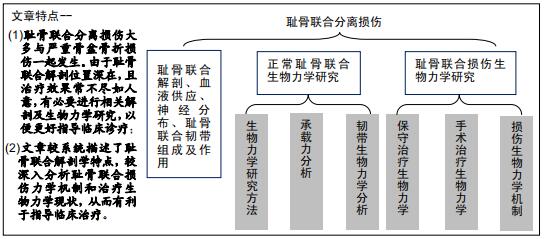
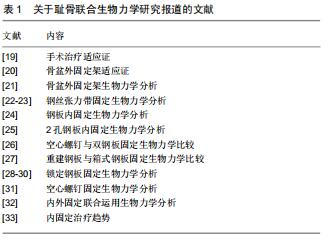
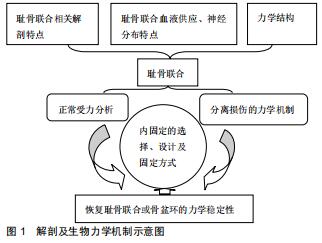
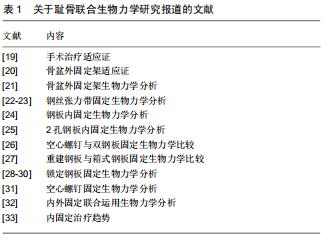
|
[1] WALHEIM G, LERUD S, IBBE T. mobility of the pubic symphysis. Measurements by an electromechanical method. Acta Orthop Scand. 1984;55(2):203-208.
[2] GARRAS DN, CAROTHERS JT, OLSON SA. Single-leg-stance (flamingo) radiographs to assess pelvic instability: how much motion is normal? J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90(10):2114-2118.
[3] AGGARWAL S, BALI K, KRISHNAN V, et al. Management outcomes in pubic diastasis:our experience with 19 patients. J Orthop Surg Res. 2011;(6):21.
[4] PUTNIS SE, PEARCE R, WALI UJ, et al. Open reduction and internal fixation of a traumatic diastasis of the pubic symphysis: one-year radiological and functional outcomes. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011; 3(1):78-84.
[5] WANG W, HAYAMI T, KAPILA S. Female hormone receptors are differentially expressed in mouse fibrocartilages. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2009;17(5):646-654.
[6] PIRES R, LABRONICI PJ, GIORDANO V, et al. Intrapartum pubic symphysis Disruption. Ann Med Health Sci Res. 2015;5(6):476.
[7] BAHLMANN F, MERZ E, MACCHIELLA D, et al. Ultrasound imaging of the symphysis fissure for evaluating damage to the symphysis in pregnancy and postpartum. Z Geburtshilfe Perinatol. 1993;197(1):27-30.
[8] BECKER I, WOODLEY SJ, STRINGER MD. The adult human pubic symphysis: a systematic review. J Anat. 2010;217(5):475-487.
[9] GARCIA JM, DOBLARE M, SERAL B, et al. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of several internal and external pelvis fixations. J Biomech Eng. 2000;122(5):516-522.
[10] KIAPOUR A, JOUKAR A, ELGAFY H, et al. Biomechanics of the sacroiliac joint: anatomy, function, biomechanics, sexual dimorphism, and causes of pain. Int J Spine Surg. 2020;14(Suppl 1):3-13.
[11] MEISSNER A, FELL M, WILK R, et al. Biomechanics of the pubic symphysis.Which forces lead to mobility of the symphysis in physiological conditions? Unfallchirurg. 1996;99(6):415-421.
[12] STEINITZ D, GUY P, PASSARIELLO A, et al. All superior pubic ramus fractures are not created equal. Can J Surg. 2004;47(6):422-425.
[13] SIMONIAN PT, ROUTT ML JR, HARRINGTON RM, et al. The acetabular T-type fracture. A biomechanical evaluation of internal fixation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1995;(314):234-240.
[14] 张少群,任茹霞,陈奕历,等.骶髂关节周围各韧带对骶髂关节稳定性的影响[J].医用生物力学,2019,34(5):500-506.
[15] HEFZY MS, EBRAHEIM N, MEKHAIL A, et al. Kinematics of the human pelvis following open book injury. Med Eng Phys. 2003;25(4):259-274.
[16] LI Z, KIM JE, DAVIDSON JS, et al. Biomechanical response of the pubic symphysis in lateral pelvic impacts:a finite element study. J Biomech. 2007;40 (12):2758-2766.
[17] EE CC, MANHEIMER E, PIROTTA MV, et al. Acupuncture for pelvicand back pain in pregnancy: a systematic review. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2008;198(3):254-259.
[18] TILE M. Acute pelvic fractures:I. causation and classification. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 1996;4(3):143-151.
[19] MU WD, WANG H, ZHOU DS, et al. Computer navigated percutaneous screw fixation for traumatic pubic symphysis diastasis of unstable pelvic ring injuries. Chin Med J (Engl). 2009;122(14):1699-1703.
[20] SCAGLIONE M, PARCHI P, DIGRANDI G, et al. External fixation in pelvic fractures. Musculoskeletal Surg, 2010;94(2):63-70.
[21] PONSEN K, JOOSSE P, VAN DIJKE GA, et al. External fxation of the pelvic ring:an experimental study on the role of pin diameter, pin position,and parasymphyseal fxator pins.Acta Orthop. 2007;78(5): 648-653.
[22] VARGA E, HEARN T, POWELL J, et al. Effects of method of internal fixation of symphyseal disruptions on stability of the pelvic ring.Injury. 1995;26(2):75-80.
[23] STUART PR, TALBOT D, MILNE DD. Internal fixation of pubic symphysis diastasis with a tension banding technique. Injury. 1990;21(4):223-224.
[24] CANO LP, GIRALDEZ SANCHEZ MA, MARTNEZ RJ, et al. Biomechanical analysis of a new minimally invasive system for osteosynthesis of pubis symphysis disruption.Injury. 2012;43:20-27.
[25] SAGI HC, PAPP S. Comparative radiographic and clinical outcome of two-hole and multi-hole symphyseal plating. J Orthop Trauma. 2008; 22(6):373-378.
[26] FENG Y, YU H, QIAN H, et al. Comparison of biomechanical characteristics and pelvic ring stability vsing different fixation methods to treat pubic symphysis diastasis: a finite element study. Medicine. 2015;94(49):2207.
[27] SIMONIAN PT, ROUTT ML, HARRINGTON RM, et al. Box plate fxation of the symphysis pubis: biomechanical evaluation of a new technique. J Orthop Trauma. 1994;8(6):483-489.
[28] LUJAN TJ, HENDERSON CE, MADEY SM, et al. Locked plating of distal femur fractures leads to inconsistent and asymmetric callus formation. J Orthop Trauma. 2010;24(3):156-162.
[29] 简争光,许运,史勇,等.锁定钢板固定修复侧方压缩旋转不稳骨盆环损伤:骨盆稳定性重建[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(48):7776-7783.
[30] PRASARN ML, ZYCH G, GASKI G. Biomechanical study of 4-hole pubic symphyseal plating: locked versus unlocked constructs. Orthopedics. 2012;35(7):1028-1032.
[31] 余可和.骨盆前环解剖研究及前环损伤空心螺钉与重建钢板治疗的有限元分析[D].济南:山东大学.2015:38.
[32] PARK M, YOON S, CHOI S, et al. Is there a clinical benefit of additional tension band wiring in plate fixation of the symphysis? BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders. 2017;18(1):40.
[33] 马坤龙,朱磊,方跃.耻骨联合分离的治疗进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2014,28(2):250-254.
|