中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (22): 3566-3572.doi: 10.12307/2022.286
• 生物材料综述 biomaterial review • 上一篇 下一篇
纳米粒子:缺血性脑卒中治疗新策略
夏克尔扎提·肖哈拉提,王晓蓓,王 琳
- 华中科技大学同济医学院附属协和医院检验科,湖北省武汉市 430000
-
收稿日期:2020-12-15修回日期:2021-02-05接受日期:2021-05-28出版日期:2022-08-08发布日期:2022-01-12 -
通讯作者:王琳,博士,教授,主任医师,华中科技大学同济医学院附属协和医院检验科,湖北省武汉市 430000 王晓蓓,博士,副教授,副主任医师,华中科技大学同济医学院附属协和医院检验科,湖北省武汉市 430000 -
作者简介:夏克尔扎提·肖哈拉提,男,1995年生,新疆维吾尔自治区克拉玛依市人,维吾尔族,华中科技大学在读硕士,主要从事中枢神经及外周神经再生方面的研究。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(8187081092,项目名称:导电丝胶神经导管联合基因编辑技术的长距离外周神经再生新策略研究;8167080922,项目名称:个性化丝胶神经导管的设计及其在外周神经损伤模型中的应用研究),项目负责人:王琳
Nanoparticles: a novel strategy for the treatment of ischemic stroke
Xiakeerzhati•Xiaohalati, Wang Xiaobei, Wang Lin
- Department of Clinical Laboratory, Wuhan Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430000, Hubei Province, China
-
Received:2020-12-15Revised:2021-02-05Accepted:2021-05-28Online:2022-08-08Published:2022-01-12 -
Contact:Wang Lin, MD, Professor, Chief physician, Department of Clinical Laboratory, Wuhan Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430000, Hubei Province, China Wang Xiaobei, MD, Associate professor, Associate chief physician, Department of Clinical Laboratory, Wuhan Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430000, Hubei Province, China -
About author:Xiakeerzhati•Xiaohalati, Master candidate, Department of Clinical Laboratory, Wuhan Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430000, Hubei Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 8187081092, No. 8167080922 (to WL)
摘要:
文题释义:
缺血性脑卒中:是由于脑血管狭窄或堵塞导致的急性脑血管疾病,俗称脑中风,具有较高的发病率和死亡率,可导致患者残疾,严重降低生活质量。
纳米粒子:是粒径在1-100 nm之间的微小颗粒,因其具有生物相容性好及渗透性、载药能力及降解能力强等特性被广泛应用于药物递送、癌症治疗、生物成像等领域。
背景:纳米粒子是一类具有纳米级尺寸的生物材料,在神经干细胞增殖与分化、神经保护性药物递送以及自由基清除等方面表现出优越的性能。
目的:归纳总结已经研发的用于缺血性脑卒中治疗的纳米粒子及性能,分析其针对缺血性脑卒中病理过程的治疗作用和相关机制。
方法:应用计算机检索2000年1月至2020年12月PubMed数据库、万方数据库及中国知网数据库收录的相关文献,英文检索词为“Ischemic stroke,Nanomaterials,Nanoparticles,Nanozyme”,中文检索词为“缺血性脑卒中或脑梗塞、纳米粒子、纳米酶”。根据纳入和排除标准最终选择 79篇文献进行综述。
结果与结论:纳米粒子在缺血性脑卒中治疗方面取得了一定的进展。有关研究表明,纳米粒子通过:①作为载药系统搭载神经保护性药物及分子,实现跨血脑屏障靶向给药;②利用本身抗氧化等固有特性,促进脑组织再生;③联合干细胞治疗,提高内源性神经发生和外源性干细胞移植治疗疗效。但是目前有关研究较少,且缺乏一个系统的适于缺血性脑卒中治疗的纳米粒子设计标准和最佳配方。未来需要在进一步探讨缺血性脑卒中疾病机制的基础上充分理解纳米粒子与生物系统之间的相互作用,从而合理设计脑靶向纳米粒子治疗系统,以促进其临床应用。
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7481-5243 (夏克尔扎提·肖哈拉提)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
夏克尔扎提·肖哈拉提, 王晓蓓, 王 琳. 纳米粒子:缺血性脑卒中治疗新策略[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(22): 3566-3572.
Xiakeerzhati•Xiaohalati, Wang Xiaobei, Wang Lin. Nanoparticles: a novel strategy for the treatment of ischemic stroke[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(22): 3566-3572.
2.1.1 缺血性脑卒中及治疗现状 脑卒中是一类突发的急性脑血管病,是人类第二大死亡病因。脑卒中主要分为脑血管破裂出血引起的出血性脑卒中和动脉粥样硬化、高脂血症、高血压等基础疾病引起的血管堵塞导致的缺血性脑卒中。临床上,脑卒中病例以缺血性脑卒中最为常见,缺血性脑卒中的发病率和死亡率极高,据报道,2015年全球出现了2 490万例缺血性脑卒中,其中有300万缺血性脑卒中患者死亡[1]。脑卒中可导致残疾,使患者生活无法自理,严重降低其生活质量的同时给患者心理及家庭带来了巨大的压力。目前,食品药品监督管理局(FDA)指南推荐的缺血性脑卒中治疗药物仅有组织纤溶酶原激活剂一种,组织纤溶酶原激活剂治疗时间窗狭窄,仅在4.5 h内能有效溶解血栓,因此极少数患者从中获益[2]。外科手术上可以通过介入治疗的方法切除血栓,恢复血流灌注,但介入治疗条件苛刻,对操作人员的技术水平及患者身体状况的要求较高,同时具有脑出血风险。因此,多年来研究人员一直在探索缺血性脑卒中新的治疗方法。随着缺血性脑卒中机制研究的不断深入,干细胞治疗及基于生物材料的促进内源性神经发生、神经保护、挽救缺血半影带、改善局部微环境等多种治疗策略应运而生[3-4]。
2.1.2 缺血性脑卒中病理特点 大脑因缺乏能量储备,对缺血缺氧极为敏感,严重依赖于氧气和葡萄糖的供给。缺血性脑卒中发生后由于血流受阻脑组织缺氧并迅速发生能量耗竭,引起神经细胞去极化,释放兴奋性神经递质——谷氨酸,谷氨酸的产生及谷氨酸受体的激活导致细胞内发生钙超载、钠钾失衡等变化,引起细胞水肿和缺氧[5]。细胞内超载的钙离子作为重要的第二信使过度激活多种酶系统,破坏细胞膜并产生大量活性氧、活性氮等自由基,攻击细胞线粒体及基因组完整性,引起神经细胞发生DNA损伤[6]。氧化应激过程中细胞分泌的大量炎性因子及脑组织受损后浸润的免疫细胞引起炎症反应,加重细胞损伤[7]。综上所述,离子失衡、氧化应激、神经炎症的共同作用导致缺血区域神经细胞的不可逆性死亡。
2.2 纳米粒子概述 纳米粒子是粒度在1-100 nm之间的微小粒子[8],因其独特的物理化学性质在药物递送[9]、癌症治疗[10]、生物成像等领域得到广泛应用[11]。近年来,在神经系统疾病治疗领域,纳米粒子因能够有效克服血脑屏障被选作搭载神经治疗药物或活性分子的载体[12]。随着研究水平的不断提高,国内外学者发现纳米粒子本身也呈现抗氧化、抑炎等活性,有助于疾病治疗,这一发现极大推进了纳米粒子在神经系统疾病治疗中的应用。作为新型的治疗体系,纳米粒子在疾病治疗方面的优势主要体现在以下方面:
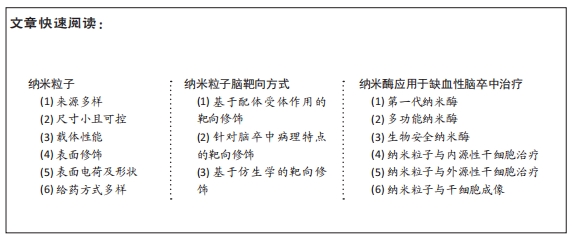
(1)来源多样:制备纳米粒子的原料来源广泛。纳米粒子可以由天然材料合成,如脂质体、壳聚糖、淀粉、透明质酸等;也可由聚乳酸、聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物、树枝状聚酰胺胺等聚合材料合成;除此之外,也有金属基、碳纳米粒子及无机杂化纳米粒子被开发[13-14]。因原材料的不同,纳米粒子具备多种特性,例如:天然材料制备的纳米粒子免疫原性低、生物相容性好、容易降解[15-16],聚合物纳米粒子具有较高的溶解性和组织渗透能力[17],金属或碳基材料则赋予纳米粒子导电性等电学性能[18]。
(2)尺寸小且可控:大多数药物及组织工程生物材料分子质量大,缺乏细胞组织穿透能力,无法透过血脑屏障,而纳米粒子尺寸小且可控。目前认为,流体动力直径小于5.5 nm的纳米粒子容易被肾脏滤出[19],而粒径在20-100 nm之间的纳米粒子既能有效透过血脑屏障进入组织细胞内,又能避免被体内系统清除。因此,普遍认为20-100 nm是治疗脑部疾病的纳米粒子可选的最佳尺寸范围[20]。
(3)载体性能:由于纳米粒子兼备表面效应、体积效应,因此具有较强的药物分子装载能力[21]。一般通过包裹、表面吸附、共价偶联等方式将药物及蛋白质、核酸、多肽等生物活性分子装载至纳米粒子上[22],并且通过控制药物和聚合物比例、反应水相pH值、药物疏水性等设计参数提高其装载效率[9,23]。
(4)表面修饰:通常采用表面配体修饰、高分子聚合物涂层、生物共轭等方式对纳米粒子表面进行改性,提高纳米粒子的有关性能,如胶体稳定性、靶向性等[24]。目前常用表面活性剂聚乙二醇提高纳米粒子的稳定性。聚乙二醇通过屏蔽表面电荷效应及空间屏障效应使纳米粒子不易被内皮网状系统清除,延长纳米粒子的循环时间。另外,使用两亲性肽分子进行表面修饰可以增加纳米粒子的疏水性[25]。纳米粒子表面固定能直接与血脑屏障或病变部位富集的表面分子或受体相互作用的抗体或多肽,可以实现纳米粒子的脑靶向,例如:表面修饰抗转铁蛋白受体抗体能更好地使纳米粒子靶向血脑屏障[26]。
(5)表面电荷及形状:除尺寸大小外,纳米粒子的表面电荷和形状也是决定和影响纳米粒子功能的关键因素,它们决定了纳米粒子的血液动力学,因此影响生物分布、吸收及与其他分子的相互作用[20]。目前有球形、棒状、立方形纳米粒子[27]。大多数情况下,球形、带负电的纳米粒子更容易被网状内皮系统吸收,而表面带正电的纳米粒子容易与循环中带负电的蛋白质形成聚合物,因此常用电中性纳米粒子[13]。但需要注意的是,纳米粒子表面电荷和形状对其生物学功能的影响因不同情况而异,设计时需要综合考虑。
(6)给药方式多样:相比其他组织工程修复材料(如水凝胶),纳米粒子尺寸小,可制成悬液制剂进行颅内注射、静脉注射、腹腔注射[14]。颅内注射能绕过血脑屏障,实现直接给药,减少了给药剂量,但是创伤性大,会增加感染及其他并发症发生的概率。静脉注射侵袭性小、操作方便,是脑卒中治疗最常用的给药方式。通过纳米粒子的工程化可以解决静脉给药时药物降解、血脑屏障渗透性低、高剂量毒性等问题。除此之外,纳米粒子逐渐实现了口服给药和鼻内给 药[28-29],使给药途径更加简便易行,提高了药物的脑内递送效率。口服和鼻内给药将会是纳米粒子在脑部疾病治疗中最有前途的给药方式[30]。
2.3 纳米粒子在缺血性脑卒中诊疗中的应用
2.3.1 纳米粒子载药系统用于缺血性脑卒中治疗 药物治疗是缺血性脑卒中治疗的重点。当前在脑卒中治疗研究领域内,尼莫地平[31]、莫达非尼[32]、姜黄素[33]、环孢素A等多种神经保护性药物及分子研发并进入临床应用[34],其中一些药物仍处于动物实验阶段[23]。
血脑屏障是药物分子进入脑实质病变部位的主要障碍。研究发现,在脑卒中发生后血脑屏障紧密结构会部分受损,但在整个卒中阶段仍能保持其完整性,因此大部分递送的药物分子还是无法有效地渗透脑组织发挥疗效[27,35];再加上大多数药物分子在血液循环中不稳定,由于半衰期短、溶解性差,低剂量容易被内皮系统清除、高剂量产生毒副作用等原因导致药物生物利用率降低。纳米粒子具有较大的表面积和血脑屏障穿透能力,其外壳还可以将药物分子包裹其中,防止降解。因此纳米粒子可以作为首选的脑卒中载药材料。
近年来,研究人员陆续开发例如西洛他唑纳米粒子等提高药物分子溶解性[36],增强脑组织递送效率,以便更好地发挥疗效。利鲁唑是一种神经保护性药物,存在水溶性差、高浓度毒副作用强等缺点。在一项研究中,研究人员合成吐温80包覆的壳聚糖共轭N-异丙基丙烯酰胺纳米粒子,将利鲁唑装载至纳米粒子上,在大鼠大脑中动脉闭塞模型中实现了药物的有效渗透,仅低剂量装载组就起到了明显的治疗效果,且未发现任何毒副作用[37]。葛根素也是一种很好的脑卒中治疗药物,但给药后到达脑内的实际浓度低,疗效受到限制。ZHAO等[38]利用聚氰基丙烯酸丁酯纳米粒子搭载葛根素,证明了在大脑中动脉闭塞模型中静脉给药搭载葛根素的纳米粒子比单独注射游离葛根素具有更好的治疗效果。通过建立这种纳米粒子载药系统,可最大程度减少传统给药达到治疗效果所需的最高剂量,使药物剂量更少,治疗更快、更有效。
药物分子的精准靶向是药物治疗成功的重要前提[39]。以上单纯地将药物分子装载到纳米粒子的方式并不能保证药物的脑靶向性。随着合成技术及表面修饰研究的不断深入,现有几种纳米粒子脑靶向方式:
(1)基于配体受体作用的靶向修饰:利用抗体或多肽对纳米粒子进行表面修饰,使纳米粒子靶向血脑屏障转铁蛋白受体、胰岛素受体、脂蛋白受体等,从而实现跨膜转运[30]。YEMISCI等[39]把壳聚糖纳米粒子与脑内皮细胞膜上转铁蛋白受体1的抗体偶联,使纳米粒子通过受体介导的跨胞转运机制穿过血脑屏障,实现了碱性成纤维细胞生长因子和半胱天冬酶3抑制剂的脑靶向递送。在另一项研究中,BAO等[40]在二氧化铈纳米粒子表面修饰Angiopep-2多肽,与血脑屏障高表达的低密度脂蛋白受体相关蛋白相互作用,通过受体介导的转胞吞作用跨越血脑屏障,成功递送了自由基清除药物依达拉奉。
(2)针对脑卒中病理特点的靶向修饰:在传统配体介导方式的基础上,下一代纳米粒子主要结合缺血性脑卒中病理特点,旨在对脑卒中微环境作出动态反应,进一步加强针对性和有效性。缺血性脑卒中时,白细胞在损伤部位聚集造成神经炎症。根据这一病理特点,有研究者使用与中性粒细胞趋化因子受体2高度亲和的脯氨酸甘氨酸脯氨酸三肽修饰载过氧化氢酶纳米粒子,使纳米粒子进入中性粒细胞内,借助中性粒细胞天然的趋化作用进入病变部位发挥作用[41]。脑缺血缺氧后,损伤部位的基质金属蛋白酶2表达增强,参与细胞外基质的降解过程。基于此,研究人员使用对基质金属蛋白酶2具有高亲和力的氯毒素肽修饰搭载神经保护药物Lexiscan的纳米粒子,使载药纳米粒子脑靶向性进一步增强[42]。目前,针对脑卒中微环境靶向修饰的可选配体数量少,需要在脑卒中机制研究的基础上进一步发现和开发。
(3)基于仿生学的靶向修饰:内源性细胞天然的构造和功能为纳米粒子的靶向修饰提供了灵感。MA等[35]利用细胞膜涂层技术将过表达趋化因子受体4的神经干细胞膜包被在聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物纳米粒子上,通过与梗死区域高表达的基质细胞衍生因子1结合,使得搭载格列本脲(一种抗脑水肿药物)纳米粒子通过趋化作用精准靶向梗死脑组织发挥疗效。LI等[43]利用天然血小板膜包被功能化磁性纳米粒子,这种纳米粒子完美继承血小板膜天然特性,表面携带多种糖蛋白以及表面分子,有效避免了免疫清除,且能够在脑卒中血栓部位黏附,实现目标分子L-精氨酸的释放。同样利用血小板在血栓部位聚集的特点,XU等[44]设计了一种血小板膜包被的搭载组织纤溶酶原激活剂的纳米粒子,准确靶向血栓部位,其溶栓治疗效果优于游离的溶栓药物。近几年来,新兴的细胞仿生技术智能递送系统因能逃避免疫清除、同源靶向等优势备受欢迎,有望成为未来纳米粒子材料修饰的发展方向。
2.3.2 纳米酶应用于缺血性脑卒中治疗 缺血性脑卒中病理过程错综复杂,其中氧化应激是脑组织损伤的主要机制。脑组织缺血再灌注后,活性氧、活性氮等有害物质的产生加重了组织损伤。正常情况下,体内的过氧化物酶、过氧化氢酶、超氧化物歧化酶等天然酶参与有害自由基的清除[45]。脑卒中期间这些抗氧化酶的表达受到抑制,不足以完全清除过量的自由基,因此需要向脑卒中部位补充抗氧化酶。由于天然酶极不稳定、半衰期短,且像其他分子一样难以渗透血脑屏障,不适于体内应用和临床推广。基于载体系统的抗氧化酶输送策略很好地解决了上述问题。研究人员相继使用酶分子聚乙二醇化、脂质体及聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物纳米粒子包埋等手段初步实现天然酶的成功包封,但其稳定性、循环时间及渗透性有待提高[46-47]。为此,有研究者将超氧化物歧化酶1或过氧化氢酶与聚阳离子结合,再通过共价交联获得纳米交联酶,由于共聚物内部结构可以保护酶分子不被降解,因此显著增强了天然超氧化物歧化酶1或过氧化氢酶的稳定性,使其持续发挥抗氧化作用。在大鼠脑卒中模型中,该交联酶能有效穿透血脑屏障,瞬时释放足够量的抗氧化酶,减少梗死体积的同时促进了脑卒中大鼠的功能恢复[48]。
众所周知,天然酶分离纯化复杂、价格昂贵、体外稳定性差,无法长期储存和循环利用,因此使用生物化学材料简单包封天然酶并不是长久之计。随着研究的不断深入,人们发现某些纳米粒子本身呈现多种酶活性,如四氧化三铁纳米粒子具有天然过氧化物酶类似的底物催化能力和酶促反应动力学[49];铂纳米粒子、二氧化锆粒子具有过氧化氢酶样活性;二氧化铈纳米粒具有超氧化物歧化酶活性[50]。人们将这类具有天然酶模拟能力的纳米材料命名为“纳米酶”。由于“纳米酶”容易大规模生产、成本低、可重复利用、在体外稳定且可以长期储存,因此在化工、环境以及生物医学领域广受青睐[51]。根据应用于缺血性脑卒中治疗纳米酶的发展趋势,该文把目前为止报道的纳米酶分为3类:
第一代纳米酶:指初次发现的具有天然酶类似活性的纳米粒子材料,一般可直接应用于缺血性脑卒中抗氧化治疗。例如,利用二氧化铈纳米粒子的天然酶活性,KIM与他的团队[52]通过尾静脉注射二氧化铈纳米粒子治疗脑卒中大鼠,发现大鼠脑梗死区活性氧水平明显下降、神经细胞凋亡减少、梗死体积减小。这项研究首次证明了二氧化铈纳米粒子的超氧化物歧化酶及过氧化氢酶双重酶活性有利于缺血性脑卒中恢复。值得注意的是,并非所有具备双重酶活性的纳米酶都有利于脑卒中损伤修复。金纳米粒子本身具有过氧化物酶和过氧化氢酶活性,但过氧化物酶的催化产物羟基自由基(?OH)对神经元具有毒性。LIU等[53]巧妙地以胺为末端的聚酰胺-胺型树枝状高分子包埋金纳米粒子,屏蔽了金纳米粒子过氧化物酶活性,仍然保留其过氧化氢酶样活性,成功保护小鼠神经元免受氧化损伤。由此可见,在使用纳米粒子时应该根据研究目的对纳米粒子进行合理的设计和修饰,选择性利用其固有酶活性,从而避免“适得其反”。
多功能纳米酶:指在第一代天然纳米酶基础上改造或人工研发的纳米酶。由于天然纳米酶的催化底物选择性强,因此应用范围受限。近年来在天然纳米酶的基础上,具有多种酶活性的新一代人工纳米酶被成功研发,通过高效清除多种自由基发挥疗效。MU等[54]报道了一种铂、钯、钼构成的三金属纳米酶,具有广泛的催化活性,可有效清除活性氧和活性氮,在脑损伤模型中改善神经炎症、提高小鼠存活率。体内的酶催化呈级联式反应,从而保证彻底清除有害自由基。为更好地模拟体内天然酶的级联反应,国内学者合成了一种基于碳纳米酶的人工过氧化物酶体,这种纳米酶体具有5种天然酶活性,在大鼠大脑中动脉闭塞模型中通过超氧化物歧化酶-过氧化氢酶级联反应使超氧阴离子自由基彻底转化成无毒的水和氧气,展现出了很好的治疗作用[55]。
生物安全纳米酶:不难发现,绝大多数纳米酶都由金属离子构成,它们虽然展现出强大的酶催化活性,但金属离子对人体尤其是对脑组织的潜在毒性不可忽略。普鲁士蓝是一种食品药品监督管理局批准的重金属解毒剂和对比剂。有研究者利用普鲁士蓝的自由基清除能力开发了中空普鲁士蓝纳米酶,中空普鲁士蓝纳米酶显现出超氧化物歧化酶活性,清除活性氧的同时发挥了抗炎、抗凋亡作用,改善了大鼠功能恢复[56]。LIU等[57]设计了黑色素纳米粒子,利用天然黑色素的活性氧及活性氮清除能力成功治疗缺血性脑卒中大鼠,显著减少了脑梗死体积。上述研究提示,在设计纳米酶时增强功效固然重要,但也必需考虑纳米酶的生物安全问题。在未来,发现更多具有清除自由基功能的天然材料将有助于制备更多生物安全的多功能纳米酶。
2.3.3 纳米粒子与缺血性脑卒中干细胞治疗 干细胞治疗是一种新型的脑卒中治疗方式,其目的是通过刺激大脑固有的内源性修复机制和植入外源性干细胞的方法,最大程度改善损伤脑组织的结构和功能。现总结到目前为止纳米粒子在内源性及外源性干细胞治疗领域中的具体应用。
纳米粒子与内源性干细胞治疗:在哺乳动物脑室下区和齿状回中具有自我更新和多向分化潜能的神经干细胞和神经母细胞,脑损伤后这些内源性干细胞可发生增殖迁移及分 化[58],但是梗死区产生的大量自由基、炎性因子会导致内源性神经干细胞和神经母细胞存活率降低,因此内源性修复过程难以有效实现[59]。目前利用功能化纳米粒子的载体性能,通过向梗死部位递送药物或分子刺激内源性神经干细胞增殖分化,取代死亡神经元的研究策略取得了一定成果。一项研究显示,多唾液酸神经细胞黏附分子抗体修饰的多孔硅纳米粒子搭载小分子药物SC-79,可特异性地靶向内源性神经母细胞,通过上调PI3K-AKT信号通路,成功促进了脑卒中大鼠内源性神经母细胞的存活、增殖及分化[60]。内源性修复受阻的另一个主要原因是,脑卒中梗死位置多发生在大脑皮质及纹状体。解剖位置上,梗死区域离脑室下区较远,内源性干细胞迁移能力有限。为促进内源性干细胞迁移,JIAN等[61]研发了一种高分子杂化水凝胶,在水凝胶内部搭载基质细胞衍生因子1的纳米粒子可原位释放,通过趋化作用成功吸引内源性干细胞到达损伤部位,显著促进大鼠功能恢复。这种交叉联合多种生物材料的复合材料应用价值高,值得进一步研究和开发。
纳米粒子与外源性干细胞治疗:外源性干细胞移植治疗是脑卒中治疗的常用策略。大量研究表明,移植后的神经干细胞可部分整合到宿主大脑并分化为包括神经元、星形胶质细胞等多种神经细胞类型,相互交流连接形成替代的神经网络[62]。此外,移植细胞可分泌如血管内皮生长因子[63]、脑源性神经营养因子等神经保护因子[64],发挥血管生成、营养支持、免疫调节等作用。但是由于大量自由基和炎性因子不利于神经干细胞的存活,因此极少数干细胞才能整合到宿主神经组织[65]。因此,促进外源性干细胞生存和分化对提高干细胞移植治疗效果极为关键。国内学者发现二氧化钛(TiO2)纳米粒子可诱导神经干细胞向神经元分化[66] 。SARAIVA等[67]合成的具有抗炎和神经保护作用的MicroRNA-124纳米粒子,在体外可以有效提高神经干细胞的存活率,使其向神经元分化。除此之外,一些纳米粒子在动物体内实验中表现出了良好的治疗效果。在大鼠大脑中动脉闭塞模型中,NAZARIAN等[68]发现载药金纳米粒子与间充质干细胞的联合治疗组与干细胞单独治疗组相比发挥了更好的恢复效果,提示纳米粒子与干细胞联合治疗的可行性和有效性。
如何增强移植干细胞功能,使其更好地适应脑卒中恶劣的微环境是目前神经干细胞移植领域亟待解决的问题。干细胞预处理、基因编辑、生物支架封装等手段初步实现了干细胞功能增强[69-71]。纳米粒子因较强的装载功能和细胞渗透能力成为了干细胞基因工程化的有效工具。研究人员在体外将搭载质粒(如脑源性神经营养因子质粒)或小干扰RNA的纳米粒子通过内吞作用转入干细胞后[72-73],利用基因转录或基因沉默作用对干细胞进行“重编程”,再将预处理后的干细胞移入体内,显著提高了干细胞的功能和治疗效果。
纳米粒子与干细胞成像:实时监测神经干细胞的踪迹有助于了解干细胞的分布、分化和命运,进一步评估干细胞治疗的可行性和安全性[74]。利用磁共振成像对移植干细胞进行监测的技术较为成熟[11,75]。目前较多使用磁性纳米粒子尤其是氧化铁纳米粒子进行成像。在缺血性脑卒中干细胞治疗方面,有研究报道了CD15抗体共轭的超顺磁性氧化铁纳米粒子,成功实现了脑卒中模型内源性神经干细胞的体内磁共振成像。作者使用阿糖胞嘧啶抑制内源性神经干细胞激活后,磁共振信号消失,证明此纳米粒子在缺血性脑卒中期间可以特异性标记内源性干细胞的行踪[76]。这项研究提供了评估内源性干细胞生成的重要成像工具。
为可视化移植神经干细胞的迁移和分布,ZHANG等[77]合成介孔硅包被的超顺磁性氧化铁纳米粒子,在缺血梗死灶成功追踪到经颅内注射和静脉注射的外源性C17.2神经干细胞,他们发现两种途径移植后的C17.2细胞都能迁移到缺血灶并主要分布在梗死核心区周围。通过目前的磁性纳米粒子成像技术虽然能够观察到移植后干细胞的去向和具体分布,但无法确切估算成功移植细胞的数量,因此具有一定的局限性。另外作为体内成像工具,用于细胞标记的纳米粒子需要具备良好的生物相容性,确保不会在标记过程中对神经干细胞产生不良影响。LIN等[78]使用阳离子型直链淀粉制备的新型生物安全纳米粒子能够高效标记间充质干细胞,并且细胞毒性很小。这项研究提示,选择和开发基于可降解材料的安全无毒纳米粒子成像工具将会有更高的临床转化潜质。

| [1] BENJAMIN EJ, VIRANI SS, CALLAWAY CW, et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2018 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2018;137(12):e67-e492. [2] KIM JS. tPA Helpers in the Treatment of Acute Ischemic Stroke: Are They Ready for Clinical Use? J Stroke. 2019;21(2):160-174. [3] BOSHUIZEN MCS, STEINBERG GK. Stem Cell-Based Immunomodulation After Stroke: Effects on Brain Repair Processes. Stroke. 2018;49(6): 1563-1570. [4] JENDELOVA P, KUBINOVA S, SANDVIG I, et al. Current developments in cell- and biomaterial-based approaches for stroke repair. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2016;16(1):43-56. [5] DIRNAGL U, IADECOLA C, MOSKOWITZ MA. Pathobiology of ischaemic stroke: an integrated view. Trends Neurosci. 1999;22(9):391-397. [6] LI P, STETLER RA, LEAK RK, et al. Oxidative stress and DNA damage after cerebral ischemia: Potential therapeutic targets to repair the genome and improve stroke recovery. Neuropharmacology. 2018;134(Pt B): 208-217. [7] PATEL AR, RITZEL R, MCCULLOUGH LD, et al. Microglia and ischemic stroke: a double-edged sword. Int J Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol. 2013;5(2):73-90. [8] HALL JB, DOBROVOLSKAIA MA, PATRI AK, et al. Characterization of nanoparticles for therapeutics. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2007;2(6):789-803. [9] AMREDDY N, BABU A, MURALIDHARAN R, et al. Recent Advances in Nanoparticle-Based Cancer Drug and Gene Delivery. Adv Cancer Res. 2018;137:115-170. [10] SHAO K, SINGHA S, CLEMENTE-CASARES X, et al. Nanoparticle-Based Immunotherapy for Cancer. ACS Nano. 2014;9(1):16-30. [11] SANGTANI A, NAG OK, FIELD LD, et al. Multifunctional nanoparticle composites: progress in the use of soft and hard nanoparticles for drug delivery and imaging. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2017;9(6):e1466. [12] TSOU YH, ZHANG XQ, ZHU H, et al. Drug Delivery to the Brain across the Blood-Brain Barrier Using Nanomaterials. Small. 2017;13(43):1701921. [13] BHARADWAJ VN, NGUYEN DT, KODIBAGKAR VD, et al. Nanoparticle-Based Therapeutics for Brain Injury. Adv Healthc Mater. 2018;7(1): 10.1002/adhm.201700668. [14] GONZALEZ-NIETO D, FERNANDEZ-SERRA R, PEREZ-RIGUEIRO J, et al. Biomaterials to Neuroprotect the Stroke Brain: A Large Opportunity for Narrow Time Windows. Cells. 2020;9(5):1074. [15] YUAN ZY, HU YL, GAO JQ. Brain Localization and Neurotoxicity Evaluation of Polysorbate 80-Modified Chitosan Nanoparticles in Rats. PLoS One. 2015;10(8):e0134722. [16] SO PW, EKONOMOU A, GALLEY K, et al. Intraperitoneal delivery of acetate-encapsulated liposomal nanoparticles for neuroprotection of the penumbra in a rat model of ischemic stroke. Int J Nanomed. 2019;14:1979-1991. [17] GAO Y, CHEN X, LIU H. A facile approach for synthesis of nano-CeO2 particles loaded co-polymer matrix and their colossal role for blood-brain barrier permeability in Cerebral Ischemia. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2018;187:184-189. [18] ZHAI L, MAIMAITIMING Z, CAO X, et al. Nitrogen-doped carbon nanocages and human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells cooperatively inhibit neuroinflammation and protect against ischemic stroke. Neurosci Lett. 2019;708:134346. [19] CHOI HS, LIU W, MISRA P, et al. Renal clearance of quantum dots. Nat Biotechnol. 2007;25(10):1165-1170. [20] JO DH, KIM JH, LEE TG, et al. Size, surface charge, and shape determine therapeutic effects of nanoparticles on brain and retinal diseases. Nanomedicine. 2015;11(7):1603-1611. [21] MASSERINI M. Nanoparticles for Brain Drug Delivery. ISRN Biochemistry. 2013;2013:1-18. [22] ZHOU Y, PENG Z, SEVEN ES, et al. Crossing the blood-brain barrier with nanoparticles. J Control Release. 2018;270:290-303. [23] DONG X. Current Strategies for Brain Drug Delivery. Theranostics. 2018; 8(6):1481-1493. [24] NAM J, WON N, BANG J, et al. Surface engineering of inorganic nanoparticles for imaging and therapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013; 65(5):622-648. [25] ERNSTING MJ, MURAKAMI M, ROY A, et al. Factors controlling the pharmacokinetics, biodistribution and intratumoral penetration of nanoparticles. J Control Release. 2013;172(3):782-794. [26] KOLHAR P, ANSELMO AC, GUPTA V, et al. Using shape effects to target antibody-coated nanoparticles to lung and brain endothelium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(26):10753-10758. [27] SARAIVA C, PRACA C, FERREIRA R, et al. Nanoparticle-mediated brain drug delivery: Overcoming blood-brain barrier to treat neurodegenerative diseases. J Control Release. 2016;235:34-47. [28] YANG X, XU L, ZHOU J, et al. Integration of phospholipid-complex nanocarrier assembly with endogenous N-oleoylethanolamine for efficient stroke therapy. J Nanobiotechnol. 2019;17(1):8. [29] AHMAD N, UMAR S, ASHAFAQ M, et al. A comparative study of PNIPAM nanoparticles of curcumin, demethoxycurcumin, and bisdemethoxycurcumin and their effects on oxidative stress markers in experimental stroke. Protoplasma. 2013;250(6):1327-1338. [30] FURTADO D, BJORNMALM M, AYTON S, et al. Overcoming the Blood-Brain Barrier: The Role of Nanomaterials in Treating Neurological Diseases. Adv Mater. 2018;30(46):e1801362. [31] HUANG S, HUANG Z, FU Z, et al. A Novel Drug Delivery Carrier Comprised of Nimodipine Drug Solution and a Nanoemulsion: Preparation, Characterization, in vitro, and in vivo Studies. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:1161-1172. [32] YOUSEFI-MANESH H, RASHIDIAN A, HEMMATI S, et al. Therapeutic effects of modafinil in ischemic stroke; possible role of NF-κB downregulation. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2019;41(5):558-564. [33] KAKKAR V, MUPPU SK, CHOPRA K, et al. Curcumin loaded solid lipid nanoparticles: an efficient formulation approach for cerebral ischemic reperfusion injury in rats. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2013;85(3 Pt A): 339-345. [34] PARTOAZAR A, NASOOHI S, REZAYAT SM, et al. Nanoliposome containing cyclosporine A reduced neuroinflammation responses and improved neurological activities in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion in rat. Fund Clin Pharmacol. 2017;31(2):185-193. [35] MA J, ZHANG S, LIU J, et al. Targeted Drug Delivery to Stroke via Chemotactic Recruitment of Nanoparticles Coated with Membrane of Engineered Neural Stem Cells. Small. 2019;15(35):e1902011. [36] NAGAI N, YOSHIOKA C, ITO Y, et al. Intravenous Administration of Cilostazol Nanoparticles Ameliorates Acute Ischemic Stroke in a Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion-Induced Injury Model. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(12):29329-29344. [37] VERMA SK, ARORA I, JAVED K, et al. Enhancement in the Neuroprotective Power of Riluzole Against Cerebral Ischemia Using a Brain Targeted Drug Delivery Vehicle. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016; 8(30):19716-19723. [38] ZHAO LX, LIU AC, YU SW, et al. The permeability of puerarin loaded poly(butylcyanoacrylate) nanoparticles coated with polysorbate 80 on the blood-brain barrier and its protective effect against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Biol Pharm Bull. 2013;36(8):1263-1270. [39] YEMISCI M, CABAN S, GURSOY-OZDEMIR Y, et al. Systemically Administered Brain-Targeted Nanoparticles Transport Peptides across the Blood—Brain Barrier and Provide Neuroprotection. J Cerebr Blood F Met. 2015;35(3):469-475. [40] BAO Q, HU P, XU Y, et al. Simultaneous Blood–Brain Barrier Crossing and Protection for Stroke Treatment Based on Edaravone-Loaded Ceria Nanoparticles. ACS Nano. 2018;12(7):6794-6805. [41] ZHANG C, LING CL, PANG L, et al. Direct Macromolecular Drug Delivery to Cerebral Ischemia Area using Neutrophil-Mediated Nanoparticles. Theranostics. 2017;7(13):3260-3275. [42] HAN L, CAI Q, TIAN D, et al. Targeted drug delivery to ischemic stroke via chlorotoxin-anchored, lexiscan-loaded nanoparticles. Nanomedicine. 2016;12(7):1833-1842. [43] LI M, LI J, CHEN J, et al. Platelet Membrane Biomimetic Magnetic Nanocarriers for Targeted Delivery and in Situ Generation of Nitric Oxide in Early Ischemic Stroke. ACS Nano. 2020;14(2):2024-2035. [44] XU J, ZHANG Y, XU J, et al. Engineered Nanoplatelets for Targeted Delivery of Plasminogen Activators to Reverse Thrombus in Multiple Mouse Thrombosis Models. Adv Mater. 2020;32(4):e1905145. [45] LEI XG, ZHU JH, CHENG WH, et al. Paradoxical Roles of Antioxidant Enzymes: Basic Mechanisms and Health Implications. Physiol Rev. 2016; 96(1):307-364. [46] JIANG Y, BRYNSKIKH AM, S-MANICKAM D, et al. SOD1 nanozyme salvages ischemic brain by locally protecting cerebral vasculature. J Control Release. 2015;213:36-44. [47] YUN X, MAXIMOV VD, YU J, et al. Nanoparticles for Targeted Delivery of Antioxidant Enzymes to the Brain after Cerebral Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury. J Cerebr Blood F Met. 2013;33(4):583-592. [48] MANICKAM DS, BRYNSKIKH AM, KOPANIC JL, et al. Well-defined cross-linked antioxidant nanozymes for treatment of ischemic brain injury. J Control Release. 2012;162(3):636-645. [49] GAO L, ZHUANG J, NIE L, et al. Intrinsic peroxidase-like activity of ferromagnetic nanoparticles. Nat Nanotechnol. 2007;2(9):577-583. [50] WEI H, WANG E. Nanomaterials with enzyme-like characteristics (nanozymes): next-generation artificial enzymes. Chem Soc Rev. 2013; 42(14):6060-6093. [51] WU J, WANG X, WANG Q, et al. Nanomaterials with enzyme-like characteristics (nanozymes): next-generation artificial enzymes (II). Chem Soc Rev. 2019;48(4):1004-1076. [52] KIM CK, KIM T, CHOI IY, et al. Ceria nanoparticles that can protect against ischemic stroke. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2012;51(44):11039-11043. [53] LIU CP, WU TH, LIN YL, et al. Tailoring Enzyme-Like Activities of Gold Nanoclusters by Polymeric Tertiary Amines for Protecting Neurons Against Oxidative Stress. Small. 2016;12(30):4127-4135. [54] MU X, WANG J, LI Y, et al. Redox Trimetallic Nanozyme with Neutral Environment Preference for Brain Injury. ACS Nano. 2019;13(2):1870-1884. [55] XI J, ZHANG R, WANG L, et al. A Nanozyme‐Based Artificial Peroxisome Ameliorates Hyperuricemia and Ischemic Stroke. Adv Func Mater. 2020:2007130. [56] ZHANG K, TU M, GAO W, et al. Hollow Prussian Blue Nanozymes Drive Neuroprotection against Ischemic Stroke via Attenuating Oxidative Stress, Counteracting Inflammation, and Suppressing Cell Apoptosis. Nano Lett. 2019;19(5):2812-2823. [57] LIU Y, AI K, JI X, et al. Comprehensive Insights into the Multi-Antioxidative Mechanisms of Melanin Nanoparticles and Their Application To Protect Brain from Injury in Ischemic Stroke. J Am Chem Soc. 2017;139(2):856-862. [58] GAGE FH, TEMPLE S. Neural stem cells: generating and regenerating the brain. Neuron. 2013;80(3):588-601. [59] LINDVALL O, KOKAIA Z. Stem Cell Research in Stroke. Stroke. 2011; 42(8):2369-2375. [60] BALASUBRAMANIAN V, DOMANSKYI A, RENKO JM, et al. Engineered antibody-functionalized porous silicon nanoparticles for therapeutic targeting of pro-survival pathway in endogenous neuroblasts after stroke. Biomaterials. 2020;227:119556. [61] JIAN WH, WANG HC, KUAN CH, et al. Glycosaminoglycan-based hybrid hydrogel encapsulated with polyelectrolyte complex nanoparticles for endogenous stem cell regulation in central nervous system regeneration. Biomaterials. 2018;174:17-30. [62] BAKER EW, KINDER HA, WEST FD. Neural stem cell therapy for stroke: A multimechanistic approach to restoring neurological function. Brain Behav. 2019;9(3):e01214. [63] HORIE N, PEREIRA MP, NIIZUMA K, et al. Transplanted Stem Cell-Secreted Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Effects Poststroke Recovery, Inflammation, and Vascular Repair. Stem Cells. 2011;29(2): 274-285. [64] JEONG CH, KIM SM, LIM JY, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells expressing brain-derived neurotrophic factor enhance endogenous neurogenesis in an ischemic stroke model. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:129145. [65] BLISS T, GUZMAN R, DAADI M, et al. Cell transplantation therapy for stroke. Stroke. 2007;38(2 Suppl):817-826. [66] LIU X, REN X, DENG X, et al. A protein interaction network for the analysis of the neuronal differentiation of neural stem cells in response to titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Biomaterials. 2010;31(11):3063-3070. [67] SARAIVA C, TALHADA D, RAI A, et al. MicroRNA-124-loaded nanoparticles increase survival and neuronal differentiation of neural stem cells in vitro but do not contribute to stroke outcome in vivo. PLoS One. 2018;13(3):e0193609. [68] NAZARIAN S, ABDOLMALEKI Z, TORFEH A, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells with modafinil (gold nanoparticles) significantly improves neurological deficits in rats after middle cerebral artery occlusion. Exp Brain Res. 2020;238(11):2589-2601. [69] SAKATA H, NARASIMHAN P, NIIZUMA K, et al. Interleukin 6-preconditioned neural stem cells reduce ischaemic injury in stroke mice. Brain. 2012;135(11):3298-3310. [70] BERNSTOCK JD, PERUZZOTTI-JAMETTI L, YE D, et al. Neural stem cell transplantation in ischemic stroke: A role for preconditioning and cellular engineering. J Cerebr Blood F Met. 2017;37(7):2314-2319. [71] BERNSTOCK JD, PERUZZOTTI-JAMETTI L, LEONARDI T, et al. SUMOylation promotes survival and integration of neural stem cell grafts in ischemic stroke. EBioMedicine. 2019;42:214-224. [72] JIANG XC, XIANG JJ, WU HH, et al. Neural Stem Cells Transfected with Reactive Oxygen Species-Responsive Polyplexes for Effective Treatment of Ischemic Stroke. Adv Mater. 2019; 31(10):e1807591. [73] WANG C, LIN G, LUAN Y, et al. HIF-prolyl hydroxylase 2 silencing using siRNA delivered by MRI-visible nanoparticles improves therapy efficacy of transplanted EPCs for ischemic stroke. Biomaterials. 2019;197:229-243. [74] MODO M, MELLODEW K, CASH D, et al. Mapping transplanted stem cell migration after a stroke: a serial, in vivo magnetic resonance imaging study. Neuroimage. 2004;21(1):311-317. [75] BULTE JW. In vivo MRI cell tracking: clinical studies. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009;193(2):314-325. [76] ZHANG F, DUAN X, LU L, et al. In Vivo Targeted MR Imaging of Endogenous Neural Stem Cells in Ischemic Stroke. Molecules. 2016; 21(9):1143. [77] ZHANG L, WANG Y, TANG Y, et al. High MRI performance fluorescent mesoporous silica-coated magnetic nanoparticles for tracking neural progenitor cells in an ischemic mouse model. Nanoscale. 2013;5(10): 4506-4516. [78] LIN BL, ZHANG JZ, LU LJ, et al. Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles-Complexed Cationic Amylose for In Vivo Magnetic Resonance Imaging Tracking of Transplanted Stem Cells in Stroke. Nanomaterials. 2017;7(5):107. [79] YUN S, SHIN TH, LEE JH, et al. Design of Magnetically Labeled Cells (Mag-Cells) for in Vivo Control of Stem Cell Migration and Differentiation. Nano Lett. 2018;18(2):838-845. |
| [1] | 姚晓玲, 彭建城, 许岳荣, 杨志东, 张顺聪. 可变角度零切迹前路椎间融合内固定系统治疗脊髓型颈椎病:30个月随访[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | 朱 婵, 韩栩珂, 姚承佼, 周 倩, 张 强, 陈 秋. 人体唾液成分与骨质疏松/骨量低下[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(9): 1439-1444. |
| [3] | 金 涛, 刘 林, 朱晓燕, 史宇悰, 牛建雄, 张同同, 吴树金, 杨青山. 骨关节炎与线粒体异常[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(9): 1452-1458. |
| [4] | 张立创, 徐 浩, 马迎辉, 熊梦婷, 韩海慧, 鲍嘉敏, 翟伟韬, 梁倩倩. 免疫调控淋巴回流功能治疗类风湿关节炎的机制及前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(9): 1459-1466. |
| [5] | 王 景, 熊 山, 曹 金, 冯林伟, 王 信. 白细胞介素3在骨代谢中的作用及机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [6] | 肖 豪, 刘 静, 周 君. 脉冲电磁场治疗绝经后骨质疏松症的研究进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [7] | 朱 婵, 韩栩珂, 姚承佼, 张 强, 刘 静, 邵 明. 针刺治疗帕金森病:动物实验显示的作用机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(8): 1272-1277. |
| [8] | 安维政, 何 萧, 任 帅, 刘建宇. 肌源干细胞在周围神经再生中的潜力[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [9] | 范一鸣, 刘方煜, 张洪宇, 李 帅, 王岩松. 脊髓损伤后室管膜区内源性神经干细胞反应的系列问题[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1137-1142. |
| [10] | 张璟琳, 冷 敏, 朱博恒, 汪 虹. 干细胞源外泌体促进糖尿病创面愈合的机制及应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [11] | 黄晨玮, 费彦亢, 朱梦梅, 李鹏昊, 于 兵. 谷胱甘肽在干细胞“干性”及调控中的重要作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1119-1124. |
| [12] | 惠小珊, 白 京, 周思远, 王 阶, 张金生, 何庆勇, 孟培培. 中医药调控干细胞诱导分化的理论机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1125-1129. |
| [13] | 田 川, 朱向情, 杨再玲, 鄢东海, 李 晔, 王严影, 杨育坤, 何 洁, 吕冠柯, 蔡学敏, 舒丽萍, 何志旭, 潘兴华. 骨髓间充质干细胞调控猕猴卵巢的衰老[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 985-991. |
| [14] | 胡 伟, 谢兴奇, 屠冠军. 骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体改善脊髓损伤后血脊髓屏障的完整性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 992-998. |
| [15] | 闻丹丹, 李 强, 沈才齐, 纪 哲, 金培生. 外用红色诺卡氏菌细胞壁骨架提高脂肪间充质干细胞活性修复糖尿病创面[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1038-1044. |
近年来随着组织再生概念的提出,研究人员相继开发了一些新的治疗方式,包括干细胞治疗、药物及营养因子注射、基于生物材料的组织再生等,极大推进了缺血性脑卒中治疗。其中,基于生物材料的脑组织再生是脑卒中治疗的研究热点。纳米粒子是一种纳米级的生物材料,其粒径主要分布在 1-100 nm,因具有轻巧的尺寸、较大的比表面积、良好的生物相容性、可控性、载体性能及多种生物学活性被广泛应用于生物医学领域。
多项研究证实,纳米粒子能够成功克服血脑屏障结构障碍,针对脑卒中微环境,通过靶向载药、自由基清除、抗氧化、联合干细胞治疗等途径弥补传统疗法的不足,对缺血性脑卒中治疗产生积极影响。因此,为归纳总结应用于治疗缺血性脑卒中治疗的纳米粒子研究现状,该文就不同纳米粒子的设计思路、性能及治疗作用与机制进行综述,为今后开发更多新的缺血性脑卒中诊疗纳米粒子提供参考。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程
1.2 文献筛选
纳入标准:选取纳米粒子应用于缺血性脑卒中药物治疗、干细胞治疗及纳米酶治疗相关研究,纳入相关领域权威杂志发表的逻辑清晰、证据可靠、观点明确且新颖的文献。
排除标准:排除其他纳米材料相关研究,排除观点陈旧、内容重复、质量差的文献。
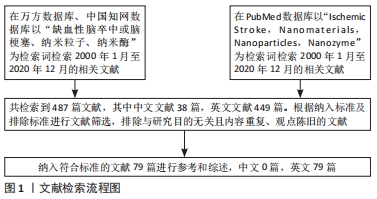
1.3 文献提取 经过初步筛选共搜集到487篇相关文献,仔细阅读文题和摘要部分后排除不符合研究目的、内容重复且陈旧的文献,最后纳入79篇涉及纳米粒子治疗缺血性脑卒中或促进卒中后脑组织再生的有关文献进行综述。文献检索流程,见图1。
目前,缺血性脑卒中机制研究不够全面,纳米粒子与生物系统尤其是与循环系统、血脑屏障之间的相互作用机制尚未阐明清楚。应用于脑卒中治疗的纳米粒子有关研究处于早期阶段,文献报道量少且比较分散,缺乏一个系统的适于缺血性脑卒中治疗的纳米粒子设计标准和实验评价体系。另外,纳米粒子不可忽略的潜在毒性,即对体内重要器官(如肝脾肺肾)功能的影响限制了其临床转化。总而言之,想要充分利用纳米粒子的优势,避开其短板,多学科研究人员应该交叉合作,在详细的机制研究的基础上探索更多对脑卒中治疗有益的原材料,从而设计合成简单、生物相容性好、半衰期长、载药能力强、靶向性好的纳米粒子,并与其他生物活性材料或各学科研究产物联合应用,为提高缺血性脑卒中治疗和脑组织再生提供可靠且有效的策略。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程

文题释义:
缺血性脑卒中:是由于脑血管狭窄或堵塞导致的急性脑血管疾病,俗称脑中风,具有较高的发病率和死亡率,可导致患者残疾,严重降低生活质量。
纳米粒子:是粒径在1-100 nm之间的微小颗粒,因其具有生物相容性好及渗透性、载药能力及降解能力强等特性被广泛应用于药物递送、癌症治疗、生物成像等领域。
该文根据国内外最新研究成果总结了应用于缺血性脑卒中治疗的纳米粒子的特点和优势,阐述了多种基于纳米粒子的治疗方法对缺血性脑卒中损伤修复和神经再生当中的作用和相关机制。纳米粒子载药系统、纳米粒子抗氧化治疗以及联合干细胞治疗将会成为缺血性脑卒中未来的研究热点。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||