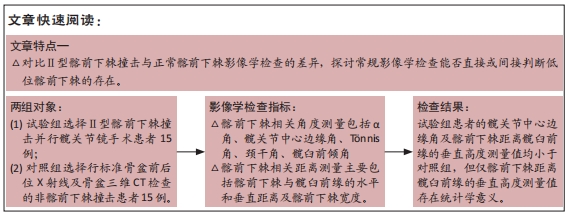
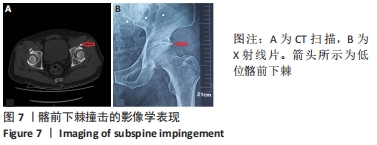
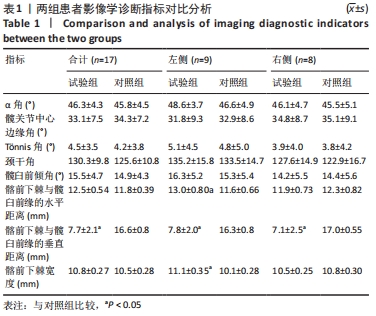
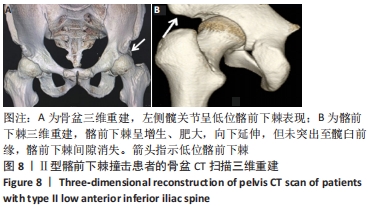
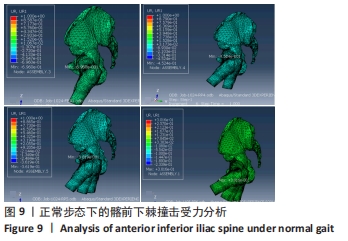
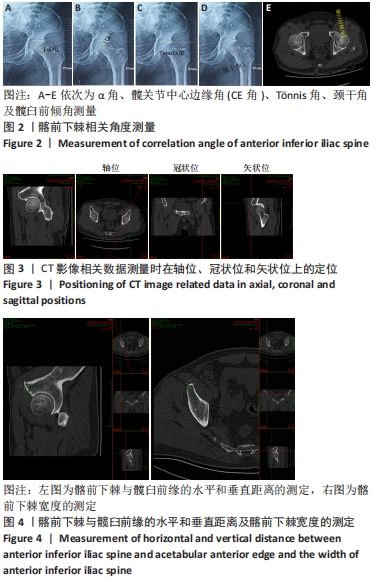
[1] 尚宏喜,张晓丽,王景梅,等.应用Mimics软件测量髋臼形态的数字解剖学研究[J].中国药物与临床,2019,19(5):706-709.
[2] 陈光兴.髋股撞击征的影像学及生物力学三维有限元研究[D].重庆:第三军医大学,2009.
[3] 杨磊,赵卫,何波.髋关节外撞击综合征——髂前下棘撞击综合征研究进展[J].影像研究与医学应用,2019,3(20):1-5.
[4] GANZ R, PARVIZI J, BECK M, et al. Femoroacetabular Impingement: A Cause for Osteoarthritis of the Hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003;417(417): 112-120.
[5] PHILIPPON MJ, MICHALSKI MP, CAMPBELL KJ, et al. An Anatomical Study of the Acetabulum with Clinical Applications to Hip Arthroscopy. JBJS. 2014;96(20):1673-1682.
[6] HETSRONI I, POULTSIDES L, BEDI A, et al. Anterior Inferior Iliac Spine Morphology Correlates With Hip Range of Motion: A Classification System and Dynamic Model. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471(8):2497-2503.
[7] PAN H, KAWANABE K, AKIYAMA H, et al. Operative treatment of hip impingement caused by hypertrophy of the anterior inferior iliac spine. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008;90-B(5):677-679.
[8] SHARFMAN ZT, GRUNDSHTEIN A, PARET M, et al. Surgical Technique: Arthroscopic Osteoplasty of Anterior Inferior Iliac Spine for Femoroacetabular Impingement. Arthrosc Tech. 2016;5(3):e601-e606.
[9] ILIZALITURRI VM JR, ARRIAGA SÁNCHEZ R, SUAREZ-AHEDO C. Arthroscopic Decompression of a Type III Subspine Impingement. Arthrosc Tech. 2016;5(6):e1425-e1431.
[10] 徐桂敏.虚拟环境中的人体运动模式研究与实现[D].武汉:武汉理工大学,2009.
[11] ANDERSON FC, PANDY MG. A Dynamic Optimization Solution for Vertical Jumping in Three Dimensions. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 1999;2(3):201-231.
[12] 范勋健,陈瑱贤,曹卓,等.个体化骨肌多体动力学和有限元联合建模的肩胛骨锁定板生物力学评估方法[J].西安交通大学学报, 2019,53(7):168-176.
[13] 陈肇辉,李忠海,付强,等.腰椎棘突间Coflex动态固定的三维有限元分析[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2010(4):87-91.
[14] 庄建.骶髂复合体稳定性的三维有限元分析及其生物力学意义[D].济南:山东中医药大学,2006.
[15] SZABO BA, BABUSKA IM. Finite Element Analysis. Math Comput. 1991; 60(201):733-739.
[16] NURFAEZAH ZS, ABD LMJ, ABDULL RNR, et al. The Effects of Physiological Biomechanical Loading on Intradiscal Pressure and Annulus Stress in Lumbar Spine: A Finite Element Analysis. J Healthc Eng. 2017;2017:1-8.
[17] 谭山.髋臼上螺钉通道的影像解剖学研究及其固定C1型骨盆骨折生物力学的有限元分析[D].重庆:重庆医科大学,2018.
[18] 童凯,刘宏哲,白浪,等.前后压缩型骨盆损伤的三维有限元模型建立及相关韧带损伤机制分析[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2018,20(3): 217-222.
[19] ISO 14242-3 AMD 1-2019,Implants for surgery - Wear of total hip-joint prostheses - Part 3: Loading and displacement parameters for orbital bearing type wear testing machines and corresponding environmental conditions for test AMENDMENT 1 (First Edition)[S].
[20] SINGH U, WASON SS. Multiaxial orthotic hip joint for squatting and cross-legged sitting with hip-knee-ankle-foot-orthosis. Prosthet Orthot Int. 1988;12(2):101-102.
[21] NURFAEZAH ZS, ABD L MJ, ABDULL RNR, et al. The Effects of Physiological Biomechanical Loading on Intradiscal Pressure and Annulus Stress in Lumbar Spine: A Finite Element Analysis. J Healthc Eng. 2017;2017:1-8.
[22] MORALES-AVALOS R, LEYVA-VILLEGAS JI, SÁNCHEZ-MEJORADA G, et al. A new Morphological Classification of the Anterior Inferior Iliac Spine: Relevance in Subspine Hip Impingement. Int J Morphol. 2015; 33(2):626-631.
[23] 汪方,党瑞山,王秋根,等.髂前下棘的解剖及其在骨盆骨折外固定中的应用[J].解剖学杂志,2008,31(4):567-569.
[24] KARNS MR, ADEYEMI TF, STEPHENS AR, et al. Revisiting the Anteroinferior Iliac Spine: Is the Subspine Pathologic? A Clinical and Radiographic Evaluation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2018;476(7):1494-1502.
[25] AGUILERA-BOHORQUEZ B, BRUGIATTI M, COAQUIRA R, et al. Frequency of Subspine Impingement in Patients With Femoroacetabular Impingement Evaluated With a 3-Dimensional Dynamic Study. Arthroscopy. 2019;35(1):91-96.
[26] SCHINDLER B, BROC R, ADEYEMI T, et al. Comparison of Radiographs and Computed Tomography for the Screening of Anterior Inferior Iliac Spine Impingement. Arthroscopy. 2017;33(4):766-772.
[27] NESTOROVSKI D, WASKO M, FOWLER LM, et al. Prominent Anterior Inferior Iliac Spine Morphologies Are Common in Patients with Acetabular Dysplasia Undergoing Periacetabular Osteotomy. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2021;479(5):991-999.
[28] 张景僚,顾立强,张美超,等.骶髂关节脱位钉板内固定与关节拉力螺钉内固定两种置入方法的三维有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2010,14(13):2329-2332.
[29] KRUEGER DR, WINDLER M, GELEIN M, et al. Is the evaluation of the anterior inferior iliac spine (AIIS) in the AP pelvis possible? Analysis of conventional X-rays and 3D-CT reconstructions. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2017;137(7):975-980.
[30] Balazs GC, Williams BC, Knaus CM, et al. Morphological Distribution of the Anterior Inferior Iliac Spine in Patients With and Without Hip Impingement. Am J Sports Med. 2017:363546516682230.
[31] WONG TT, IGBINOBA Z, BLOOM MC, et al. Anterior Inferior Iliac Spine Morphology: Comparison of Symptomatic Hips With Femoroacetabular Impingement and Asymptomatic Hips. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2019; 212(1):166-172.
[32] 毕丽霞,刘大军,石校伟,等.应用锥形束CT建立单侧上颌骨缺损三维有限元模型的研究[J].中华老年口腔医学杂志,2012,10(6): 347-349,354.
[33] 张海峰,宋翠荣,庞胤,等.基于CT数据建立髋关节三维有限元模型的研究[J].中国临床医学影像杂志,2015(9):65-68.
[34] 贺宇,周东生,邱贵兴,等.四种内固定方式治疗耻骨联合分离生物力学特性的有限元分析[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2017,19(4):317-322.
[35] FEGHHI D, BHARAM S, SHEARIN J. Outcomes After Arthroscopic Management of Subspinous Impingement in Borderline Hip Dysplasia. Orthop J Sports Med. 2018;6(7 suppl4):2325967118S00112.
[36] 魏俊强,潘进社,张英泽,等.髂前下棘的解剖学研究及其在骨盆骨折中的应用[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2010,25(4):309-311.
[37] 张少群,冯梓誉,陈燕萍,等.成年人正常骶髂关节间隙的CT影像解剖学观测及其临床意义[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2019,37(1):14-19.
[38] TABATA T, KAKU N, TAGOMORI H, et al. Influence of hip center position, anterior inferior iliac spine morphology, and ball head diameter on range of motion in total hip arthroplasty. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2019;105(1):23-28.
[39] 刘骞,王万春,姚长海.构建Cam型髋关节撞击综合征有限元模型及力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(40):6513-6518.
[40] HETSRONI I, LARSON CM, TORRE KD, et al. Anterior Inferior Iliac Spine Deformity as an Extra-Articular Source for Hip Impingement: A Series of 10 Patients Treated With Arthroscopic Decompression. Arthroscopy. 2012;28(11):1644-1653.
|