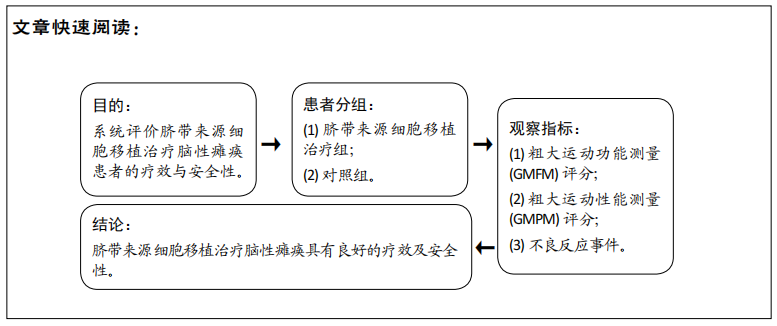
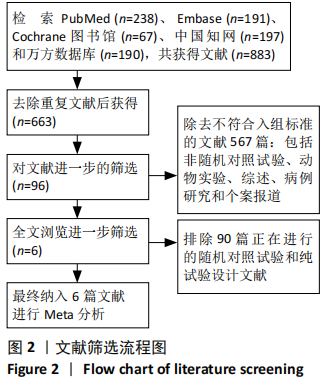
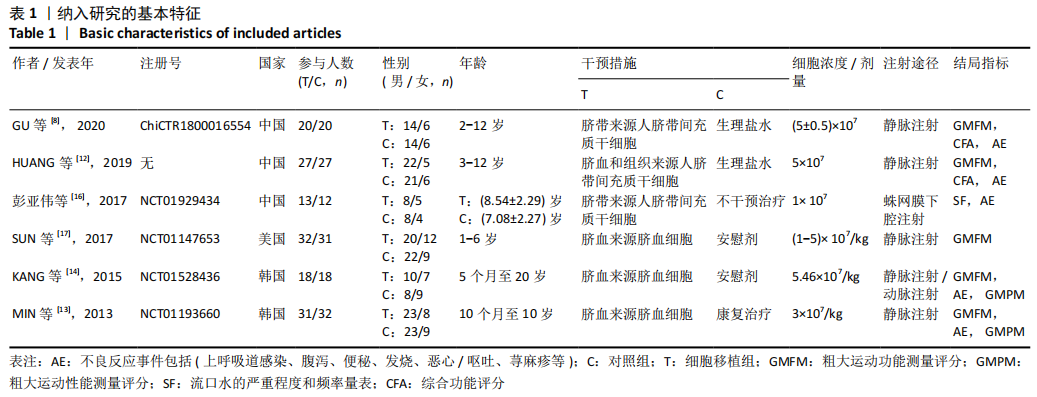
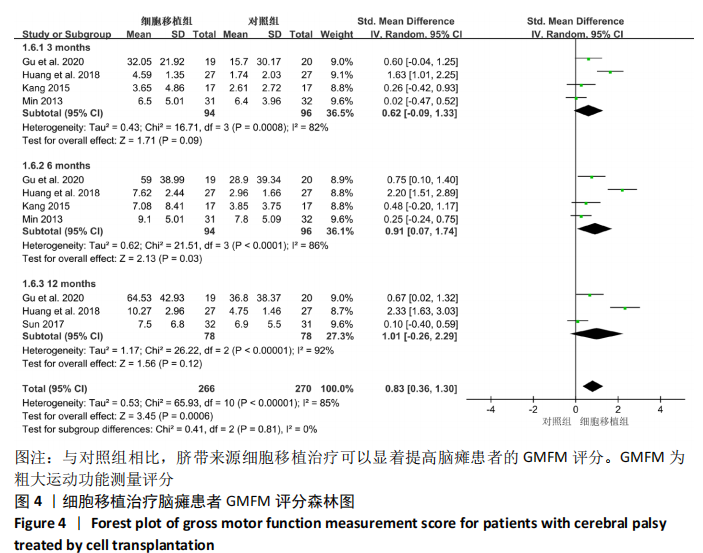
[1] 中国康复医学会儿童康复专业委员会, 中国残疾人康复协会小儿脑瘫康复专业委员会. 小儿脑性瘫痪的定义、分型和诊断条件[J]. 中华物理医学与康复杂志,2007,29(5):309.
[2] 中华医学会儿科学分会康复学组.儿童脑性瘫痪运动障碍的康复建议[J].中华儿科杂志, 2020,58(2):91-95.
[3] 中国康复医学会儿童康复专业委员会,中国残疾人康复协会小儿脑性瘫痪康复专业委员会,编委会中国脑性瘫痪康复指南.中国脑性瘫痪康复指南(2015):第一部分[J].中国康复医学杂志,2015,30(7):747-754.
[4] TOYOKAWA S, MAEDA E, KOBAYASHI Y. Estimation of the number of children with cerebral palsy using nationwide health insurance claims data in Japan. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2017;59(3):317-321.
[5] SELLIER E, SURMAN G, HIMMELMANN K, et al. Trends in prevalence of cerebral palsy in children born with a birthweight of 2,500 g or over in Europe from 1980 to 1998. Eur J Epidemiol. 2010;25(9):635-642.
[6] LIU X, FU X, DAI G, et al. Comparative analysis of curative effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell and bone marrow mononuclear cell transplantation for spastic cerebral palsy. J Transl Med. 2017;15(1):48.
[7] RAH W, LEE Y, MOON J, et al. Neuroregenerative potential of intravenous G-CSF and autologous peripheral blood stem cells in children with cerebral palsy: a randomized, double-blind, cross-over study. J Transl Med. 2017;15(1):16.
[8] GU J, HUANG L, ZHANG C, et al. Therapeutic evidence of umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for cerebral palsy: a randomized, controlled trial. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):43.
[9] 刘梦婷,饶巍,韩兵,等.人脐带间充质干细胞的体外免疫调节特性[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(7):1063-1068.
[10] 孙自敏.脐血移植临床应用30年的回顾及展望[J].器官移植,2020,11(2):199-203.
[11] JIAO Y, LI X Y, LIU J. A New approach to cerebral palsy treatment: discussion of the effective components of umbilical cord blood and its mechanisms of action. Cell Transplant. 2019; 28(5):497-509.
[12] HUANG L, ZHANG C, GU J, et al. A randomized, placebo-controlled trial of human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cell infusion for children with cerebral palsy. Cell Transplant. 2018;27(2):325-334.
[13] MIN K, SONG J, KANG J Y, et al. Umbilical cord blood therapy potentiated with erythropoietin for children with cerebral palsy: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Stem Cells. 2013;31(3):581-591.
[14] KANG M, MIN K, JANG J, et al. Involvement of immune responses in the efficacy of cord blood cell therapy for cerebral palsy. Stem Cells Dev. 2015;24(19):2259-2268.
[15] XIE B, CHEN M, HU R, et al. Therapeutic evidence of human mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for cerebral palsy: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Stem Cells Int. 2020;2020:5701920.
[16] 彭亚伟,王晓东,徐成娥,等.脐带间充质干细胞移植治疗脑瘫患儿流涎症疗效观察[J].武警医学,2017,28(5):478-482.
[17] SUN JM, SONG AW, CASE LE, et al. Effect of autologous cord blood infusion on motor function and brain connectivity in young children with cerebral palsy: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(12):2071-2078.
[18] 谢保城,王清辉,许周媚,等.自体干细胞移植联合血管成形术治疗糖尿病足或肢体缺血性疾病的系统评价[J].中国普通外科杂志,2017,26(12):1589-1598.
[19] EGGENBERGER S, BOUCARD C, SCHOEBERLEIN A, et al. Stem cell treatment and cerebral palsy: Systemic review and meta-analysis. World J Stem Cell. 2019;11(10):891-903.
[20] KOMAN LA, SMITH BP, SHILT JS. Cerebral palsy. Lancet. 2004;363(9421):1619-1631.
[21] WIMALASUNDERA N, STEVENSON V L. Cerebral palsy. Pract Neurol. 2016;16(3):184-194.
[22] SCHIARITI V, SELB M, CIEZA A, et al. International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health Core Sets for children and youth with cerebral palsy: a consensus meeting. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2015;57(2): 149-158.
[23] ALOTAIBI M, LONG T, KENNEDY E, et al. The efficacy of GMFM-88 and GMFM-66 to detect changes in gross motor function in children with cerebral palsy (CP): a literature review. Disabil Rehabil. 2014;36(8):617-627.
[24] WANG X, HU H, HUA R, et al. Effect of umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cells on motor functions of identical twins with cerebral palsy: pilot study on the correlation of efficacy and hereditary factors. Cytotherapy. 2015;17(2): 224-231.
[25] ZHANG C, HUANG L, GU J, et al. Therapy for cerebral palsy by human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal Stem Cells Transplantation combined with basic rehabilitation treatment: a case report. Glob Pediatr Health. 2015.doi:10.11177/2333794X-15574091X.
[26] KO J, KIM M. Inter-rater Reliability of the K-GMFM-88 and the GMPM for Children with Cerebral Palsy. Ann Rehabil Med. 2012;36(2): 233-239.
[27] 王佃亮.脐带间充质干细胞制剂的质量管理及有效性和安全性[J].转化医学杂志,2020, 9(2):65-69.
[28] LIU M, LEI H, DONG P, et al. Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells from the Elderly Exhibit Decreased Migration and Differentiation Abilities with Senescent Properties. Cell Transplant. 2017;26(9):1505-1519.
[29] PACHóN-PEñA G, SERENA C, EJARQUE M, et al. Obesity Determines the Immunophenotypic Profile and Functional Characteristics of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells From Adipose Tissue. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016;5(4):464-475.
[30] XIE B, LUO H, ZHANG Y, et al. Autologous stem cell therapy in critical limb ischemia: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Stem Cells Int. 2018;2018:7528464. |