中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (3): 440-445.doi: 10.12307/2022.073
• 生物材料临床实践 clinical practice of biomaterials • 上一篇 下一篇
踝关节骨折术后踝穴形态变化与踝关节功能的相关因素分析
刘玉波1,张会增1,张同润1,睢更义1,马 楠1,程 旭1,高旭鹏1,许 敬2,王朝亮3
- 1冀中能源邢台矿业集团有限责任公司总医院,河北省邢台市 054000;2邢台市中医院,河北省邢台市 054001;3山东第一医科大学附属济南人民医院,山东省济南市 250014
Correlation analysis between the morphological changes of ankle acupoints and the ankle function after ankle fracture surgery
Liu Yubo1, Zhang Huizeng1, Zhang Tongrun1, Sui Gengyi1, Ma Nan1, Cheng Xu1, Gao Xupeng1, Xu Jing2, Wang Chaoliang3
- 1General Hospital of Jizhong Energy Xingtai Mining Group Co., Ltd., Xingtai 054000, Hebei Province, China; 2Xingtai Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Xingtai 054001, Hebei Province, China; 3Jinan People’s Hospital Affiliated to Shandong First Medical University, Jinan 250014, Shandong Province, China
摘要:

文题释义:
踝穴:是踝关节重要的骨性结构,对维持踝关节的稳定具有重要作用。
Mazur评分:是指一种踝关节功能评分系统,是由Mazur等1979年在《JBJS》杂志发表。
背景:踝关节骨折手术后关节解剖形态的恢复,对关节的活动度和关节功能有极大的影响,以往研究仅仅关注术后踝穴高度恢复情况,因此研究骨折术后踝穴形态变化与功能变化的相关性具有重要意义。
目的:探讨踝关节骨折术后踝穴形态变化与踝关节功能及踝关节活动度之间的相关性,并分析踝关节功能的预后影响因素。
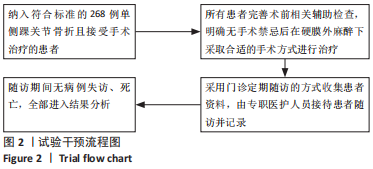
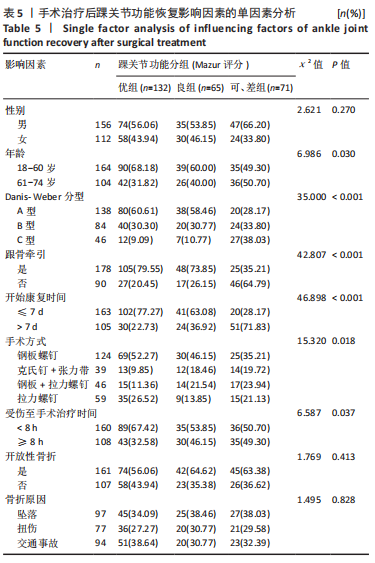
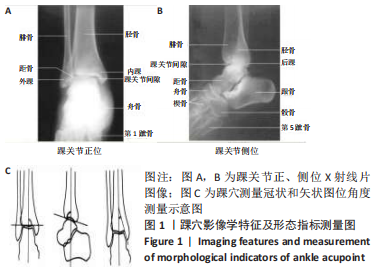
方法:纳入冀中能源邢台矿业集团有限责任公司总医院于2017年1月至2018年12月期间收治的268例单侧踝关节骨折患者,根据Mazur评分法对所有患者患侧踝关节功能进行评分并分组:Mazur评分优(93-100分)132例,良(87-92分)65例,可、差(< 87分)71例。对比不同分组患者末次随访时患侧与健侧踝穴形态相关指标(踝穴宽度、深度、矢状位角度及冠状位角度)之间的差值差异;采用Pearson相关性分析法观察各踝穴形态变化指标与踝关节功能及踝关节活动度之间的相关性,并采用多元有序logistic回归分析影响患者踝关节功能恢复的相关独立危险因素。
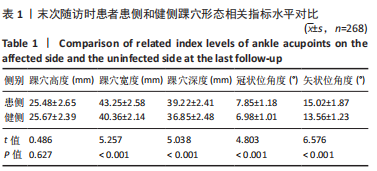
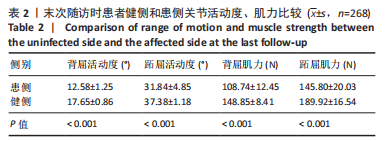
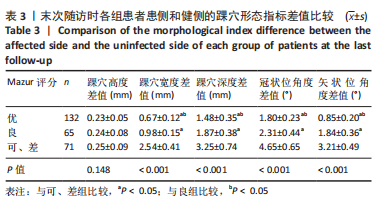
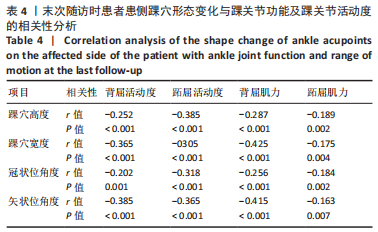
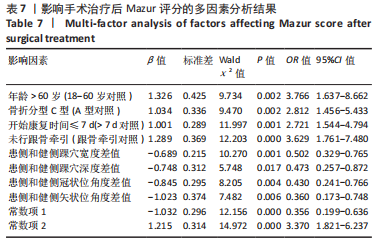
结果与结论:①与健侧比较,患者患侧踝穴宽度、深度以及冠状和矢状位角度均明显增大(P < 0.001),且患者患侧背屈活动度、跖屈活动度以及背屈肌力、跖屈肌力均明显下降(P < 0.001);②末次随访时,Mazur评分优组、良组及可、差组患者患侧和健侧的踝穴宽度、踝穴深度、冠状位角度以及矢状位角度差值之间差异有显著性意义(P < 0.001);③Pearson相关性分析显示,患者患侧踝穴宽度、踝穴深度、冠状位角度、矢状位角度均与背屈活动度、跖屈活动度、背屈肌力、跖屈肌力呈显著负相关性(P < 0.05);④多元有序Logistic回归分析结果显示,年龄> 60岁、骨折分型C型、开始康复时间> 7 d、未行跟骨牵引以及踝穴形态指标(患侧和健侧踝穴宽度、踝穴深度、冠状位角度以及矢状位角度差值大)均为影响踝关节骨折患者手术后功能恢复的独立危险因素,不利于踝关节功能恢复;⑤上述结果证实,踝穴形态变化与踝关节功能及踝关节活动度之间存在负相关性,患者患侧和健侧踝穴宽度、踝穴深度、冠状位角度以及矢状位角度差值增大以及高龄、未做跟骨牵引、康复训练时间晚以及C型骨折为患者膝关节功能下降的独立影响因素,因此临床中需对这类患者引起重视。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0538-4125 (刘玉波) ;https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7735-7137 (王朝亮)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: