中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (22): 3556-3565.doi: 10.12307/2022.285
• 生物材料综述 biomaterial review • 上一篇 下一篇
镁合金生物材料动物体内实验的研究热点
郭洋妍1,喻正文2,张 剑1
- 1 遵义医科大学口腔医学院,贵州省遵义市 563000;2 贵州省普通高等学校口腔疾病研究特色重点实验室,遵义医科大学,贵州省遵义市 563000
-
收稿日期:2021-05-18修回日期:2021-07-16接受日期:2021-08-02出版日期:2022-08-08发布日期:2022-01-12 -
通讯作者:张剑,副教授,硕士生导师,遵义医科大学口腔医学院,贵州省遵义市 563000 -
作者简介:郭洋妍,女,1995年生,2019年山西医科大学毕业,贵州省人,汉族,遵义医科大学在读硕士。 -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划项目(2016YFC1102800),项目参与人:喻正文;贵州省医用生物材料研发人才基地(黔人领发
[2018]3号),项目参与人:喻正文;遵义市科学技术局、遵义医科大学附属口腔医院联合科技研发资金项目(遵市科合社字(2018)240),项目参与人:喻正文;遵义医科大学学术新苗培养及创新探索专项项目(黔科合平台人才[2017]5733-057),项目参与人:喻正文
Research hotspots of magnesium alloy biomaterials in an in vivo animal
Guo Yangyan1, Yu Zhengwen2, Zhang Jian1
- 1School of Stomatology, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China; 2Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases Research in Colleges and Universities of Guizhou Province, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2021-05-18Revised:2021-07-16Accepted:2021-08-02Online:2022-08-08Published:2022-01-12 -
Contact:Zhang Jian, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, School of Stomatology, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Guo Yangyan, Master candidate, School of Stomatology, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:National Key Research & Development Program Project of the Ministry of Science and Technology, No. 2016YFC1102800 (to YZW); Talent Base of Medical Biomaterials Research of Guizhou Province, No. QRLF[2018]3 (to YZW); Joint Technology Research and Development Fund Project of Zunyi Science and Technology Bureau and Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, No. ZSKHSZ(2018)240 (to YZW); Academic Talents and Innovation Program of Zunyi Medical University, No. QKHPTRC[2017]5733-057 (to YZW)
摘要:
文题释义:
镁合金生物材料:镁合金因具有优良的机械性能、良好的生物相容性及可降解性能,在医学和材料学领域都得到了广泛的关注与研究,其作为新一代医用金属材料,被誉为“革命性的金属生物材料”,未来在骨科及心血管等领域的应用前景十分广阔。
动物实验:是现代科学技术的重要组成部分,是生命科学的基础和条件,它是为了获得有关生物学、医学等方面的新知识或解决具体问题而使用动物进行的科学研究。动物实验的最终目的是要通过对动物本身生命现象的研究,进而推用到人类,用于探索人类生命的奥秘,控制人类的疾病,延长人类的生命。
背景:作为新一代可降解生物材料,镁合金具有良好的力学性能、生物相容性及可降解性能,是当前生物材料学领域的研究热点之一。
目的:综述近年来镁合金生物材料动物体内实验研究的现状及问题。
方法:利用计算机检索PubMed及中国知网数据库中的相关文献,以“金属生物材料、可降解金属、镁合金材料、镁基植入物、血管支架、动物实验、腐蚀速率、生物安全性”为中文检索词,以“Metal biomaterials,degradable metals,magnesium alloy materials,magnesium-based implants,vascular stents,animal experiment,corrosion rate,biosafety”为英文检索词进行检索,检索时限为2016年1月至2021年6月,通过阅读文题和摘要进行初步筛选,最终纳入70篇文献进行结果分析。
结果与结论:①镁合金的安全性和降解速率是其能否作为可降解生物医用材料应用于临床的主要影响因素。②镁合金在骨折的内固定、骨肿瘤术后骨缺损的修复、韧带固定及冠状动脉狭窄中作为血管支架等方面的应用具有巨大潜力,镁合金具有优良的组织相容性,短期应用无安全性隐患,但尚缺乏长期生物安全性的研究结果。③镁合金血管支架在血管病变部位前期可起支撑血管作用,待该部位血管恢复正常功能后,支架被机体吸收和代谢,待血管再次发生狭窄和阻塞等病变时可再次植入镁合金支架,达到重复修复的目的。④当前镁合金已成为医疗器械研究领域的热点材料,但目前的研究结果仅是在动物实验或小样本临床试验中获得。⑤目前研究者们已基本达成共识,镁合金的合金化、表面处理和复合材料的制备等方法已可有效解决其安全性问题和降解速率过快的缺陷,但既往研究显示在镁合金实验中关于动物选择、植入物制备和评价方法等方面还缺少标准化的参考标准。⑥因此,在未来完善和制定镁合金实验的相关参考标准,对制定严谨和良好的临床前研究十分必要,这也将为镁合金材料的有效性和安全性评估提供有力的理论支撑。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9480-3167 (张剑)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
郭洋妍, 喻正文, 张 剑. 镁合金生物材料动物体内实验的研究热点[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(22): 3556-3565.
Guo Yangyan, Yu Zhengwen, Zhang Jian. Research hotspots of magnesium alloy biomaterials in an in vivo animal[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(22): 3556-3565.
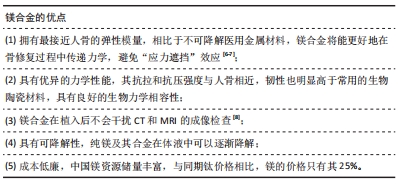
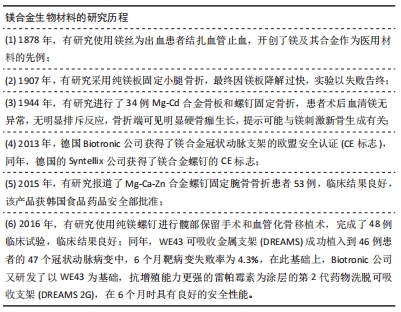
纯镁及镁合金因具有以上特性,使其十分适合作为暂时性植入材料,目前其在生物医用材料领域的应用主要在可降解硬组织修复植入物和可降解血管支架两个方面。然而,由于纯镁存在力学强度不足、降解速度过快、局部气肿形成等问题,难以直接取代传统医用金属材料制备成可植入器械应用于临床,特别是用于承力部位的植入器械。从材料学的角度看,合金化是最常用的改善金属材料性能的措施之一,是解决以上问题最简单、直接和有效的途径[9]。此外,镁合金生物材料在人体的研究最早可追溯到1878年,以下为其在人体内研究大概历程。
2.2 镁合金硬组织植入物
2.2.1 镁铝系合金 特定成分的合金元素可以改善镁合金的强度、塑性和耐腐蚀性能,合金元素的添加细化了组织的晶粒度,形成大量第二相粒子,改变了合金的微观形貌,其中元素Al是较常用于改善镁金属性能的元素之一。
廖穗祥等[10]使用镁铝合金固定系统对兔尺骨骨折进行固定,术后16周采用应力分析测试尺骨的生物力学特性,Micro-CT测算其腐蚀率,结果显示两组力学载荷差异无显著性意义;Micro-CT测算术后8周螺钉的腐蚀率为(0.40±0.04)mm/年,但螺帽比螺杆腐蚀快,接骨板的腐蚀率为(0.55±0.02)mm/年;得出了该合金可作为一种理想的新型内固定材料应用,对成骨无不良影响,并可促进骨增殖的结论。YU等[11]也建立了兔股骨缺损模型评估含氟涂层镁铝合金多孔支架的降解情况和骨体积变化,发现氟涂层增强了镁合金的抗腐蚀性能且使其具有更好的生物相容性,能诱导更多的新骨形成。也有研究将经微弧氧化处理的AZ31镁合金棒植入兔股骨,利用Micro-CT定量地对镁合金的降解进行分析和评价,发现植入后10-20周是镁合金降解的高峰期,随着镁合金的降解其含量降低,但密度并不因材料降解而降低[12]。MIURA等[13]将镁铝合金板植入大鼠头部、背部皮下和股骨骨膜下,发现其在头部腐蚀最快,背部次之,股骨最慢;同时在板周围有血管化的纤维囊形成,并随时间而成熟,且发现不同解剖部位的合金体积损失与囊厚度相关。SATO等[14]的研究也发现镁合金板在腹部的体积减少最快,其次是头部、背部、胫骨和股骨。
上述研究中镁铝合金及经过氟涂层及微弧氧化处理的镁铝合金都表现出良好的生物相容性,但经处理的镁铝合金生物相容性更佳。此外,研究中发现其在动物体内的降解与特定的体内环境有关,这提示在今后的应用中可以考虑根据其在机体不同部位降解速率不同的特点来进行相应处理,在口腔颌面区域修复材料的应用也应该根据镁合金在颌面区域相对容易降解的特性来选择;同样表明为了促进镁合金的临床应用,有必要进一步了解它们与特定体内环境的相互作用,为不同部位的镁合金植入提供一定参考。ZHAO等[15]测试了镁合金ZJ41、WKX41、和AZ31在动物体内的腐蚀降解速率,证实这些合金是可生物降解植入物应用的潜在候选者。
2.2.2 镁锌系合金 锌是人体必需的微量元素,参与300多种酶反应,对免疫系统、生长发育有重要影响,对维持很多生物大分子的结构和功能稳定性具有至关重要的作用[16]。锌具有良好的生物相容性,成年人每日需要摄入约15 mg的锌满足人体的新陈代谢,过量的锌可通过肠胃和肾脏代谢排出体外,锌缺乏会降低成骨细胞活性和碱性磷酸酶活性[17],影响成骨进程。
锌是镁合金的重要合金强化元素之一,通过固溶、时效析出强化能够大幅度提高镁金属的力学性能,同时锌的加入可提高镁的腐蚀电位,因为锌与钙、稀土等元素一样,具有稳定镁腐蚀产物膜的作用,能够提高镁的抗腐蚀能力,降低镁的降解速率。含涂层的镁锌复合材料具有更高的耐腐蚀性、良好的生物相容性和更强的骨诱导能力,可用于骨科的植入器械制造[18]。JIANG等[19]探讨MgF2包覆的镁合金的生物降解特性和生物学特性,将有MgF2涂层的镁合金及无涂层镁合金植入兔股骨;采用扫描电子显微镜扫描、X射线片、Micro-CT和力学性能检测等方式进行观察,发现涂层组周围松质骨的密度增加更均匀、骨小梁的结构相对完整;由此得出结论,MgF2涂层可有效降低镁合金的体内降解速率,延迟镁离子释放,涂层本身具有良好的生物相容性和生物活性。ZHANG等[20]进行了类似的研究,发现经微弧氧化处理的镁锌钙合金支架能够有效修复临界性骨缺损;同时也能有效改善镁锌钙合金支架的骨修复效果,耐腐蚀性及生物相容性。以上研究结果证实镁合金表面涂层处理可有效提高镁合金的耐腐蚀性能,使镁合金具有更优良的生物相容性和骨修复效果。
赵维康[21]选用大鼠股骨缺损填充模型,模拟作为骨科材料在骨内的降解情况,在术后24 h检测发现镁合金各组的白细胞介素6水平升高较对照组Ti与空白组更明显,这提示早期的降解以及产生的气体会加强大鼠的炎症反应;随后在术后7,14 d,所有炎症指标无显著性差异,可见在长期植入后并没有明显影响。BAO等[22]的实验表明HP-Mg、Mg-1Ca和Mg-2Zn植入早期呈急性炎症反应,随植入时间的延长,逐渐呈现为慢性炎症反应;1个月时,可见材料周围包裹着一层结缔组织,这与赵维康[21]的研究结果相似,但2项研究持续的时间都较短,缺乏长期实验研究结果的支持,今后可开展体内长期研究,验证镁合金材料降解对周围组织及全身情况的影响。ELKAIAM等[23]进行了镁锌合金的体内评估,组织学分析没有发现任何严重的炎症表现,这与前面2项研究结果不一致,分析原因可能如下:选择的合金成分不一致、检测时间点不同、检测方式有差异及动物个体差异等;此外,该项研究中还观察到明显的皮下气肿,这是合金植入物的降解产物,气腔内还含有合金碎屑,将局部的气腔刺穿会导致合金完全降解,这表明气体的惰性性质阻止了合金在被人体自然吸收之前的降解,这样的结果或可为今后的研究提供新思路。刘天甲等[24]发现镁合金颅骨固定系统具有良好的组织相容性,植入兔体内安全有效。也有研究者将多孔镁合金支架植入兔下颌骨,证实多孔镁合金支架具备优良的生物安全性能[25]。王湛等[26]将镁合金植入大鼠胫骨,在切口处注射金黄色葡萄球菌菌液或大肠杆菌菌液,结果表明该材料植入体内对金黄色葡萄球菌或大肠杆菌感染具有明显抑制作用,并随着镁合金中Ag含量的增多,抑菌效果更加明显。此类镁合金材料的抗菌性能研究或可为解决临床植入物感染问题提供新措施,待研究成熟应用于临床后可显著降低临床植入物感染发生率,为骨折患者减轻痛苦与经济负担。
有研究者将中国科学院金属研究所研发制备的镁合金屏障膜用于犬下颌骨牵张成骨术,发现该屏障膜无全身毒性反应,具有良好的生物安全性和相容性[27]。也有研究者使用镁合金制备了一种引导性骨再生膜,该膜对MC3T3E-1细胞具有良好的体外细胞相容性,同时对大肠杆菌、表皮葡萄球菌和金黄色葡萄球菌具有良好的抗菌作用;兔颅骨缺损模型也证实Ca-P包被的合金膜在术后1.5个月和3个月均进行性降解,无炎症反应,新骨形成明显改善;这表明Ca-P涂层的镁合金膜作为引导性骨再生膜具有很大的临床应用潜力[28]。然而,尽管一些动物实验证实镁合金屏障膜具有良好的生物安全性,组织相容性及一定的抗菌作用,但要想将镁合金屏障膜、再生膜应用于临床,还需要进一步设计实验对其安全性进行验证。
WANG等[29]将镁合金螺钉与市售的聚丙交酯螺钉用于前交叉韧带重建的兔模型中,结果表明该镁合金螺钉在前交叉韧带重建中具有潜在临床应用价值。LI等[30]构建了抗分解代谢药物唑来膦酸集成的镁基植入物,在骨质疏松大鼠模型中植入髓内钉固定股骨骨折12周,结果表明与传统不锈钢相比,镁基植入物可通过促进骨痂形成来增强骨质疏松性骨折的修复,而与植入物涂层局部释放的唑来膦酸组合治疗进一步提高了骨再生率,由于两者的协同作用,抑制了破骨细胞和骨重塑,显著提高了骨质量和机械强度;且体外和体内研究都表明,它刺激了新骨形成,同时抑制了骨重塑,这归因于镁降解产物和唑来膦酸的局部释放,说明镁基植入物可以以可控的方式缓慢释放镁基降解产物和唑来膦酸,并且可作为骨质疏松症相关骨折重建的优越替代品;该实验证实了镁基植入物可以增强骨质疏松性骨折动物的骨折修复能力,这说明该生物降解镁合金的骨科植入物具有巨大的潜力,未来或可替代目前用于治疗骨质疏松性骨折的内固定装置。这种将镁合金与特定药物结合,两者协同发挥作用的研究可以为临床试验设计提供参考。XU等[31]研究镁锌合金支架在颈椎前路椎间盘切除术和融合术中的性能,并评估经微弧氧化修饰的镁锌合金支架的表面降解情况;结果显示该支架具有理想的生物相容性和生物力学特性,但是通过放射学和组织学评估的融合状态欠佳;通过微弧氧化改性,镁锌合金支架的降解速率是可控的,但比预期慢,最终显示该支架降解呈过度控制和融合失败。
由此可见,未来需要进一步的研究来改善该类镁基材料的性能,为今后的临床应用提供实验依据。镁合金降解速率的控制是一个难题,降解太快不足以发挥材料本身的功能,降解太慢又会影响、阻碍植入物周围组织的愈合、重建。因此,应根据植入部位的不同来调控镁合金的降解速率。
2.2.3 镁钙系合金 钙是人体所必需的金属元素,在体内参与大量维持人体正常新陈代谢和生理功能的生理生化反应[32]。骨中贮存着人体内大量的钙,且钙离子能够促进骨组织的愈合。作为镁的合金化元素,钙的加入不仅能够形成热稳定的金属间化合物,还能有效细化镁合金晶粒,提高合金在高温下的强度和蠕变性能[33];此外,钙的加入不仅能增强合金的力学性能,还能提高合金的抗腐蚀能力。研究者们发现将镁钙合金植入大鼠股骨4周后,该合金植入物与周围骨结合良好,可以观察到缓慢均匀的降解,对周围组织未产生不利影响,表明该合金可以用作新的临时植入材料[34]。
有报道评估人标准尺寸的镁板和螺钉系统在犬面部骨折中的生物相容性和有效性,证实该镁板和螺钉具有良好的生物相容性,并为面部骨折的早期骨愈合提供了相当大的稳定性[35]。WANG等[36]应用真空表面臭氧活化方法,用天然丝素蛋白涂层处理镁锌钙合金表面,获得均匀的丝素膜作为防护屏障,将该镁锌钙合金植入兔的一侧脊柱进行为期180 d的动物研究,显示其体内耐腐蚀性能显著提高,降解速率是裸镁锌钙合金的1/18。这些结果展现了镁合金板和螺钉在人颅颌面骨折固定中的临床应用潜力。
2.2.4 镁锶系合金 锶、镁和钙同属第二主族元素,具有与镁、钙相近的化学性能、冶金性能和生物学功能。锶也是人体的必需金属元素之一,99%的锶都贮存于人骨中;它能促进成骨细胞的生长、抑制骨吸收,同时也能促进成骨胶原的合成。在临床上雷尼酸锶作为一种提高骨强度和骨密度的药物,已经被广泛应用于治疗骨质疏松症。
骨巨细胞瘤是一种良性肿瘤但具有侵袭性和转移性,有术后复发和发生溶骨反应的风险,单纯手术切除的治疗方法不能根治骨巨细胞瘤。有报道研发了可抑制骨巨细胞瘤术后复发和发生溶骨反应的负载唑来膦酸的镁锶合金,并研究了这种抑制作用的分子和细胞机制,表明唑来膦酸负载的镁锶合金可能是在骨巨细胞瘤治疗中修复骨缺损的潜在植入物[37]。这项研究中负载唑来膦酸的镁锶合金与LI等[30]构建的唑来膦酸集成的镁基植入物类似,将来在体外细胞实验的基础上可构建骨巨细胞瘤动物模型进行体内实验,进一步验证其在骨巨细胞瘤治疗中修复骨缺损的应用效果。
也有研究者试图通过控制含锶镁合金中抗菌物质的释放来解决植入物细菌感染的问题,动物骨髓炎模型实验表明,这种微量添加的锶降低了镁合金的降解速率,与纯镁和钛相比,含锶镁合金植入物周围的纤维组织生长速度更快;同时发现该镁合金植入物表面金黄色葡萄球菌的密度最小[38]。这样的验证性研究提供了一种新的可行策略,或可以用于解决骨折治疗过程中的面临的植入物感染问题,该研究结果与王湛等[26]的研究结果类似。
有研究者研发了一种新的双膦酸盐负载微弧氧化涂层的镁锶合金丸,该研究证实双膦酸盐包被的镁颗粒不仅在细胞培养环境中诱导骨肉瘤细胞凋亡和坏死,在体内水平上双膦酸盐包被的镁颗粒也可以通过镁降解和药物释放的协同作用来破坏肿瘤和防止肿瘤复发;这些结果表明,双膦酸盐包覆的镁丸是未来骨肉瘤治疗中针对肿瘤切除术后缺损修复的潜在选择[39]。以上研究表明镁锶合金在骨肿瘤切除术后的骨缺损修复方面具有极大的研究、应用价值。
2.2.5 镁锰系合金 锰在软骨发育、维持结缔组织结构与功能完整等方面有很大的影响,是维持正常骨结构、生殖中枢系统的必需元素[40]。同时锰有助于细化镁合金晶粒尺寸,提高其延展性、抗拉强度;少量锰元素的添加已被证明可以改善镁合金的耐腐蚀性能,并有助于减少金属杂质的影响[41]。耿芳等[42]进行了镁锰合金的体内外研究,体外实验观察镁锰合金在人工组织液中的降解情况;体内实验将表面经微弧氧化处理含有硅涂层的镁锰合金植入物及同尺寸未经表面处理的镁锰合金、钛合金植入兔颈椎椎体,观察不同时间植入物的体内降解情况;实验表明镁锰合金颈椎植入物制备成功,该颈椎植入物可用于小动物颈椎部位实验,经表面处理后的镁锰合金体内、体外抗腐蚀性能明显改善,说明适当的表面处理能够有效改进合金的抗腐蚀性能。镁锰合金材料具有优异的力学性能,相对较低的弹性模量[43]。
近来研究镁锰骨修复材料降解性能及体外细胞生物学性能发现镁锰合金具备较为优异的耐腐蚀降解性能,对骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨能力有促进作用[44]。今后可通过将镁锰合金材料植入动物体内,进一步探讨该材料动物体内腐蚀降解性能及其血液相容性、组织相容性等生物安全性,为该修复材料后续实验研究提供理论支撑和经验指导,有望为该材料的进一步应用提供理论基础。
2.2.6 镁稀土合金 可生物降解的镁合金由于具有优良的医疗性能,目前正受到广泛的研究,为了提高合金的力学性能和耐腐蚀性能,常选择稀土元素作为合金的添加元素来改善合金的性能。有研究指出在各类镁合金中,镁稀土合金降解速率一般最低,有望作为外科植入物应用[45-46],其中研究最多的镁稀土合金为WE43,其主要成分为钇(Y)、锆(Zr)和稀土金属(RE),其中W代表钇元素,E代表稀土元素,4代表钇元素的质量百分数,3代表稀土元素的质量百分数。
SCHALLER等[47]进行了WE43在猪肋骨模型中的研究,将含涂层WE43板/螺钉系统、无涂层WE43板/螺钉系统及钛板/螺钉系统植入猪肋骨;通过CT、Micro-CT、组织学和组织形态学分析了骨块;放射学观察发现,固定在肋骨上的未涂层镁板组气体形成量较多;术后12周Micro-CT显示涂层组周围的骨愈合情况较无涂层组更好;组织学检查未观察到镁降解对骨愈合的负面影响。
这项研究显示含涂层的WE43具有良好的成骨作用,为进一步开发用于骨固定的镁板/螺钉系统提供了积极有力的支持。LIN等[48]使用等离子体浸入离子注入技术在WE43表面构建了功能化的TiO2/Mg2TiO4纳米层并进行了动物研究,研究显示在术后12周,经离子体浸入处理的镁合金周围的新骨形成量与对照组相比明显增加,其新骨的杨氏模量是周围成熟骨的82%;此外,还发现在被紫外线照射时,这种特殊的TiO2/Mg2TiO4层表现出一定的细菌消毒能力,这归因于细胞内活性氧的产生。
通过这些观察结果,可以认为经离子体浸入处理的镁植入物上的TiO2/Mg2TiO4纳米层在改善镁合金耐腐蚀性能的同时可以显著促进新骨形成和抑制细菌感染。MARUKAWA等[49]评估WE43植入物在体内的生物反应和其作为板/螺钉固定系统的有效性;WE43镁合金和聚1-乳酸是临床中常用的材料,使用犬胫骨骨折模型评估镁合金植入物作为板/螺钉固定系统的有效性;结果发现WE43具有足够的强度来固定、支撑犬胫骨骨折的愈合。该研究表明其在骨科、口腔颌面外科等用于承重部位的骨折固定方面具有巨大的潜力,因此可以认为这些可生物降解的镁合金是替代可生物降解聚合物的良好候选者。
也有学者将镁合金和聚丙交酯-共乙交酯聚合物植入猪颌面骨中发现镁合金和聚合物组的骨折部位均愈合良好,在所有植入部位都观察到良好的骨结合和逐渐消失的骨折线;组织学分析发现两种材料的骨折愈合结果相似,这表明它们都具有良好的生物相容性,镁合金可在承担一定负荷的环境中支持骨折愈合[50]。这两项研究结果都表明镁合金WE43可在承担一定负荷的环境中进行骨折固定,促进骨折的愈合,且与生物降解聚合物具有相似的功效,但具有更加优越的力学性能。
OSHIBE等[51]研究WE43的降解和生物相容性,将具有和不具有阳极氧化的WE43圆棒植入大鼠胫骨;在术后1年,两组植入物周围都出现了成熟骨结构,这说明WE43植入物在骨组织中显示出良好的长期稳定性和生物相容性。TORRONI等[52]的研究也表明镁合金WE43在小鼠体内生物相容性良好。MYRISSA等[53]将Mg-10Gd针植入大鼠,在持续36周的研究中,发现Mg-10Gd是一种快速降解材料;元素在动物体内分布的结果令人意外,因为在研究的整个时间跨度内,被研究的器官中都可以观察到钆的积累,但血清样本中没有镁和钆的积累;这是首次观察到含钆可降解镁基植入物在动物器官中出现钆积聚。这些发现表明了未来研究新型生物可降解材料的成分在体内分布的重要性,以确保后期临床应用中患者的安全。
LEVOROVA等[54]将WE43和钛螺钉植入兔胫骨,发现WE43植入物周围的骨愈合情况良好。相比于四肢的负重骨而言,颌面部骨骼所受应力较小,因此镁合金材料有望首先应用于颌面部骨折的固定、牙槽嵴高度保存、颌骨囊肿术后的骨修复等方面[14]。TORRONI等[55]在绵羊模型上测试了未经处理(铸态)和人工老化(T5)的WE43作为骨膜下植入物的生物相容性和降解特性;研究显示两种合金均展现出优异的生物相容性,WE43-as(铸态)显示出更高的降解率,增加了骨重塑能力;WE43-T5显示出更高的骨/植入物界面稳定性,更适合用于制造骨膜内螺钉。在该研究者的前期研究中将WE43-as和WE43-T5植入绵羊的额鼻区骨膜下测试局部生物相容性,结果显示与WE43-as相比,WE43-T5合金具有更强的机械性能,两种合金均显示出良好的生物相容性和促进成骨的性能[56]。该学者的研究证实了WE43具有出色的生物相容性和促成骨能力,为进一步研究镁合金在颌面部骨折环境中的应用,提供了动物实验基础,同时证明WE43-T5比WE43-as表现出更高的稳定性和更低的降解率。
BAI等[57]使用微弧氧化技术在镁合金表面制备复合涂层并使用水热沉积法在涂层上涂覆2 h和24 h;将制备的各样品植入兔股骨髓腔,通过X射线片、CT和血清Mg2+检查来评估植入物的体内腐蚀行为;结果表明经复合涂层处理后的镁合金降解速率减慢了,且与经过2 h水热处理的镁合金相比经过24 h水热处理的复合涂层镁合金的降解速度更慢。该研究证实了微弧氧化技术可减缓镁合金的降解,在此基础上经过水热沉积可进一步减缓镁合金的降解,且减缓效果与处理时间有一定关系,该实验呈现为正相关,具体的时间关系还有待进一步研究证实。同时也说明镁合金可同时使用2种处理措施来进行表面处理减缓合金自身的降解,这为今后的研究提供了新方向,可同时采用两种甚至多种措施同时对镁合金进行处理,从而优化其各项性能。
镁合金的安全性和降解速率是其能否成为标准商用可降解生物医用材料的主要影响因素。镁合金材料在应用于骨科、口腔颌面外科等领域时需要具有适宜的降解速率,以保证其力学性能和避免毒性反应。目前降低镁合金材料降解速率的方法主要有提高镁纯度、添加合金成分和表面处理改性如增加涂层等。
镁合金硬组织植入物动物模型及实验结果,见表1,2。
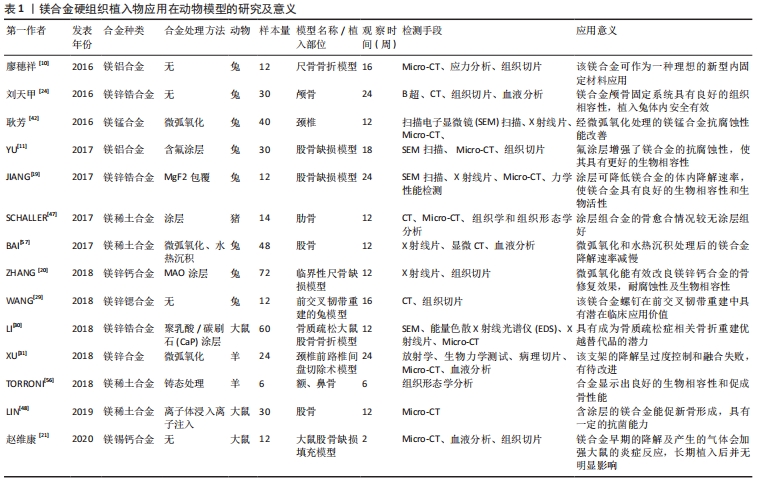
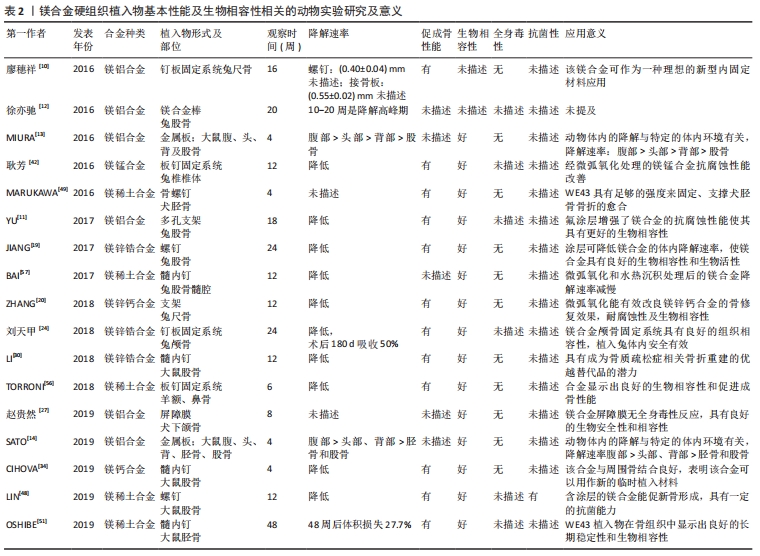
近年来,学者们针对镁合金的各项特性进行了大量体外研究,动物体内研究方面也进行了一系列的实验研究,在测试镁合金的综合性能方面取得了一定的进展。大量动物体内研究表明镁合金经合金化、表面涂层、微弧氧化、离子注入、阳极氧化等措施处理后耐腐蚀性能得到了明显改善,具有优良的组织相容性、促成骨性能、抗菌性能、无明显的全身毒性反应;通过观察可以发现在镁合金硬组织植入实验中检测手段多采用电镜扫描、X射线片检查、CT检查、Micro-CT检查、力学性能检测、组织病理检查及血液分析等;实验动物多选择为小鼠、大鼠、兔等小型动物,当然也有采用猪、犬、羊等为研究对象的实验,但相对较少。与选择犬、羊、猪的研究相比,对鼠和兔等小型动物的研究倾向于使用更多的动物,但同一物种中动物的数量有很大差异;同样的情况也存在于观察时间的设置中。既往的研究显示,在动物选择、植入物制备和评价方法等方面还缺少标准化的参考标准。在实验中有标准化的参考指标不仅有利于实验的科学设计,更有利于实验结果的科学评判,使实验理论更好地服务于临床前研究;此外,设计严谨和良好的临床前研究对可降解镁合金材料的有效性和安全性进行评估是十分必要的。因此,在今后的实验研究中,需要以更精确、更具体和更统一的评估方式来评测镁合金材料的长期生物安全性、降解性能、促成骨等性能;特别是镁合金植入物对组织器官长期影响的研究,以便获得更多、更可靠的生物安全信息,为临床应用做准备。
2.3 镁合金血管支架 镁合金具有的可自行降解的特性为其在同一病变部位进行多次介入干预治疗提供了可能。此外,镁合金表面带有负电荷,使其具有低血栓源性,降低了支架内急性血栓形成的可能;同时镁合金的降解产物镁离子是ATP的辅因子,也是生理性的钙拮抗剂,它可以有效预防各种缺血再灌注引起的钙超载损伤,这些特性都让镁合金成为最具潜力的可生物降解血管支架材料之一[58]。
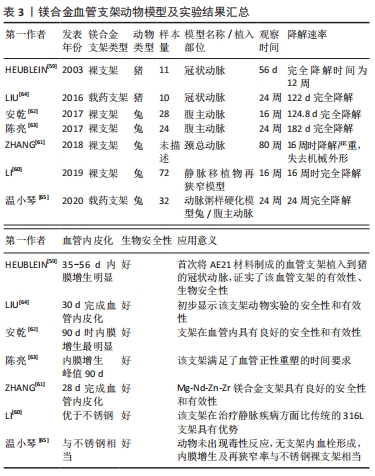
HEUBLEIN等[59]首次将AE21材料制成的血管支架植入到猪的冠状动脉,植入过程中没有发生支架破损和血栓栓塞等不良事件,后期的观察结果也显示,支架周围的炎症反应和血栓形成均维持在较低的水平;该研究证实了镁合金血管支架的有效性和生物安全性,展现了其在心血管领域应用的巨大潜力。LI等[60]探讨生物可降解镁合金支架对静脉移植物吻合口再狭窄重塑的影响,建立兔静脉移植物再狭窄模型,生物可降解镁合金支架组和316L组分别植入生物可降解镁合金支架和316L不锈钢支架,而无治疗对照组未植入支架;观察结果表明生物可降解镁合金支架组的血管再内皮化效果优于316L组;生物可降解镁合金支架在4个月时完全降解,该研究发现生物可降解镁合金支架能促进静脉移植物吻合术后血管的正向重塑,在治疗静脉疾病方面比传统的316L支架具有优势。以上研究支持可降解血管支架在血管领域的应用。有研究报道将Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr(Jiao Da Bio-MagnesiumSeries,JDBM)镁合金支架植入兔颈总动脉,结果表明JDBM支架具有良好的安全性和有效性,并在28 d时完成血管内皮化,所有合金元素在兔的主要器官中均未显示出持续的富集[61]。这些发现在一定程度上减少了心外科医生对镁合金支架植入后可能发生的血管钙化和元素富集的担忧。
针对镁合金裸支架,安乾等[62]探讨AZ31镁合金支架在兔腹主动脉中的降解情况,研究表明AZ31镁合金支架在兔腹主动脉内完全降解时间为124.8 d,在支架植入90 d时血管内膜增生和管腔狭窄最明显,90 d后血管内膜增生和管腔狭窄情况逐渐减轻。陈亮等[63]进行了类似的研究,将镁合金支架植入兔腹主动脉;结果发现支架在180 d时基本降解,血管内膜增生在90 d时达峰值,整个降解过程中血管都保持通畅;可降解镁合金支架完全降解时间为182 d,可满足血管正性重塑的时间要求。上述研究中镁合金支架在兔腹主动脉内完全降解时间虽然不一致,但最终结果都表明在支架植入90 d时血管内膜增生和管腔狭窄最明显,支架降解过程中血管都保持通畅,可满足血管的正性重塑。
支架对于血管而言是异物,会刺激血管壁平滑肌细胞增殖、迁移,有较大的再狭窄率,研究表明冠状动脉支架再狭窄最多见于术后6个月,以上研究中镁合金支架降解时间为4-6个月,基本可以满足血管正性重塑的时间要求。相较于不可降解支架,镁合金支架避免了支架长期存在于血管内对血管收缩功能及血管重塑的不良影响,也在植入前期起到了支撑血管的作用,而当血管恢复正常功能后,又可被机体吸收、代谢,对机体无毒害作用,即使后期发生血管再狭窄,镁合金支架也可以被再次植入该部位支撑血管,辅助血管功能恢复。LIU等[64]研发的经3-氨基丙基三甲氧基硅烷处理的镁合金支架植入小型猪冠状动脉,发现其在6个月植入周期内具备优异的组织相容性和血管内皮化能力,与生物降解药物涂层冠脉支架系统(BuMA)不锈钢支架相比未造成明显的血管损伤、炎症、血栓和再狭窄现象,初步显示其动物实验的安全性和有效性。
除镁合金裸支架的研究外,也有不少关于镁合金药物支架的实验报道。温小琴等[65]观察镁合金紫杉醇药物洗脱支架置入兔腹主动脉的安全性及有效性,将动脉粥样硬化模型兔随机分为观察组和对照组,观察组置入1个紫杉醇药物洗脱支架,对照组置入不锈钢裸支架;观察至6个月发现镁合金药物洗脱支架完全降解,动物未出现毒性反应,无支架内血栓形成,内膜增生及再狭窄率与不锈钢裸支架相当。有研究评估在兔动脉粥样硬化模型中镁合金支架和金属厚支撑药物洗脱支架之间新动脉粥样硬化的形成情况;该研究表明镁合金支架的新动脉粥样硬化形成比药物洗脱支架的少;大剂量他汀类药物治疗本身或与以靶点为基础的器械治疗相结合,这两种治疗方法可能是减少新动脉粥样硬化进展的有前途的措施[66]。
上述研究结果表明镁合金药物洗脱支架在兔体内表现出优良的机械性能、良好的生物相容性和生物安全性。也有研究者进行了药物洗脱支架的临床实验研究,HAUDE等[67]报道了雷帕霉素药物洗脱镁合金支架(DREAMS 2G)临床试验的随访结果,发现DREAMS 2G植入12个月后平均支架内管腔丢失0.44 mm,血管舒缩功能在6个月时恢复正常;该研究表明在新生冠状动脉病变中植入DREAMS 2G装置是可行的,且在6个月时具有良好的安全性和性能。减缓镁合金支架的降解速度不仅是评价支架性质的重要因素, 更是对机体保护性的要求,可以避免毒性反应。所以,延长镁合金降解时间是目前镁合金支架的重要研究方向之一,优化支架构型和改进合金组分是改变镁合金支架降解速率的2种方法。
可生物降解血管支架有关的一系列体内研究已充分证实了镁合金血管支架,包括裸支架和药物洗脱支架的生物安全性和有效性。随着生物医用可降解金属材料研究的进一步深入,可以通过建立新型合金体系、改进现有合金组分、优化支架结构和支架表面处理等措施来逐步完善镁合金血管支架的性能。但是,由于人体内环境的复杂性、多样性,需要对镁及镁合金体内降解吸收进行更深入更系统的研究,以确保其临床应用的安全性。相信在不久的将来,可降解镁合金血管支架会在治疗心血管疾病等方面发挥重大作用。此外也有学者对镁合金在输尿管支架[68]、气管支架方面的应用进行了动物实验[69],取得了一定的成果。镁合金血管支架动物模型及实验结果汇总如下,表3。
| [1] 张永涛,刘汉源,王昌,等.生物医用金属材料的研究应用现状及发展趋势[J].热加工工艺,2017,46(4):21-26. [2] 张文毓.生物医用金属材料研究现状与应用进展[J].金属世界, 2020(1):21-27. [3] DOLATI S, RIKHTEGAR R, MEHDIZADEH A, et al. The role of magnesium in pathophysiology and migraine treatment. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2020; 196(2):375-383. [4] DEE P, YOU HY, TEOH SH, et al. Bioinspired approaches to toughen calcium phosphate-based ceramics for bone repair. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2020;112:104078. [5] NABIYOUNI M, BRÜCKNER T, ZHOU H, et al. Magnesium-based bioceramics in orthopedic applications. Acta Biomater. 2018;66:23-43. [6] ABHISHEK, JAISWAL S, DUBEY A, et al. Biocompatibility and biodegradability evaluation of magnesium-based intramedullary bone implants in avian model. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2021;109(8):1479-1489. [7] GARTZKE AK, JULMI S, KLOSE C, et al. A simulation model for the degradation of magnesium-based bone implants. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2020;101:103411. [8] ESPIRITU J, MEIER M, SEITZ JM. The current performance of biodegradable magnesium-based implants in magnetic resonance imaging: a review. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(12):4360-4367. [9] 郑玉峰,刘嘉宁.从可降解金属的角度审视医用镁合金的元素选择[J].中国材料进展,2020;39(2):92-112. [10] 廖穗祥,郑冠,史成龙,等.镁合金内固定物的降解与力学强度[J].广东医学,2016,37(1):45-49. [11] YU W, ZHAO H, DING Z, et al. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of MgF(2) coated AZ31 magnesium alloy porous scaffolds for bone regeneration. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2017;149:330-340. [12] 徐亦驰,尹合勇,孙振,等.AZ31镁合金材料植入物在兔股骨髁内的降解:Micro-CT评价[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(16):2303-2309. [13] MIURA C, SHIMIZU Y, IMAI Y, et al. In vivo corrosion behaviour of magnesium alloy in association with surrounding tissue response in rats. Biomed Mater. 2016;11(2):025001. [14] SATO T, SHIMIZU Y, ODASHIMA K, et al. In vitro and in vivo analysis of the biodegradable behavior of a magnesium alloy for biomedical applications. Dent Mater J. 2019;38(1):11-21. [15] ZHAO D, WANG T, NAHAN K, et al. In vivo characterization of magnesium alloy biodegradation using electrochemical H(2) monitoring, ICP-MS, and XPS. Acta Biomater. 2017;50:556-565. [16] LIU K, LU Y, AI L, et al. Association between FOXE1 and non-syndromic orofacial clefts in a northeastern Chinese population. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2015;53(8):705-710. [17] WANG X, SHAO X, DAI T, et al. In vivo study of the efficacy, biosafety, and degradation of a zinc alloy osteosynthesis system. Acta Biomater. 2019;92:351-361. [18] GRÜN NG, HOLWEG P, TANGL S, et al. Comparison of a resorbable magnesium implant in small and large growing-animal models. Acta Biomater. 2018;78:378-386. [19] JIANG H, WANG J, CHEN M, et al. Biological activity evaluation of magnesium fluoride coated Mg-Zn-Zr alloy in vivo. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;75:1068-1074. [20] ZHANG N, LIU N, SUN C, et al. In vivo study of a novel micro-arc oxidation coated magnesium-zinc-calcium alloy scaffold/autologous bone particles repairing critical size bone defect in rabbit. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2018;32(3):298-305. [21] 赵维康.骨科新型镁合金(Mg-1.5Sn-xZn)材料制备、生物活性及抗菌性研究[D].重庆:重庆医科大学,2020. [22] BAO G, FAN Q, GE D, et al. In vitro and in vivo studies on magnesium alloys to evaluate the feasibility of their use in obstetrics and gynecology. Acta Biomater. 2019;97:623-636. [23] ELKAIAM L, HAKIMI O, YOSAFOVICH-DOITCH G, et al. In vivo evaluation of mg-5%zn-2%nd alloy as an innovative biodegradable implant material. Ann Biomed Eng. 2020;48(1):380-392. [24] 刘天甲,顾硕,周璐,等.可降解镁合金颅骨固定系统在动物实验中的安全性及有效性[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(30):4876-4881. [25] 王亮,郭玉兴,黄华,等.颌骨缺损修复用多孔镁合金支架材料的生物安全性评价研究[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(26):4121-4128. [26] 王湛,杨军,李建军.植入体内新型镁合金材料的抗菌性能[J].中国组织工程研究,2018;22(22):3451-3455. [27] 赵贵然,马竞,王玉,等.镁合金屏障膜在犬下颌骨牵张成骨中的全身毒性研究[J].全科口腔医学电子杂志,2019,6(19):81-83. [28] SI J, SHEN H, MIAO H, et al. In vitro and in vivo evaluations of Mg-Zn-Gd alloy membrane on guided bone regeneration for rabbit calvarial defect. J Magn Alloys. 2021;9(1):281-291. [29] WANG J, WU Y, LI H, et al. Magnesium alloy based interference screw developed for ACL reconstruction attenuates peri-tunnel bone loss in rabbits. Biomaterials. 2018;157:86-97. [30] LI G, ZHANG L, WANG L, et al. Dual modulation of bone formation and resorption with zoledronic acid-loaded biodegradable magnesium alloy implants improves osteoporotic fracture healing: an in vitro and in vivo study. Acta Biomater. 2018;65:486-500. [31] XU H, ZHANG F, WANG H, et al. Evaluation of a porous bioabsorbable interbody Mg-Zn alloy cage in a goat cervical spine model. Biomed Res Int. 2018;2018:7961509. [32] WANG C, ZHANG R, WEI X, et al. Metalloimmunology: the metal ion-controlled immunity. Adv Immunol. 2020;145:187-241. [33] ZHANG C, LIN J, NGUYEN N T, et al. Antimicrobial bioresorbable mg-zn-ca alloy for bone repair in a comparison study with Mg-Zn-Sr alloy and pure Mg. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2020;6(1):517-538. [34] CIHOVA M, MARTINELLI E, SCHMUTZ P, et al. The role of zinc in the biocorrosion behavior of resorbable Mg-Zn-Ca alloys. Acta Biomater. 2019;100:398-414. [35] KIM BJ, PIAO Y, WUFUER M, et al. Biocompatibility and efficiency of biodegradable magnesium-based plates and screws in the facial fracture model of beagles. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2018;76(5):1055.e1-e9. [36] WANG C, FANG H, QI X, et al. Silk fibroin film-coated MgZnCa alloy with enhanced in vitro and in vivo performance prepared using surface activation. Acta Biomater. 2019;91:99-111. [37] LI M, WANG W, ZHU Y, et al. Molecular and cellular mechanisms for zoledronic acid-loaded magnesium-strontium alloys to inhibit giant cell tumors of bone. Acta Biomater. 2018;77:365-379. [38] GAO Z, SONG M, LIU RL, et al. Improving in vitro and in vivo antibacterial functionality of Mg alloys through micro-alloying with Sr and Ga. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;104:109926. [39] LI M, YAO M, WANG W, et al. Nitrogen-containing bisphosphonate-loaded micro-arc oxidation coating for biodegradable magnesium alloy pellets inhibits osteosarcoma through targeting of the mevalonate pathway. Acta Biomater. 2021;121:682-694. [40] DOS SANTOS NR, RODRIGUES JLG, BANDEIRA MJ, et al. Manganese exposure and association with hormone imbalance in children living near a ferro-manganese alloy plant. Environ Res. 2019;172:166-174. [41] YANG Y, WU P, WANG Q, et al. The enhancement of mg corrosion resistance by alloying mn and laser-melting. Materials (Basel). 2016; 9(4):216. [42] 耿芳,姜明威,夏天.小动物实验用镁锰合金颈椎植入物制备及其可行性研究[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2016,13(5):5-8, 12. [43] HU Y, DONG D, WANG X, et al. Synthesis and properties of Mg-Mn-Zn alloys for medical applications. Materials (Basel). 2021;14(8):1855. [44] 彭泽惠.Mg-1Mn颌面骨修复材料体外降解与细胞生物学性能研究[D].遵义:遵义医科大学,2020. [45] ECHEVERRY-RENDON M, ALLAIN J P, ROBLEDO SM, et al. Coatings for biodegradable magnesium-based supports for therapy of vascular disease: a general view. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;102:150-163. [46] LIU J, BIAN D, ZHENG Y, et al. Comparative in vitro study on binary Mg-RE (Sc, Y, La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb and Lu) alloy systems. Acta Biomater. 2020;102:508-528. [47] SCHALLER B, SAULACIC N, BECK S, et al. Osteosynthesis of partial rib osteotomy in a miniature pig model using human standard-sized magnesium plate/screw systems: effect of cyclic deformation on implant integrity and bone healing. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2017; 45(6):862-871. [48] LIN Z, ZHAO Y, CHU PK, et al. A functionalized TiO(2)/Mg(2)TiO(4) nano-layer on biodegradable magnesium implant enables superior bone-implant integration and bacterial disinfection. Biomaterials. 2019;219: 119372. [49] MARUKAWA E, TAMAI M, TAKAHASHI Y, et al. Comparison of magnesium alloys and poly-l-lactide screws as degradable implants in a canine fracture model. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2016; 104(7):1282-1289. [50] SCHALLER B, MATTHIAS BURKHARD JP, CHAGNON M, et al. Fracture healing and bone remodeling with human standard-sized magnesium versus polylactide-co-glycolide plate and screw systems using a mini-swine craniomaxillofacial osteotomy fixation model. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2018;76(10):2138-2150. [51] OSHIBE N, MARUKAWA E, YODA T, et al. Degradation and interaction with bone of magnesium alloy WE43 implants: a long-term follow-up in vivo rat tibia study. J Biomater Appl. 2019;33(9):1157-1167. [52] TORRONI A, WITEK L, FAHLIOGULLARI HP, et al. WE43 and WE43-T5 Mg alloys screws tested in-vitro cellular adhesion and differentiation assay and in-vivo histomorphologic analysis in an ovine model. J Biomater Appl. 2021;35(8):901-911. [53] MYRISSA A, BRAEUER S, MARTINELLI E, et al. Gadolinium accumulation in organs of Sprague-Dawley® rats after implantation of a biodegradable magnesium-gadolinium alloy. Acta Biomater. 2017;48:521-529. [54] LEVOROVA J, DUSKOVA J, DRAHOS M, et al. In vivo study on biodegradable magnesium alloys: bone healing around WE43 screws. J Biomater Appl. 2018;32(7):886-895. [55] TORRONI A, XIANG C, WITEK L, et al. Histo-morphologic characteristics of intra-osseous implants of WE43 Mg alloys with and without heat treatment in an in vivo cranial bone sheep model. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2018;46(3):473-478. [56] TORRONI A, XIANG C, WITEK L, et al. Biocompatibility and degradation properties of WE43 Mg alloys with and without heat treatment: In vivo evaluation and comparison in a cranial bone sheep model. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2017;45(12):2075-2083. [57] BAI CY, LI JW, TA WB, et al. In vivo study on the corrosion behavior of magnesium alloy surface treated with micro-arc oxidation and hydrothermal deposition. Orthop Surg. 2017;9(3):296-303. [58] PAN C, ZHAO Y, YANG Y, et al. Immobilization of bioactive complex on the surface of magnesium alloy stent material to simultaneously improve anticorrosion, hemocompatibility and antibacterial activities. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2021;199:111541. [59] HEUBLEIN B, ROHDE R, KAESE V, et al. Biocorrosion of magnesium alloys: a new principle in cardiovascular implant technology? Heart. 2003;89(6):651-656. [60] LI Y, WANG L, CHEN S, et al. Biodegradable magnesium alloy stents as a treatment for vein graft restenosis. Yonsei Med J. 2019;60(5):429-439. [61] ZHANG J, LI H, WANG W, et al. The degradation and transport mechanism of a Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr stent in rabbit common carotid artery: a 20-month study. Acta Biomater. 2018;69:372-84. [62] 安乾,崔文军,司江涛,等.镁合金支架在兔腹主动脉中的降解[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(18):2864-2869. [63] 陈亮,丁健,王永利,等.镁合金支架植入兔腹主动脉后降解时间及血管内膜增生观察[J].介入放射学杂志,2017,26(5):443-446. [64] LIU J, ZHENG B, WANG P, et al. Enhanced in vitro and in vivo performance of Mg-Zn-Y-Nd alloy achieved with APTES pretreatment for drug-eluting vascular stent application. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(28):17842-17858. [65] 温小琴,黄奎,高明东,等.可控性生物吸收镁合金药物洗脱支架动物实验研究[J].重庆医学,2020,49(8):1233-1236,1242. [66] NICOL P, BULIN A, CASTELLANOS M I, et al. Preclinical investigation of neoatherosclerosis in magnesium-based bioresorbable scaffolds versus thick-strut drug-eluting stents. EuroIntervention. 2020;16(11): e922-e929. [67] HAUDE M, INCE H, ABIZAID A, et al. Safety and performance of the second-generation drug-eluting absorbable metal scaffold in patients with de-novo coronary artery lesions (BIOSOLVE-II): 6 month results of a prospective, multicentre, non-randomised, first-in-man trial. Lancet. 2016;387(10013):31-39. [68] TIE D, LIU H, GUAN R, et al. In vivo assessment of biodegradable magnesium alloy ureteral stents in a pig model. Acta Biomater. 2020; 116:415-425. [69] XUE B, LIANG B, YUAN G, et al. A pilot study of a novel biodegradable magnesium alloy airway stent in a rabbit model. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2019;117:88-95. [70] 尹林,黄华,袁广银,等.可降解镁合金临床应用的最新研究进展[J].中国材料进展,2019,38(2):126-137. |
| [1] | 谭国忠, 涂欣冉, 郭黎洋, 钟嘉琳, 张 阳, 江千舟. 3D打印明胶/海藻酸钠/58S生物玻璃骨缺损修复支架的生物安全性评价[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(4): 521-527. |
| [2] | 王书韵, 谢君辉, 余学锋. 间充质干细胞治疗糖尿病肾病的作用与机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(1): 148-152. |
| [3] | 张 超, 吕 欣. 髋臼骨折固定后的异位骨化:危险因素、预防及其治疗进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1434-1439. |
| [4] | 李芳, 吴可通, 赵珺, 李刚. 血管支架及其在动脉瘤治疗中的发展趋势[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(34): 5561-5569. |
| [5] | 申瑞秋, 刘志明, 宋俊祎, 胡碧茹. 具有一氧化氮释放功能的人工血管材料[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(28): 4531-4538. |
| [6] | 李 洁, 许楗桢, 胡 萍, 雷琪琪, 张文柠, 敖宁建. 用于慢性伤口羧甲基壳聚糖/氧化葡甘聚糖/三七总皂苷复合海绵的制备及性能评价[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(16): 2528-2534. |
| [7] | 纪 琦, 喻正文, 张 剑. 3D打印金属基生物材料工艺和临床应用的问题与趋势[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(16): 2597-2604. |
| [8] | 赵彬彬, 仲维剑, 马国武, 李永奇, 王 宁. 三种不同骨移植材料成骨效果的比较[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(10): 1507-1510. |
| [9] | 霍少川, 王海彬, 唐宏宇, 王粤淇, 陈群群, 冯梓誉, 李义凯. 补肾健脾活血中药干预膝骨关节炎模型大鼠软骨细胞IL-1β/ERRα/SOX9/Col2α1信号通路的变化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020, 24(35): 5577-5581. |
| [10] | 雷森林, 刘宏远, 杨红胜, 熊 燕, 段 宏. 超声辅助可吸收螺钉的体内生物安全性及组织相容性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020, 24(34): 5454-5460. |
| [11] | 崔庆达, 王海革, 赵海军, 刘 伟, 毕郑钢. 跨骺钢板固定一定周期取出:继续观察一段时间后骺板的生长抑制情况[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020, 24(3): 372-377. |
| [12] | 尚志忠, 姜彦彪, 姚 蓝, 王安安, 王红霞, 田圆新, 刘登瑞, 马 彬, . 基于动物实验系统评价干细胞治疗肾脏缺血再灌注损伤的可行性 [J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020, 24(25): 4094-4100. |
| [13] | 林云志, 方国芳, 李修往, 吴家昌, 吴铭杰, 谭 亮, 赖国华, 叶灼烽, 桑宏勋. 半自动脊柱手术机器人系统在脊柱外科治疗中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020, 24(24): 3792-3796. |
| [14] | 孙溪饶, 王程越, 赵 远, 张振保. 纯镁膜体外腐蚀及体内的生物安全性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020, 24(16): 2578-2584. |
| [15] | 程 磊, 金 健, 胡敬国, 卢雨松. 聚乳酸肋骨钉与纯钛环抱器植入动物体内后炎性反应及乳酸浓度的对比[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020, 24(16): 2567-2571. |
随着医学观念的逐渐转变,人们期待植入材料是暂时性存在于体内,随着组织修复的进程,植入材料在完成其力学和生物学功能后逐渐降解,可以避免二次手术取出的创伤,并且其降解产物能被人体吸收或代谢出体外,对人体无不良影响。因此进入21世纪,可降解金属逐渐成为生物医用材料领域的研究热点,作为新一代医用金属材料,镁合金因具有优良的机械性能、良好的生物相容性及可降解性能,在医学和材料学领域都得到了广泛的关注与研究[2],镁合金用作硬组织植入材料时,可以有效避免应力遮挡效应,促进成骨,加速骨愈合;用作血管支架材料时,可在血管内经过一段时间的支架支撑和药物治疗完成正性重构后自行降解消失,从而降低血管再狭窄的风险。镁合金具有的这些特性,使其十分适合应用于组织工程领域,可作为支架辅助种子细胞修复组织缺损,行暂时性替代作用,待组织修复完成后又可自行降解,避免了二次手术给患者带来的痛苦及经济压力,因此镁合金作为可降解医用材料具有很广阔的临床应用前景。
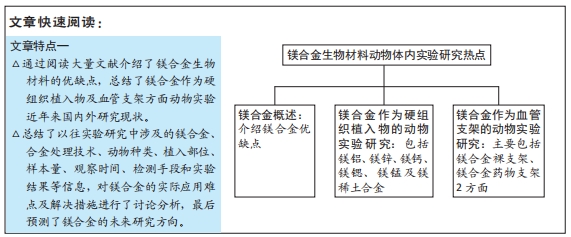
文章回顾近几年来镁合金生物材料在动物体内实验研究的国内外现状,首先对镁合金的优缺点进行了介绍,然后对目前研究较多的镁合金体系,包括镁铝、镁锌、镁钙、镁锶、镁锰及镁稀土合金作为硬组织植入物实验中涉及的合金处理技术、动物种类、植入部位、样本含量、观察时间、检测手段和实验结果等进行了归纳总结,也对镁合金作为血管支架的动物实验进行了汇总,最后对镁合金的实际应用难点及解决措施进行了讨论分析并表达了自己对镁合金未来研究方向的观点,以期为镁合金的进一步研究及临床应用提供一定参考。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 第一作者在2021年6月进行检索。
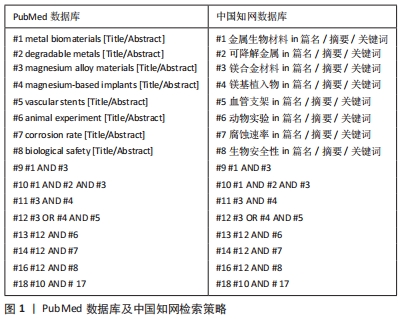
1.1.2 检索文献时限 检索时间为2016年1月至2021年6月。
1.1.3 检索数据库 PubMed和中国知网数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 中文检索词为“金属生物材料、可降解金属、镁合金材料、镁基植入物、血管支架、动物实验、腐蚀速率、生物安全性”,英文检索词为“Metal biomaterials,degradable metals,magnesium alloy materials,magnesium-based implants,vascular stents,animal experiment,corrosion rate,biosafety.”
1.1.5 检索文献类型 研究原著和综述。
1.1.6 检索策略 中英文文献检索策略,见图1。
1.1.7 检索文献量 初步共检索到文献708篇,其中中文文献233篇,英文文献475篇。
1.2 入组标准
1.2.1 纳入标准 ①有关镁合金动物体内实验介绍的文献;②有关镁合金可降解血管支架研究的文献;③优先选择近两三年发表的,同一领域主题中心相近、论据可靠的文献。
1.2.2 排除标准 ①与研究目的无相关性的文章;②重复性研究文章;③论点论据不明确文章。
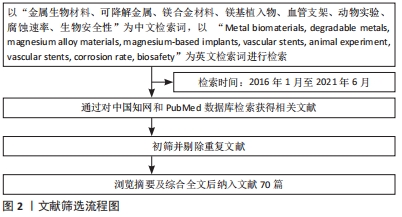
1.3 质量评估及数据提取 应用计算机检索,共检索到708篇参考文献。按照筛选标准,通过阅读文题、摘要进行初步筛选,排除与主题相关性差及重复陈旧的文献,最终纳入70篇文献[1-70],纳入的文献包括研究原著和综述。文献检索流程图,见图2。
大量动物体内研究表明镁合金经合金化、表面涂层、微弧氧化、离子注入和阳极氧化等措施处理后耐腐蚀性能得到了明显改善,具有优良的组织相容性、促成骨性能、抗菌性能,无明显的全身毒性反应;但这几种方案仍然没有彻底解决镁合金在实用化道路上所遇到的所有问题。此外,既往的镁合金动物实验研究显示在动物选择、植入物制备和评价方法等方面还缺少标准化的参考标准。因此,今后可考虑从以下几个方面着手应对以上难题:①选择对生物机体无毒无害的合金元素掺入镁合金体系,调控镁合金的降解速率,使其综合性能得到提高;②将合金化、表面处理、复合材料等两种甚至多种处理措施同时用于对镁合金的处理,从而达到同时优化其各项性能的目的;③进一步完善和规范镁合金生物材料的体内评测标准,建立可降解金属的体内风险评估标准等。
除大量动物体内研究外,目前可降解医用镁合金的临床研究已经取得一定的进展,德国Syntellix公司的MAGNEZIX空心加压螺钉、Biotronik公司的DREAMS 2G支架都已取得欧洲CE认证,韩国U&i公司生产的K-MET螺钉也获得韩国KFDA认证[70]。镁合金的临床应用前景十分广阔,因此今后需要更多更加系统深入的研究来阐明可降解镁合金在生理环境中的腐蚀降解过程和机制、降解过程控制方法、长期生物相容性等问题,为镁合金的临床应用提供更加可靠的科学实验依据。
3.2 作者综述区别于他人他篇的特点 文章总结近年来镁合金生物材料作为硬组织植入物及心血管支架方面的动物体内实验研究的现状,归纳总结硬组织植入实验中涉及的镁合金、合金处理技术、动物种类、植入部位、样本量、观察时间、检测手段和实验结果等,对镁合金裸支架及载药支架的动物实验研究做了相应的介绍,最后对镁合金的实际应用难点及应对措施进行了讨论分析并表达了自己对镁合金生物材料未来研究方向的观点。
3.3 综述的局限性 纳入文献的范围不够广,表述研究结果不够深入,对镁合金的应用难点应对措施的分析尚有待补充。
3.4 综述的重要意义 通过多篇文献的归纳总结,既肯定了既往镁合金动物实验的研究成果,镁合金的合金化、表面处理、复合材料等措施确实改善了镁合金的性能,但也从中发现了一些问题,例如实验研究显示在动物选择、植入物制备和评价方法等方面还缺少标准化的参考标准,即镁合金生物材料的体内风险评测标准还不完善,提示研究者们在今后的实验研究中,需要以更精确、更具体和更统一的评估方式来评测镁合金材料的长期生物安全性、降解性能、促成骨等性能。当前的研究也显示镁合金在骨折的内固定、骨肿瘤术后骨缺损的修复、韧带固定及冠状动脉狭窄中作为血管支架等方面的应用具有巨大潜力,实验研究结果展示了镁合金在体内的降解速率、促成骨性能、抗菌性能及生物相容性等,均显示镁合金具有优良的组织相容性,短期应用无安全性隐患,但长期生物安全性研究还有待增加。
理想的硬组织植入物应满足在骨愈合前不被降解,具有足够的机械性能,为骨愈合提供稳定的环境,在骨愈合后又能自行降解,对机体无毒无害;对于血管支架应用同样如此,在血管病变部位前期起支撑血管作用,待该部位血管恢复正常功能后,支架被机体吸收、代谢,待血管再次发生狭窄、阻塞等病变时可再次植入镁合金支架,重复该修复过程。镁合金具有的特点使其成为医疗器械研究的热点材料,但目前的实验结果仅是在动物实验或小群体人类中获得,未来仍需要更多大规模、随机对照试验来进行验证。
相信随着材料学的发展及临床应用的需求,未来在动物实验的基础上会开展更多的临床试验,使镁合金在骨科、心血管外科及口腔等多领域得到广泛的应用,为患者带来更小的伤害和更大的益处。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程

文题释义:
镁合金生物材料:镁合金因具有优良的机械性能、良好的生物相容性及可降解性能,在医学和材料学领域都得到了广泛的关注与研究,其作为新一代医用金属材料,被誉为“革命性的金属生物材料”,未来在骨科及心血管等领域的应用前景十分广阔。
动物实验:是现代科学技术的重要组成部分,是生命科学的基础和条件,它是为了获得有关生物学、医学等方面的新知识或解决具体问题而使用动物进行的科学研究。动物实验的最终目的是要通过对动物本身生命现象的研究,进而推用到人类,用于探索人类生命的奥秘,控制人类的疾病,延长人类的生命。
文章阐述了近年来镁合金生物材料作为硬组织植入物及心血管支架方面的动物体内实验研究的国内外现状。#br# 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程#br#
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||