[1] PRIETO-ALHAMBRA D, JUDGE A, JAVAID MK, et al. Incidence and risk factors for clinically diagnosed knee, hip and hand osteoarthritis: influences of age, gender and osteoarthritis affecting other joints. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(9):1659-1664.
[2] HUNTER DJ, SCHOFIELD D, CALLANDER E. The individual and socioeconomic impact of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2014; 10(7):437-441.
[3] MARCUS DM. Pharmacologic interventions for knee osteoarthritis. Ann Intern Med. 2015;162(9):672.
[4] INTERNATIONAL ORS. Osteoarthritis: A serious disease. Osteoarthritis Research Society International. 2016:1-103.
[5] RUNCIMAN WB, HUNT TD, HANNAFORD NA, et al. CareTrack: assessing the appropriateness of health care delivery in Australia. Med J Aust. 2012;197(2):100-105.
[6] DA COSTA BR, REICHENBACH S, KELLER N, et al. RETRACTED: Effectiveness of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for the treatment of pain in knee and hip osteoarthritis: a network meta-analysis. Lancet. 2016;387(10033):2093-2105.
[7] SCOTT DL. CHAPTER 70 – Arthritis in the Elderly. Brocklehurst’s Textbook of Geriatric Medicine and Gerontology (SEVENTH EDITION), 2010:566-576.
[8] APPLETON CT. Osteoarthritis year in review 2017: biology. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018;26(3):296-303.
[9] COOPER C, BARDIN T, BRANDI ML, et al. Balancing benefits and risks of glucocorticoids in rheumatic diseases and other inflammatory joint disorders: new insights from emerging data. An expert consensus paper from the European Society for Clinical and Economic Aspects of Osteoporosis and Osteoarthritis (ESCEO). Aging Clin Exp Res. 2016; 28(1):1-16.
[10] MAZZIOTTI G, ANGELI A, BILEZIKIAN JP, et al. Glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis: an update. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2006;17(4):144-149.
[11] CHEVALIER X, RAVAUD P, MAHEU E, et al. Adalimumab in patients with hand osteoarthritis refractory to analgesics and NSAIDs: a randomised, multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74(9):1697-1705.
[12] VAN LAAR M, PERGOLIZZI JV JR, MELLINGHOFF HU, et al. Pain treatment in arthritis-related pain: beyond NSAIDs. Open Rheumatol J. 2012;6:320-330.
[13] LI C, ZOU M, ZHENG Z. Current medication for osteoarthritis. Acta Scientific Orthopaedics. 2018;1:9-12.
[14] LI C, ZHENG Z. What’s the future of osteoarthritis treatment. Acta Scientific Orthopaedics. 2018;1:1-2.
[15] LI C, JIANG J, ZHENG Z, et al. Neural EGFL-Like 1 Is a Downstream Regulator of Runt-Related Transcription Factor 2 in Chondrogenic Differentiation and Maturation. Am J Pathol. 2017;187(5):963-972.
[16] LI CS, ZHANG X, PÉAULT B, et al. Accelerated Chondrogenic Differentiation of Human Perivascular Stem Cells with NELL-1. Tissue Eng Part A. 2016;22(3-4):272-285.
[17] SIU RK, ZARA JN, HOU Y, et al. NELL-1 promotes cartilage regeneration in an in vivo rabbit model. Tissue Eng Part A. 2012;18(3-4):252-261.
[18] LI C, ZHENG Z, HA P, et al. Neural EGFL like 1 as a potential pro-chondrogenic, anti-inflammatory dual-functional disease-modifying osteoarthritis drug. Biomaterials. 2020;226:119541.
[19] LI C, ZHENG Z, JIANG J, et al. Neural EGFL-Like 1 Regulates Cartilage Maturation through Runt-Related Transcription Factor 3-Mediated Indian Hedgehog Signaling. Am J Pathol. 2018;188(2):392-403.
[20] LI C, ZHENG Z, ZHANG X, et al. Nfatc1 Is a Functional Transcriptional Factor Mediating Nell-1-Induced Runx3 Upregulation in Chondrocytes. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(1):168.
[21] MARTEL-PELLETIER J, BARR AJ, CICUTTINI FM, et al. Osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16072.
[22] FU K, ROBBINS SR, MCDOUGALL JJ. Osteoarthritis: the genesis of pain. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2018;57(suppl_4):iv43-iv50.
[23] LOESER RF, COLLINS JA, DIEKMAN BO. Ageing and the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016;12(7):412-420.
[24] HSIA AW, EMAMI AJ, TARKE FD, et al. Osteophytes and fracture calluses share developmental milestones and are diminished by unloading. J Orthop Res. 2018;36(2):699-710.
[25] DEVEZA LA, LOESER RF. Is osteoarthritis one disease or a collection of many? Rheumatology (Oxford). 2018;57(suppl_4):iv34-iv42.
[26] HUNTER DJ, BIERMA-ZEINSTRA S. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2019;393 (10182):1745-1759.
[27] SCANZELLO CR. Role of low-grade inflammation in osteoarthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2017;29(1):79-85.
[28] BIERMA-ZEINSTRA SM, VAN MIDDELKOOP M. Osteoarthritis: In search of phenotypes. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2017;13(12):705-706.
[29] COURTIES A, SELLAM J, BERENBAUM F. Metabolic syndrome-associated osteoarthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2017;29(2):214-222.
[30] JEON OH, KIM C, LABERGE RM, et al. Local clearance of senescent cells attenuates the development of post-traumatic osteoarthritis and creates a pro-regenerative environment. Nat Med. 2017;23(6):775-781.
[31] AKKIRAJU H, NOHE A. Role of Chondrocytes in Cartilage Formation, Progression of Osteoarthritis and Cartilage Regeneration. J Dev Biol. 2015;3(4):177-192.
[32] LEE M, SIU RK, TING K, et al. Effect of Nell-1 delivery on chondrocyte proliferation and cartilaginous extracellular matrix deposition. Tissue Eng Part A. 2010;16(5):1791-1800.
[33] WANG C, HOU W, GUO X, et al. Two-phase electrospinning to incorporate growth factors loaded chitosan nanoparticles into electrospun fibrous scaffolds for bioactivity retention and cartilage regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;79:507-515.
[34] LI W, ZARA JN, SIU RK, et al. Nell-1 enhances bone regeneration in a rat critical-sized femoral segmental defect model. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2011;127(2):580-587.
[35] SIU RK, LU SS, LI W, et al. Nell-1 protein promotes bone formation in a sheep spinal fusion model. Tissue Eng Part A. 2011;17(7-8):1123-1135.
[36] ZHU S, ZHANG B, MAN C, et al. NEL-like molecule-1-modified bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells/poly lactic-co-glycolic acid composite improves repair of large osteochondral defects in mandibular condyle. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2011;19(6):743-750.
[37] OEGEMA TR JR, CARPENTER RJ, HOFMEISTER F, et al. The interaction of the zone of calcified cartilage and subchondral bone in osteoarthritis. Microsc Res Tech. 1997;37(4):324-332.
[38] LI W, LEE M, WHANG J, et al. Delivery of lyophilized Nell-1 in a rat spinal fusion model. Tissue Eng Part A. 2010;16(9):2861-2870.
[39] PAN J, ZHOU X, LI W, et al. In situ measurement of transport between subchondral bone and articular cartilage. J Orthop Res. 2009;27(10): 1347-1352.
[40] QI H, KIM JK, HA P, et al. Inactivation of Nell-1 in Chondrocytes Significantly Impedes Appendicular Skeletogenesis. J Bone Miner Res. 2019;34(3):533-546.
[41] DESAI J, SHANNON ME, JOHNSON MD, et al. Nell1-deficient mice have reduced expression of extracellular matrix proteins causing cranial and vertebral defects. Hum Mol Genet. 2006;15(8):1329-1341.
[42] KIM EJ, CHO SW, SHIN JO, et al. Ihh and Runx2/Runx3 signaling interact to coordinate early chondrogenesis: a mouse model. PLoS One. 2013; 8(2):e55296.
[43] KIM IS, OTTO F, ZABEL B, et al. Regulation of chondrocyte differentiation by Cbfa1. Mech Dev. 1999;80(2):159-170.
[44] YOSHIDA CA, YAMAMOTO H, FUJITA T, et al. Runx2 and Runx3 are essential for chondrocyte maturation, and Runx2 regulates limb growth through induction of Indian hedgehog. Genes Dev. 2004;18(8):952-963.
[45] CHEN H, GHORI-JAVED FY, RASHID H, et al. Runx2 regulates endochondral ossification through control of chondrocyte proliferation and differentiation. J Bone Miner Res. 2014;29(12):2653-2665.
[46] WIGNER NA, SOUNG DO Y, EINHORN TA, et al. Functional role of Runx3 in the regulation of aggrecan expression during cartilage development. J Cell Physiol. 2013;228(11):2232-2242.
[47] CHEN W, ZHANG X, SIU RK, et al. Nfatc2 is a primary response gene of Nell-1 regulating chondrogenesis in ATDC5 cells. J Bone Miner Res. 2011;26(6):1230-1241.
[48] SOKOLOVE J, LEPUS CM. Role of inflammation in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis: latest findings and interpretations. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2013;5(2):77-94.
[49] PEARSON MJ, HERNDLER-BRANDSTETTER D, TARIQ MA, et al. IL-6 secretion in osteoarthritis patients is mediated by chondrocyte-synovial fibroblast cross-talk and is enhanced by obesity. Sci Rep. 2017; 7(1):3451.
[50] GOLDRING MB, OTERO M. Inflammation in osteoarthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2011;23(5):471-478.
[51] WANG M, SAMPSON ER, JIN H, et al. MMP13 is a critical target gene during the progression of osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013;15(1):R5.
[52] ALLEN KD, ADAMS SB JR, MATA BA, et al. Gait and behavior in an IL1β-mediated model of rat knee arthritis and effects of an IL1 antagonist. J Orthop Res. 2011;29(5):694-703.
[53] SHEN J, JAMES AW, ZARA JN, et al. BMP2-induced inflammation can be suppressed by the osteoinductive growth factor NELL-1. Tissue Eng Part A. 2013;19(21-22):2390-2401.
[54] JAMES AW, SHEN J, ZHANG X, et al. NELL-1 in the treatment of osteoporotic bone loss. Nat Commun. 2015;6:7362.
[55] Beier F. NFATs are good for your cartilage! Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2014;22(7):893-895.
[56] WANG J, GARDNER BM, LU Q, et al. Transcription factor Nfat1 deficiency causes osteoarthritis through dysfunction of adult articular chondrocytes. J Pathol. 2009;219(2):163-172.
[57] YOO SA, PARK BH, YOON HJ, et al. Calcineurin modulates the catabolic and anabolic activity of chondrocytes and participates in the progression of experimental osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56(7):2299-2311.
[58] MICLEA RL, SIEBELT M, FINOS L, et al. Inhibition of Gsk3β in cartilage induces osteoarthritic features through activation of the canonical Wnt signaling pathway. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2011;19(11):1363-1372.
[59] YAYKASLI KO, OOHASHI T, HIROHATA S, et al. ADAMTS9 activation by interleukin 1 beta via NFATc1 in OUMS-27 chondrosarcoma cells and in human chondrocytes. Mol Cell Biochem. 2009;323(1-2):69-79.
[60] GREENBLATT MB, RITTER SY, WRIGHT J, et al. NFATc1 and NFATc2 repress spontaneous osteoarthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013; 110(49):19914-19919.
[61] AINI H, ITAKA K, FUJISAWA A, et al. Messenger RNA delivery of a cartilage-anabolic transcription factor as a disease-modifying strategy for osteoarthritis treatment. Sci Rep. 2016;6:18743.
[62] KWAK JH, ZHANG Y, PARK J, et al. Pharmacokinetics and osteogenic potential of PEGylated NELL-1 in vivo after systemic administration. Biomaterials. 2015;57:73-83.
[63] VIMALRAJ S, ARUMUGAM B, MIRANDA PJ, et al. Runx2: Structure, function, and phosphorylation in osteoblast differentiation. Int J Biol Macromol. 2015;78:202-208.
[64] SHEN J, JAMES AW, ZHANG X, et al. Novel Wnt Regulator NEL-Like Molecule-1 Antagonizes Adipogenesis and Augments Osteogenesis Induced by Bone Morphogenetic Protein 2. Am J Pathol. 2016;186(2):419-434.
[65] GREGORY MH, CAPITO N, KUROKI K, et al. A review of translational animal models for knee osteoarthritis. Arthritis. 2012;2012:764621.
[66] KUYINU EL, NARAYANAN G, NAIR LS, et al. Animal models of osteoarthritis: classification, update, and measurement of outcomes. J Orthop Surg Res. 2016;11:19.
[67] PUNZI L, GALOZZI P, LUISETTO R, et al. Post-traumatic arthritis: overview on pathogenic mechanisms and role of inflammation. RMD Open. 2016;2(2):e000279.
[68] PROFFEN BL, MCELFRESH M, FLEMING BC, et al. A comparative anatomical study of the human knee and six animal species. Knee. 2012;19(4):493-499.
[69] LI C, ZHENG Z, HA P, et al. Neurexin Superfamily Cell Membrane Receptor Contactin-Associated Protein Like-4 (Cntnap4) Is Involved in Neural EGFL-Like 1 (Nell-1)-Responsive Osteogenesis. J Bone Miner Res. 2018;33(10):1813-1825.
[70] LEE YH, BAE SC, KIM JH, et al. Meta-analysis of SLC22A4 and RUNX1 polymorphisms : Associations with rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility. Z Rheumatol. 2015;74(4):351-358.
[71] BRANDT KD, RADIN EL, DIEPPE PA, et al. Yet more evidence that osteoarthritis is not a cartilage disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006;65(10): 1261-1264.
[72] ZHANG X, ZARA J, SIU RK, et al. The role of NELL-1, a growth factor associated with craniosynostosis, in promoting bone regeneration. Version 2. J Dent Res. 2010;89(9):865-878.
[73] ZHANG J, CHEN Y, XU J, et al. Tissue engineering using 3D printed nano-bioactive glass loaded with NELL1 gene for repairing alveolar bone defects. Regen Biomater. 2018;5(4):213-220.
[74] LEE S, ZHANG X, SHEN J, et al. Brief Report: Human Perivascular Stem Cells and Nel-Like Protein-1 Synergistically Enhance Spinal Fusion in Osteoporotic Rats. Stem Cells. 2015;33(10):3158-3163.
[75] JAMES AW, SHEN J, TSUEI R, et al. NELL-1 induces Sca-1+ mesenchymal progenitor cell expansion in models of bone maintenance and repair. JCI Insight. 2017;2(12):e92573.
[76] JAMES AW, LACHAUD G, SHEN J, et al. A Review of the Clinical Side Effects of Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2016; 22(4):284-297.
[77] PAKVASA M, ALVERDY A, MOSTAFA S, et al. Neural EGF-like protein 1 (NELL-1): Signaling crosstalk in mesenchymal stem cells and applications in regenerative medicine. Version 2. Genes Dis. 2017;4(3):127-137.
[78] FAHMY-GARCIA S, VAN DRIEL M, WITTE-BUOMA J, et al. NELL-1, HMGB1, and CCN2 Enhance Migration and Vasculogenesis, But Not Osteogenic Differentiation Compared to BMP2. Tissue Eng Part A. 2018;24(3-4):207-218.
[79] GAO C, ZHANG Q, KONG D, et al. MALDI-TOF Mass Array Analysis of Nell-1 Promoter Methylation Patterns in Human Gastric Cancer. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:136941.
[80] WANG Z, KAMBHAMPATI S, CHENG Y, et al. Methylation Biomarker Panel Performance in EsophaCap Cytology Samples for Diagnosing Barrett’s Esophagus: A Prospective Validation Study. Clin Cancer Res. 2019;25(7):2127-2135.
[81] SLOVAK ML, BEDELL V, HSU YH, et al. Molecular karyotypes of Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells at disease onset reveal distinct copy number alterations in chemosensitive versus refractory Hodgkin lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17(10):3443-3454.
[82] NAKAMURA R, OYAMA T, TAJIRI R, et al. Expression and regulatory effects on cancer cell behavior of NELL1 and NELL2 in human renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2015;106(5):656-664.
[83] TOMBOLAN L, POLI E, MARTINI P, et al. NELL1, whose high expression correlates with negative outcomes, has different methylation patterns in alveolar and embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma. Oncotarget. 2017;8(20):33086-33099.
[84] SHEN J, LACHAUD G, KHADARIAN K, et al. NELL-1 expression in benign and malignant bone tumors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015; 460(2):368-374.
[85] SHEN J, LACHAUD G, SHRESTHA S, et al. NELL-1 expression in tumors of cartilage. J Orthop. 2015;12(Suppl 2):S223-229.
[86] ZHAI Y, WEI R, SHA S, et al. Effect of NELL1 on lung cancer stem‑like cell differentiation. Oncol Rep. 2019;41(3):1817-1826.
[87] MATHIEU F, ETAIN B, DIZIER MH, et al. Genetics of emotional reactivity in bipolar disorders. J Affect Disord. 2015;188:101-106.
[88] LIN E, KUO PH, LIU YL, et al. A Deep Learning Approach for Predicting Antidepressant Response in Major Depression Using Clinical and Genetic Biomarkers. Front Psychiatry. 2018;9:290.
|
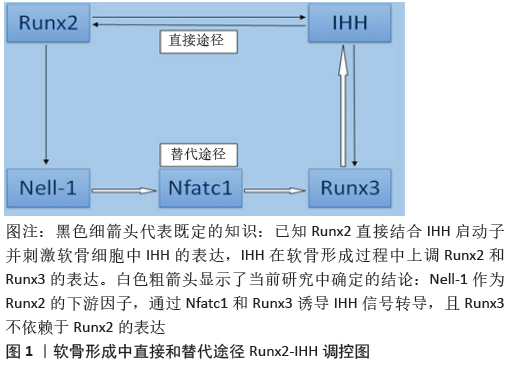
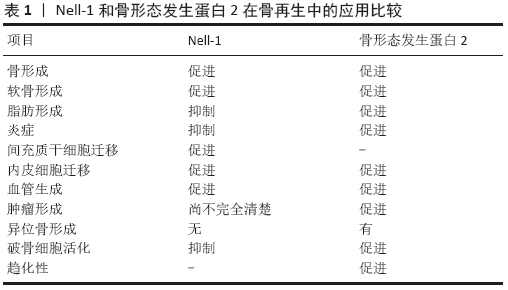
 文题释义:
文题释义: