOSE S, ROY M, BANDYOPADHYAY A. Recent advances in bone tissue engineering scaffolds. Trends Biotechnol. 2012;30(10):546-554.
[11] REAKASAME S, BOCCACCINI AR. Oxidized alginate-based hydrogels for tissue engineering applications: a review. Biomacromolecules. 2018;19(1):3-21.
[12] RANA D, KUMAR TSS, RAMALINGAM M. Cell-laden hydrogels for tissue engineering. J Biomater Tissue Eng. 2014;4(7):507-535.
[13] SPICER C D. Hydrogel scaffolds for tissue engineering:the importance of polymer choice. Polym Chem. 2020;11(2):184-219.
[14] GONG T, XIE J, LIAO JF, et al. Nanomaterials and bone regeneration. Bone Res. 2015;3:15029.
[15] MAO A S, MOONEY DJ. Regenerative medicine: current therapies and future directions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112(47):14452-14459.
[16] LALZAWMLIANA V, ANAND A, MUKHERJEE P, et al. Marine organisms as a source of natural matrix for bone tissue engineering. Ceram Int. 2019;45(2):1469-1481.
[17] LIU J, YANG SQ, LI XT, et al. Alginate oligosaccharides:production, biological activities, and potential applications. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2019;18(6):1859-1881.
[18] TIBBITT MW, ANSETH KS. Hydrogels as extracellular matrix mimics for 3D cell culture. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2009;103(4):655-663.
[19] XIANG G, LIPPENS E, HAFEEZ S, et al. Oxidized alginate beads for tunable release of osteogenically potent mesenchymal stromal cells. Mater Sci Eng C-Mater Biol Appl. 2019;104:8.
[20] AL-SHAMKHANI A, DUNCAN R. Radioiodination of alginate via covalently-bound tyrosinamide allows monitoring of its fate in vivo. J Bioact Compat Polym. 1995;10(1):4-13.
[21] LIANG Y, LIU WS, HAN BQ, et al. An in situ formed biodegradable hydrogel for reconstruction of the corneal endothelium. Colloid Surf B-Biointerfaces. 2011;82(1):1-7.
[22] BALAKRISHNAN B, LESIEUR S, LABARRE D, et al. Periodate oxidation of sodium alginate in water and in ethanol-water mixture:a comparative study. Carbohydr Res. 2005;340(7):1425-1429.
[23] ALSBERG E, KONG HJ, HIRANO Y, et al. Regulating bone formation via controlled scaffold degradation. J Dent Res. 2003;82(11):903-908.
[24] PLAZINSKI W. Molecular basis of calcium binding by polyguluronate chains. revising the egg-box model. J Comput Chem. 2011;32(14): 2988-2995.
[25] LIU YG, TONG YS, WANG SB, et al. Influence of different divalent metal ions on the properties of alginate microcapsules and microencapsulated cells. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol. 2013;67(1):66-76.
[26] ISKANDAR L, ROJO L, DI SILVIO L, et al. The effect of chelation of sodium alginate with osteogenic ions, calcium, zinc, and strontium. J Biomater Appl. 2019;34(4):573-584.
[27] CATTALINI JP, HOPPE A, PISHBIN F, et al. Novel nanocomposite biomaterials with controlled copper/calcium release capability for bone tissue engineering multifunctional scaffolds. J R Soc Interface. 2015;12(110):13.
[28] LUECKGEN A, GARSKE DS, ELLINGHAUS A, et al. Hydrolytically-degradable click-crosslinked alginate hydrogels. Biomaterials. 2018; 181:189-198.
[29] YAN HQ, CHEN XQ, FENG MX, et al. Layer-by-layer assembly of 3D alginate-chitosan-gelatin composite scaffold incorporating bacterial cellulose nanocrystals for bone tissue engineering. Mater Lett. 2017; 209:492-496.
[30] JEON O, BOUHADIR KH, MANSOUR JM, et al. Photocrosslinked alginate hydrogels with tunable biodegradation rates and mechanical properties. Biomaterials. 2009;30(14):2724-2734.
[31] JEON O, POWELL C, AHMED SM, et al. Biodegradable, photocrosslinked alginate hydrogels with independently tailorable physical properties and cell adhesivity. Tissue Eng Part A. 2010;16(9):2915-2925.
[32] HUEBSCH N, ARANY PR, MAO AS, et al. Harnessing traction-mediated manipulation of the cell/matrix interface to control stem-cell fate. Nat Mater. 2010;9(6):518-526.
[33] 赵德路,铁朝荣,王新,等.复合锶离子光交联海藻酸盐水凝胶支架的机械和生物学性能[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(18):2880-2887.
[34] KAYGUSUZ H, EVINGUR GA, PEKCAN O, et al. Surfactant and metal ion effects on the mechanical properties of alginate hydrogels. Int J Biol Macromol. 2016;92:220-224.
[35] 张漫,李昊,徐婷,等.含锶交联藻酸钠凝胶对前成骨细胞黏附和增殖的影响[J].上海口腔医学,2019,28(2):123-127.
[36] AMIN AK, HUNTLEY JS, BUSH PG, et al. Chondrocyte death in mechanically injured articular cartilage-the influence of extracellular calcium. J Orthop Res. 2009;27(6):778-784.
[37] DIAZ-RODRIGUEZ P, GARCIA-TRINANES P, LOPEZ MME, et al. Mineralized alginate hydrogels using marine carbonates for bone tissue engineering applications. Carbohydr Polym. 2018;195:235-242.
[38] SUN XJ, LI ZY, CUI ZD, et al. Preparation and physicochemical properties of an injectable alginate-based hydrogel by the regulated release of divalent ions via the hydrolysis of d-glucono-delta-lactone. J Biomater Appl. 2020;34(7):891-901.
[39] PATIL SS, NUNE KC, MISRA RDK. Alginate/poly(amidoamine) injectable hybrid hydrogel for cell delivery. J Biomater Appl. 2018;33(2):295-314.
[40] LEE C, SHIN J, LEE JS, et al. Bioinspired, calcium-free alginate hydrogels with tunable physical and mechanical properties and improved biocompatibility. Biomacromolecules. 2013;14(6):2004-2013.
[41] SALGADO AJ, COUTINHO OP, REIS RL. Bone tissue engineering: state of the art and future trends. Macromol Biosci. 2004;4(8):743-765.
[42] LOURENCO AH, NEVES N, RIBEIRO-MACHADO C, et al. Injectable hybrid system for strontium local delivery promotes bone regeneration in a rat criticalsized defect model. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):15.
[43] INGAVLE GC, GIONET-GONZALES M, VORWALD CE, et al. Injectable mineralized microsphere-loaded composite hydrogels for bone repair in a sheep bone defect model. Biomaterials. 2019;197:119-128.
[44] CECOLTAN S, STANCU IC, DRAGUSIN DM, et al. Nanocomposite particles with improved microstructure for 3D culture systems and bone regeneration. J Mater Sci-Mater Med. 2017;28(10):153.
[45] CUI YT, ZHU TT, LI D, et al. Bisphosphonate-functionalized scaffolds for enhanced bone regeneration. Adv Healthc Mater. 2019;8(23): e1901073.
[46] LOI F, CORDOVA LA, PAJARINEN J, et al. Inflammation, fracture and bone repair. Bone. 2016;86:119-130.
[47] ZHOU WY, LIN JX, ZHAO K, et al. Single-cell profiles and clinically useful properties of human mesenchymal stem cells of adipose and bone marrow origin. Am J Sports Med. 2019;47(7):1722-1733.
[48] 王俊钢,李聪聪,毛广显,等.骨生物材料复合骨髓间充质干细胞异位成骨修复肋骨大段缺损[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(2): 182-186.
[49] HASANI-SADRABADI MM, SARRION P, POURAGHAEI S, et al. An engineered cell-laden adhesive hydrogel promotes craniofacial bone tissue regeneration in rats. Sci Transl Med. 2020;12(534):eaay6853.
[50] KOLAMBKAR YM, DUPONT KM, BOERCKEL JD, et al. An alginate-based hybrid system for growth factor delivery in the functional repair of large bone defects. Biomaterials. 2011;32(1):65-74.
[51] CHEN F, BI D, CAO G, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein 7-transduced human dermal-derived fibroblast cells differentiate into osteoblasts and form bone in vivo. Connecti Tissue Res. 2018;59(3):223-232.
[52] KAIGLER D, SILVA EA, MOONEY DJ. Guided bone regeneration using injectable vascular endothelial growth factor delivery gel. J Periodontol. 2013;84(2):230-238.
[53] SUBBIAH R, CHENG A, RUEHLE MA, et al. Effects of controlled dual growth factor delivery on bone regeneration following composite bone-muscle injury. Acta Biomaterialia. 2020;114:63-75.
[54] SIMMONS CA, ALSBERG E, HSIONG S, et al. Dual growth factor delivery and controlled scaffold degradation enhance in vivo bone formation by transplanted bone marrow stromal cells. Bone. 2004;35(2):562-569.
[55] BAYER EA, JORDAN J, ROY A, et al. Programmed platelet-derived growth factor-bb and bone morphogenetic protein-2 delivery from a hybrid calcium phosphate/alginate scaffold. Tissue Eng Part A. 2017;23(23-24): 1382-1393.
[56] SEVARI SP, SHAHNAZI F, CHEN C, et al. Bioactive glass-containing hydrogel delivery system for osteogenic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells. J Biomed Mater Res Part A. 2020;108(3): 557-564.
[57] GE Q, GREEN DW, LEE DJ, et al. Mineralized polysaccharide transplantation modules supporting human msc conversion into osteogenic cells and osteoid tissue in a non-union defect. Mol Cells. 2018;41(12):1016-1023.
[58] KUMAR A, NUNE KC, MISRA R DK. Design and biological functionality of a novel hybrid Ti-6Al-4V/hydrogel system for reconstruction of bone defects. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12(4):1133-1144.
[59] CIPITRIA A, BOETTCHER K, SCHOENHALS S, et al. In-situ tissue regeneration through SDF-1 alpha driven cell recruitment and stiffness-mediated bone regeneration in a critical-sized segmental femoral defect. Acta Biomateri. 2017;60:50-63.
[60] 郑旺,高丽娜,李西成,等.胶原蛋白膜包裹藻酸钙凝胶/骨髓基质细胞/BMP-2复合体修复兔桡骨缺损[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012, 20(4):363-366.
[61] QIU G, HUANG M, LIU J, et al. Antibacterial calcium phosphate cement with human periodontal ligament stem cell-microbeads to enhance bone regeneration and combat infection. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2021;15(3):232-243.
[62] SANGEETHA K, GIRIJA EK. Tailor made alginate hydrogel for local infection prophylaxis in orthopedic applications. Mater Sci Eng C-Mater Biol Appl. 2017;78:1046-1053.
[63] MA FB, LI SJ, RUIZ-ORTEGA LI, et al. Effects of alginate/chondroitin sulfate-based hydrogels on bone defects healing. Mater Sci Eng C-Mater Biol Appl. 2020;116:11212.
[64] DIMITRIOU R, JONES E, MCGONAGLE D, et al. Bone regeneration: current concepts and future directions. BMC Med. 2011;9:66.
[65] RAPHEL J, KARLSSON J, GALLI S, et al. Engineered protein coatings to improve the osseointegration of dental and orthopaedic implants. Biomaterials. 2016;83:269-282.
[66] MUDERRISOGLU C, SAVELEVA M, ABALYMOV A, et al. Nanostructured biointerfaces based on bioceramic calcium carbonate/hydrogel coatings on titanium with an active enzyme for stimulating osteoblasts growth. Adv Mater Interfaces. 2018;5(19):1800452.
[67] ZHAO LA, WEIR MD, XU HHK. An injectable calcium phosphate-alginate hydrogel-umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell paste for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2010;31(25):6502-6510.
[68] WEIR MD, XU HHK, SIMON CG. Strong calcium phosphate cement-chitosan-mesh construct containing cell-encapsulating hydrogel beads for bone tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res Part A. 2006; 77A(3):487-496.
[69] XU C, WANG XY, ZHOU J, et al. Bioactive tricalcium silicate/alginate composite bone cements with enhanced physicochemical properties. J Biomed Mater Res Part B. 2018;106(1):237-244.
|