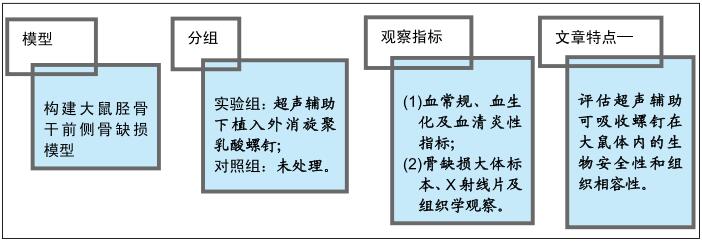
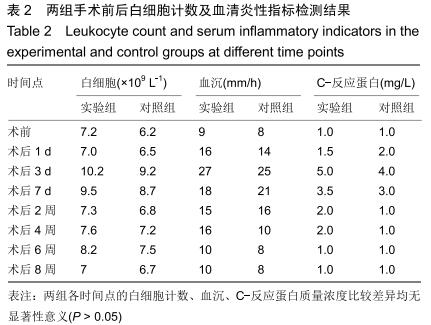
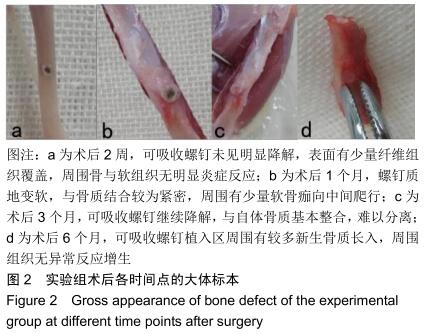
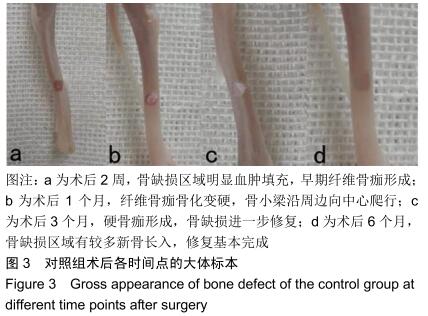
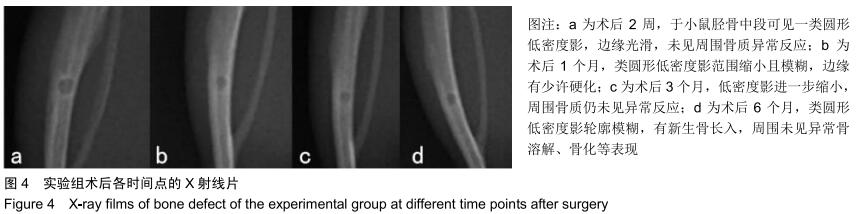
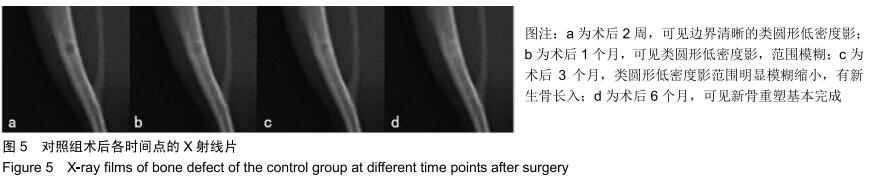
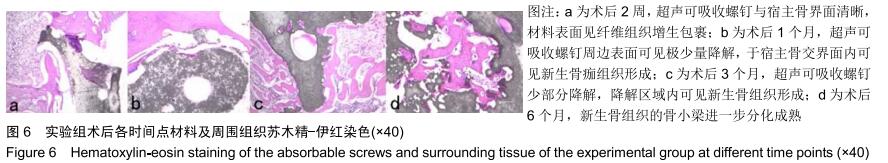
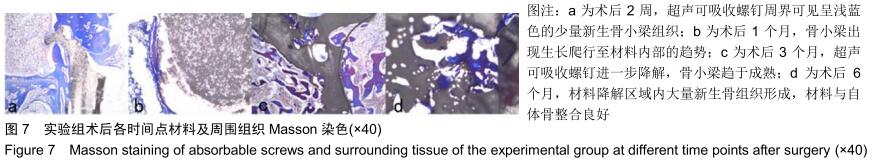
|
[1] PISTNER H, GUTWALD R, ORDUNG R, et al. Poly(L-lactide): a long-term degradation study in vivo. I.Biological results. Biomaterials.1993;14(9):671-677.
[2] ITO H, MATSUNO T, MINAMI A. Fixation with poly-L-lactide screws in hip osteotomies. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;(444): 169-175.
[3] SUURONEN R, POHJONEN T, HIETANEN J, et al. A 5-year in vitro and in vivo study of the biodegradation of polylactide plates.J Oral Maxillofac Surg.1998;56(5):604-615.
[4] PILONE A, DE MAIO N, PRESS K, et al. Ring-opening homo and copolymerization of lactides and-caprolactone by salalen aluminum complexes.Dalton Trans.2015;44(5):2157-2165.
[5] 王勇平,刘小荣,蒋垚.可吸收材料在骨折内固定中的临床应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(4):712-719.
[6] TANG J, HU JF, GUO WC, et al. Research and application of absorbable screw in orthopedics: a clinical review comparing PDLLA screw with metal screw in patients with simple medial malleolus fracture.Chin J Traumatol.2013;16(1):27-30.
[7] PERREN SM. Evolution of the internal fixation of long bone fractures.J Bone Joint Surg Br.2002;84(8):1093-1110.
[8] 刘桂桢.外消旋聚乳酸/多壁碳纳米管复合材料的制备及表征[D].湘潭:湘潭大学,2011.
[9] 刘亚慧,林书玉,郭树琴,等.高强度聚焦超声的原理和应用[J].现代生物医学进展,2008,8(7):1344-1345,1352.
[10] ROCCHIO TM. Resorbable Polymer Pin Inserted with Ultrasound Activated BoneWelding Technique Compared with a Screw for Osteotomy Fixation in the Reverse L Bunion Correction.Clin Podiatr Med Surg.2018;35(4):373-385.
[11] RHA EY, PAIK H, BYEON J. Bioabsorbable plates and screws fixation in mandible fractures: clinical retrospective research during a 10-year period.Ann Plast Surg.2015;74(4):432-436.
[12] REN J, ZHAO P, REN T, et al. Poly (D, L-lactide)/ nano-hydroxyapatite composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering and biocompatibility evaluation.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2008;19(3):1075-1082.
[13] SINIKUMPU J, SERLO W. Biodegradable poly-L-lactide-co- glycolide copolymer pin fixation of a traumatic patellar osteochondral fragment in an 11-year-old child: A novel surgical approach. Exp Ther Med.2017;13(1):242-246.
[14] TAN JS, FOO AT, CHEW WC, et al. Articularly placed interfragmentary screw fixation of difficult condylar fractures of the hand.J Hand Surg.2011;36(4):604-609.
[15] LINTZ F, PUJOL N, PANDEIRADA C, et al. Hybrid fixation: evaluation of a novel technique in adult osteochondritis dissecans of the knee.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011;19(4):568-571.
[16] 赵学寨,李海军,孟彩云,等.可吸收螺钉与金属螺钉内固定修复踝关节骨折:生物相容性及踝关节功能比较[J].中国组织工程研究, 2016,20(31):4687-4692.
[17] BIAN D, ZHOU W, DENG J, et al. Development of magnesium-based biodegradable metals with dietary trace element germanium as orthopaedic implant applications.Acta Biomater.2017;64:421-436.
[18] 魏世成,郑谦,赵宗林.超高分子量聚D,L乳酸小夹板螺钉的组织反应与降解动物实验研究[J].华西口腔医学杂志,1999,17(1): 66-68.
[19] CAMATHIAS C, GÖGÜS U, HIRSCHMANN MT, et al.Implant failure after biodegradable screw fixation in osteochondritis dissecans of the knee in skeletally immature patients. Arthroscopy. 2014;31(3):410-415.
[20] AN J, JIA P, ZHANG Y, et al. Use of biodegradable plates and screws in the treatment of pediatric facial bone fractures. Egypt J Oral Maxillofac Surg.2016;7(3):86-93.
[21] MATSUSUE T, HANAFUSA S, YAMAMURA T, et al. Tissue reaction of bioabsorbable ultra high strength poly (L-Lactide) rod.A long-term study in rabbits.Clin Orthop Relat Res.1995; 317:246-253.
[22] HOOGENBOOM M, EIKELENBOOM D, DEN BROK MH, et al. Mechanical High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound Destruction of Soft Tissue: Working Mechanisms and Physiologic Effects. Ultrasound Med Biol.2015;41(6):1500-1517.
[23] RICHLAND BK, ELLSTROM C, AHMAD A, et al. Resorbable Plates Prevent Regression in Pediatric Mandibular Distraction Osteogenesis.Ann Plast Surg.2017;78:S204-S207.
[24] MCLEOD NMH, GIJN DV. Use of ultrasound-activated resorbable sheets and pins in the management of fractures of the condylar neck of the mandible: a case series.Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg.2018;56(3):182-185.
[25] ABDELGALIL K, LOUKOTA R. Fixation of comminuted diacapitular fractures of the mandibular condyle with ultrasound-activated resorbable screws.Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg.2008;46(6):482-484.
[26] LEE J H, PARK JH. The Clinical Usefulness of Ultrasound-Aided Fixation Using an Absorbable Plate System in Patients with Zygomatico-Maxillary Fracture.Arch Plast Surg. 2013;40(4):330-334.
[27] 陈犹白,张海钟.超声辅助内固定术治疗面中部骨折的疗效分析[J].中华医学杂志,2013,93(18):1418-1421.
[28] NEUMANN H, BREER S, REIMERS N, et al. Osteosynthesis- screw augmentation by ultrasound-activated biopolyme-an ovine in vivo study assessing biocompatibility and bone-to-implant contact. J Orthop Surg Res. 2015;10(1): 18-24.
[29] SCHNEIDER M, SEINIGE C, PILLING E, et al. Ultrasound-aided resorbable osteosynthesis of fractures of the mandibular condylar base: an experimental study in sheep.Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg.2012;50(6):528-532.
[30] MAI R, LAUER G, PILLING E, et al. Bone welding-A histological evaluation in the jaw.Ann Anat.2007;189(4): 350-355.
[31] LANGHOFF JD, KUEMMERLE JM, MAYER J, et al. An Ultrasound Assisted Anchoring Technique (BoneWelding® Technology) for Fixation of Implants to Bone-A Histological Pilot Study in Sheep. Open Orthop J.2009;3(1):40-47.
[32] PILLING E, MAI R, THEISSIG F, et al. An experimental in vivo analysis of the resorption to ultrasound activated pins (Sonic weld) and standard biodegradable screws (ResorbX) in sheep. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg.2007;45(6):447-450.
[33] ARNOLDI J, HENRY P, PROCTER P, et al. In Vivo Tissue Response to Ultrasound Assisted Application of Biodegradable Pins into Cortical and Cancellous Bone Structures: A Histological and Densitometric Analysis in Rabbits. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed.2012;23(5):663-676.
[34] DAVIDSON SR, JAMES DF. Drilling in Bone: Modeling Heat Generation and Temperature Distribution.J Biomech Eng. 2003;125(3):305-314.
[35] 陈蕾,戴红莲,闵玉华.聚乳酸及其复合材料的研究进展[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2005,8(2):45-48.
[36] CARVALHO AC, QUEIROZ TP, OKAMOTO R, et al. Evaluation of bone heating, immediate bone cell viability, and wear of high-resistance drills after the creation of implant osteotomies in rabbit tibias.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2011;26(6):1193-1201.
[37] MEAD RN, RYU J, LIU S, et al. Supraphysiologic temperature enhances cytotoxic effects of bupivacaine on bovine articular chondrocytes in an in vitro study.Arthroscopy. 2012;28(3): 397-404.
[38] NEUMANN H, SCHULZ AP, BREER S, et al. Refixation of Osteochondral Fractures by an Ultrasound-Activated Pin System–An Ovine In Vivo Examination Using CT and Scanning Electron Microscope.Open Orthop J. 2015;9(1): 7-14.
[39] 贺争鸣,邢瑞昌,方喜业,等.论实验动物福利、动物实验与动物实验替代方法[J].实验动物科学,2005,22(1):61-64.
[40] 孙立魁,辛仁东,谢克勤.浅谈医疗器械安全性评价的动物试验替代趋势[J].中国医疗器械信息,2010,16(8):53-54.
|