中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (3): 435-439.doi: 10.12307/2022.072
• 骨与关节临床实践 clinical practice of the bone and joint • 上一篇 下一篇
肩胛盂扭转角与退变性肩袖全层撕裂的关系:配对病例对照试验
武亚飞1,2,朱 梁1,任秋健1,2,李大恩1,2,李大地1,2,高绪仁1,郭开今1
- 1徐州医科大学附属医院骨科,江苏省徐州市 221000;2徐州医科大学,江苏省徐州市 221000
Relationship between glenoid version angle and degenerative rotator cuff full-thickness tear: matched case control trial
Wu Yafei1, 2, Zhu Liang1, Ren Qiujian1, 2, Li Daen1, 2, Li Dadi1, 2, Gao Xuren1, Guo Kaijin1
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou 221000, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou 221000, Jiangsu Province, China
摘要:

文题释义:
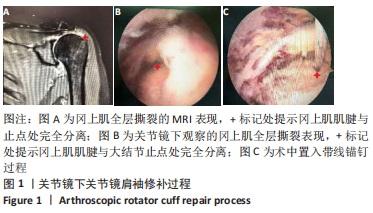
肩袖撕裂:是引起肩关节疼痛和功能障碍的常见原因。肩袖由冈上肌、后方的冈下肌和小圆肌以及前方的肩胛下肌组成,对维持肩关节的稳定和功能起重要作用,治疗的目的是使得肌腱得到最大程度的愈合,若诊断或治疗不及时,常易引起冻结肩、巨大肩袖撕裂等后遗症。
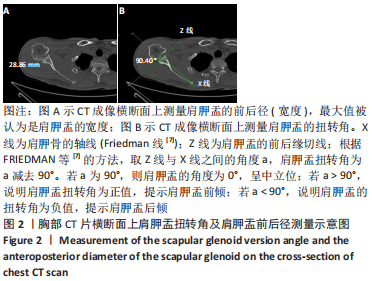
肩胛盂扭转角:表示肩胛盂在横轴位上向前或向后倾斜的程度,分为向前的扭转角(即前倾)和向后的扭转角(即后倾),角度为肩胛盂后缘切线与肩胛骨轴线的夹角减去90°的角度值,正值代表肩胛盂前倾,负值代表后倾,零值代表肩胛盂呈中立位。肩胛盂扭转角对全层肩袖撕裂、肩关节不稳、肩关节假体设计等研究具有重要的参考意义。
背景:肩袖撕裂是引起肩关节疼痛和功能障碍的常见原因,肩胛盂的形态学一直是退变性肩袖撕裂的重要研究课题。
目的:探究肩胛盂扭转角、肩胛盂前后径与退变性肩袖全层撕裂之间的关系。
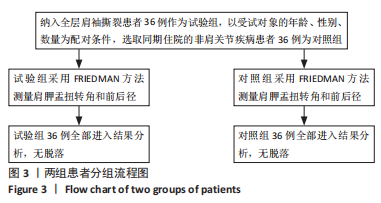
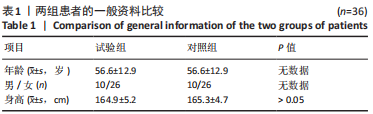
方法:应用配对病例对照研究,选取2020年2月至2021年2月徐州医科大学附属医院收治经MRI及肩关节镜检测确诊为全层肩袖撕裂的患者36例为试验组,以受试对象的年龄、性别、数量为配对条件,选取同期住院的非肩关节疾病的患者36例为对照组。两组患者都在入院时做了胸部CT,并由同一名骨科医师在胸部CT上测得肩胛盂扭转角以及肩胛盂前后径,对两组之间肩胛盂扭转角度的差异性进行统计学分析。
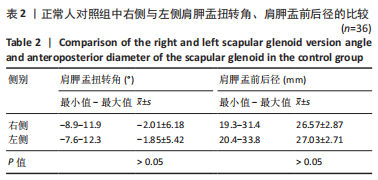
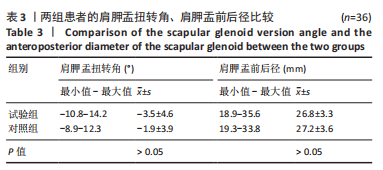
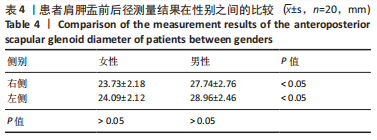
结果与结论:①试验组肩胛盂扭转角为(-3.5±4.6)°,与对照组(-1.9±3.9)°相比,有着更加明显的后倾(P < 0.05);②试验组肩胛盂前后径为(26.8±3.3) mm,对照组肩胛盂前后径为(27.2±3.6) mm,两组间差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);③将对照组肩关节进行左右分组,结果显示左侧肩胛盂扭转角为(-1.85±5.42)°,右侧肩胛盂扭转角为(-2.01±6.18)°,差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);④患者根据性别进行分组时,发现肩胛盂前后径在男性和女性之间差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);⑤提示肩胛盂大小(前后径)与肩袖的全层撕裂不存在显著相关性,但此次研究所发现的肩胛盂大小的特征性、左右肩的一致性以及男女性别之间的差异性,可以为国人肩关节假体的设计提供指导意见。肩胛盂扭转角与肩袖全层撕裂有显著相关性,肩胛盂过度后倾可能是退行性全层肩袖撕裂的危险因素,测定肩胛盂的扭转角度有助于诊断性评估肩袖全层撕裂。
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3411-9192 (武亚飞)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: