中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (25): 4025-4031.doi: 10.12307/2021.015
• 干细胞培养与分化 stem cell culture and differentiation • 上一篇 下一篇
超声微泡沉默S100A4基因对胃癌干细胞干性和上皮间质转化的调控
徐桂兰1,宋建生2,杨世疆2
- 1华中科技大学同济医学院附属武汉儿童医院妇幼超声科,湖北省武汉市 430015;2华中科技大学同济医学院附属武汉市中心医院急诊外科,湖北省武汉市 430014
Regulation of S100A4 gene silencing by ultrasound microbubbles on the stemness and epithelial-mesenchymal transformation of gastric cancer stem cells#br#
Xu Guilan1, Song Jiansheng2, Yang Shijiang2
- 1Department of Ultrasonography, Wuhan Children’s Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430015, Hubei Province, China; 2Department of Emergency Surgery, The Central Hospital of Wuhan, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430014, Hubei Province, China 3Fujian Armed Police Corps Hospital, Fuzhou 350003, Fujian Province, China; 4Fujian Provincial Governmental Hospital, Fuzhou 350003, Fujian Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
超声靶向破坏微泡技术:是利用超声介导微泡靶向释放所携带基因,超声波的空化效应可以导致组织细胞膜的通透性增加,从而使目的基因容易进入组织细胞内,增强基因的转染及表达。
S100A4的功能:S100A4属于钙离子结合蛋白S100蛋白家族,该家族成员均可参与细胞骨架及胞膜的相互作用以及钙离子信号传递和细胞的分化等。S100A4在肿瘤中的作用主要表现为促进肿瘤进展,导致肿瘤细胞的侵袭和活动能力增强。
背景:S100A4是钙离子结合蛋白S100家族的一员,可以与相应的靶蛋白结合,进而对肿瘤细胞、多能干细胞的增殖与转移产生重要的影响,近年研究表明超声靶向破坏微泡技术能增强基因转染效率。
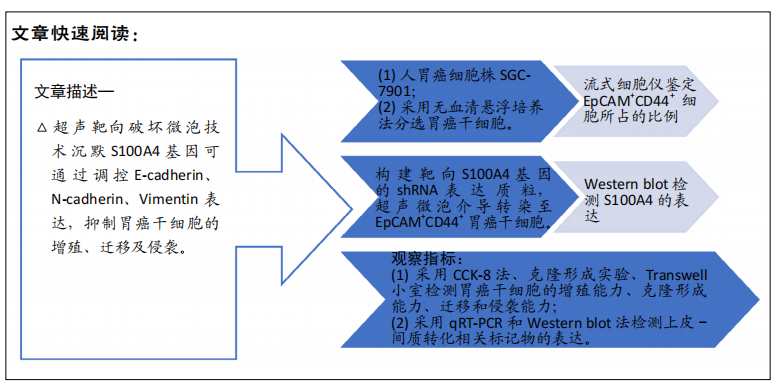
目的:探讨超声靶向破坏微泡技术沉默S100A4基因对胃癌干细胞干性、上皮间质转化的影响。
方法:取对数生长期的人胃癌细胞株SGC-7901,采用无血清悬浮培养法分离肿瘤干细胞球,流式细胞仪检测肿瘤干细胞表面标记EpCAM+CD44+表达。构建靶向S100A4基因的shRNA表达质粒,超声微泡介导转染至EpCAM+CD44+胃癌干细胞。转染后48 h,Western blot检测S100A4的表达;采用CCK-8实验、克隆形成实验、Transwell小室检测胃癌干细胞的增殖、克隆形成、迁移、侵袭能力;采用Western blot与qRT-PCR检测上皮-间质转化相关标记物的表达。
结果与结论:流式细胞仪检测结果显示,在胃癌干细胞富集培养后表达EpCAM+CD44+细胞的比例明显高于富集培养前(P < 0.05)。超声微泡转染S100A4-shRNA质粒48 h后S100A4的蛋白表达量明显低于未转染组(P < 0.01)。转染后48 h,胃癌干细胞的增殖速度、克隆形成能力、迁移、侵袭能力明显下降,上皮标志物E-cadherin表达升高,间质细胞标志物N-cadherin、Vimentin表达降低。结果表明,超声靶向破坏微泡技术沉默S100A4基因可通过调控E-cadherin、N-cadherin、Vimentin表达抑制胃癌干细胞的增殖及克隆形成、迁移、侵袭能力。
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5749-0715(徐桂兰)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号: