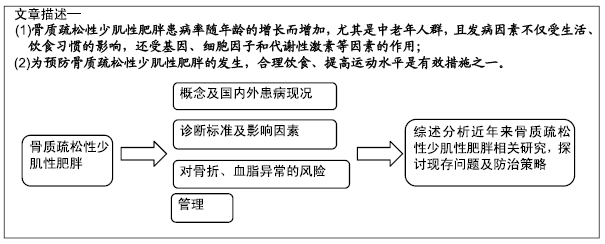
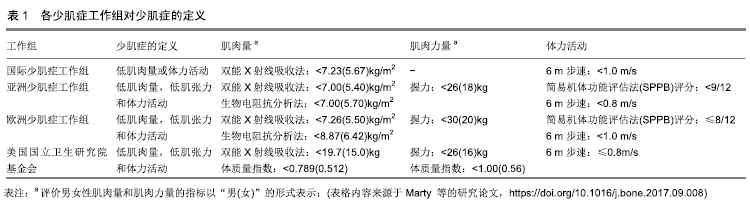
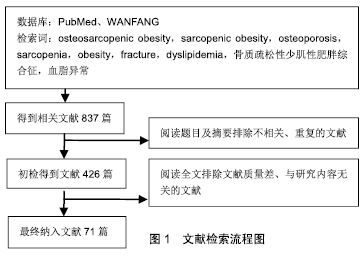
[1] ORMSBEE MJ, PRADO CM, ILICH JZ, et al. Osteosarcopenic obesity: the role of bone, muscle, and fat on health. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle.2014;5(3):183-192.
[2] SØGAARD AJ, HOLVIK K, OMSLAND TK, et al. Abdominal obesity increases the risk of hip fracture. A population-based study of 43,000 women and men aged 60-79 years followed for 8 years. Cohort of Norway. J Intern Med.2015;277(3):306-317.
[3] MO D, HSIEH P, YU H, et al. Osteosarcopenic obesity and its relationship with dyslipidemia in women from different ethnic groups of China. Arch Osteoporos.2018;13(1):65.
[4] ILICH JZ, INGLIS JE, KELLY OJ, et al. Osteosarcopenic obesity is associated with reduced handgrip strength, walking abilities, and balance in postmenopausal women [J].Osteoporos Int,2015,26 (11): 2587-2595.
[5] SZLEJF C, PARRA-RODRÍGUEZ L, ROSAS-CARRASCO O. Osteosarcopenic Obesity: Prevalence and Relation With Frailty and Physical Performance in Middle-Aged and Older Women.J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2017;18(8):733.e1-733.e5.
[6] KIM J, LEE Y, KYE S,et al.Association of serum vitamin D with osteosarcopenic obesity: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2008-2010. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2017;8(2):259-266.
[7] ENSRUD KE,CRANDALL CJ.Osteoporosis. Ann Intern Med.2017;167 (3):ITC17-ITC32.
[8] THE WHO STUDY GROUP. Assessment of fracture risk and its application to screening for postmenopausal osteoporosisGeneva: WHO.1994.
[9] Oliveros E, Somers VK, Sochor O, et al. The concept of normal weight obesity. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2014;56(4):426-433.
[10] HUNG SP, CHEN CY, GUO FR, et al. Combine body mass index and body fat percentage measures to improve the accuracy of obesity screening in young adults.Obes Res Clin Pract.2017;11(1): 11 -18.
[11] MCCARTHY HD, ASHWELL M.A study of central fatness using waist- to-height ratios in UK children and adolescents over two decades supports the simple message--'keep your waist circumference to less than half your height'.Int J Obes (Lond).2006;30(6):988-992.
[12] BACOPOULOU F, EFTHYMIOU V, LANDIS G, et al.Waist circumference, waist-to-hip ratio and waist-to-height ratio reference percentiles for abdominal obesity among Greek adolescents.BMC Pediatr.2015;15(1):50.
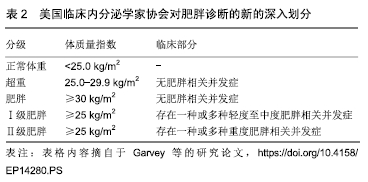
[13] GARVEY WT, GARBER AJ, MECHANICK JI, et al. American association of clinical endocrinologists and american college of endocrinology position statement on the 2014 advanced framework for a new diagnosis of obesity as a chronic disease. Endocr Pract.2014; 20(9):977-989.
[14] BIJELIC R, MILICEVIC S, BALABAN J. Risk Factors for Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women. Med Arch. 2017;71(1):25-28.
[15] ZHANG X,YU Z,YU M,et al.Alcohol consumption and hip fracture risk.Osteoporos Int. 2015;26(2):531-542.
[16] LI S, DAI Z, WU Q. Effect of coffee intake on hip fracture: a meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies.Nutr J.2015;14(1): 38.
[17] HOFBAUER LC, GORI F, RIGGS BL, et al.Stimulation of Osteoprotegerin Ligand and Inhibition of Osteoprotegerin Production by Glucocorticoids in Human Osteoblastic Lineage Cells: Potential Paracrine Mechanisms of Glucocorticoid- Induced Osteoporosis. Endocrinology. 1999;140(10):4382-4389.
[18] FRANCIOSI LG, PAGE CP, CELLI BR, et al. Markers of disease severity in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Pulm Pharmacol Ther.2006;19(3):189–199.
[19] RIVADENEIRA F, MÄKITIE O. Osteoporosis and Bone Mass Disorders: From Gene Pathways to Treatments. Trends Endocrinol Metab.2016; 27(5):262-281.
[20] GONG Y, SLEE RB,FUKAI N, et al. LDL receptor-related protein 5 (LRP5) affects bone accrual and eye development.Cell.2001;107(4):513-523.
[21] SZULC P,DELMAS PD.Biochemical markers of bone turnover: potential use in the investigation and management of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int.2008;19(12):1683- 1704.
[22] DREY M, KRIEGER B, SIEBER CC, et al. Motoneuron loss is associated with sarcopenia.J Am Med Dir Assoc.2014;15(6): 435-439.
[23] PERRINI S,LAVIOLA L,CARREIRA MC,et al.The GH/IGF1 axis and signaling pathways in the muscle and bone: mechanisms underlying age-related skeletal muscle wasting and osteoporosis.J Endocrinol. 2010;205(3):201-210.
[24] LI M, LI C,PARKHOUSE WS.Age-related differences in the des IGF-I-mediated activation of Akt-1 and p70 S6K in mouse skeletal muscle.Mech Ageing Dev.2003;124(7):771-778.
[25] MENG SJ,YU LJ.Oxidative stress, molecular inflammation and sarcopenia.Int J Mol Sci.2010;11(4):1509-1526.
[26] KARASIK D. How pleiotropic genetics of the musculoskeletal system can inform genomics and phenomics of aging. Age (Dordr).2011;33(1): 49-62.
[27] TRAMONTANO A, VERONESE N, SERGI G, et al.Prevalence of sarcopenia and associated factors in the healthy older adults of the Peruvian Andes. Arch Gerontol Geriatr.2017;68:49-54.
[28] CLARK DJ, PATTEN C, REID KF, et al.Impaired voluntary neuromuscular activation limits muscle power in mobility-limited older adults.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci.2010;65(5):495- 502.
[29] BIJLSMA AY, MESKERS CG, LING CH, et al.Defining sarcopenia: the impact of different diagnostic criteria on the prevalence of sarcopenia in a large middle aged cohort.Age (Dordr).2013; 35(3):871-881.
[30] LLOYD BD, WILLIAMSON DA, SINGH NA, et al.Recurrent and injurious falls in the year following hip fracture: a prospective study of incidence and risk factors from the Sarcopenia and Hip Fracture study.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci.2009;64(5): 599-609.
[31] SAMSON MM, MEEUWSEN IB, CROWE A, et al. Relationships between physical performance measures, age, height and body weight in healthy adults.Age Ageing.2000;29(3):235-242.
[32] LOWE DA, BALTGALVIS KA,GREISING SM.Mechanisms behind estrogen's beneficial effect on muscle strength in females. Exerc Sport Sci Rev.2010;38(2):61-67.
[33] EL-KASSAS G, ZIADE F.Exploration of the Risk Factors of Generalized and Central Obesity among Adolescents in North Lebanon.J Environ Public Health.2017;2017:1-13.
[34] FRASER LK, CLARKE GP, CADE JE, et al.Fast food and obesity: a spatial analysis in a large United Kingdom population of children aged 13-15.Am J Prev Med.2012;42(5):e77-85.
[35] MOZAFFARIAN D, HAO T, RIMM EB, et al.Changes in diet and lifestyle and long-term weight gain in women and men.N Engl J Med. 2011;364(25):2392–2404.
[36] PARRA-ROJAS I, DEL MORAL-HERNA´NDEZ O, SALGADO- BERNABE´ AB, et al. Adenovirus-36 seropositivity and its relation with obesity and metabolic profile in children.Int J Endocrinol.2013; 2013(10): 463194.
[37] ALMGREN M, ATKINSON R, HE J, et al. Adenovirus-36 is associated with obesity in children and adults in Sweden as determined by rapid ELISA.PloS One.2012;7(7):e41652.
[38] SANMIGUEL C, GUPTA A, MAYER EA. Gut Microbiome and Obesity: A Plausible Explanation for Obesity.Curr Obes Rep.2015;4(2): 250-261.
[39] SINGH RK, KUMAR P, MAHALINGAM K. Molecular genetics of human obesity: A comprehensive review.C R Biol.2017;340(2): 87-108.
[40] MCNULTY JC, JACKSON PJ,THOMPSON DA,et al.Structures of the agouti signaling protein.J Mol Biol.2005;346(4):1059-1070.
[41] PETSCHOW B, DORE J, HIBBERD P, et al. Probiotics, prebiotics, and the host microbiome: the science of translation.Ann N Y Acad Sci.2013; 1306(1):1-17.
[42] GASKINS HR, COLLIER CT, Anderson DB. Antibiotics as growth promotants: mode of action [J].Anim Biotechnol,2002,13(1): 29-42.
[43] PREMAOR MO, PILBROW L, TONKIN C, et al.Obesity and fractures in post- menopausal women.J Bone Miner Res.2010;25(2):292-297.
[44] PREMAOR MO, COMIM FV, COMPSTON JE.Obesity and fractures. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol.2014;58(5):470-477.
[45] LANG T, CAULEY JA, TYLAVSKY F, et al.Computed tomographic measurements of thigh muscle cross-sectional area and attenuation coefficient predict hip fracture: the health, aging, and body composition study.J Bone Miner Res.2010;25(3): 513-519.
[46] SCOTT D, SEIBEL M, CUMMING R, et al. Sarcopenic Obesity and Its Temporal Associations With Changes in Bone Mineral Density, Incident Falls, and Fractures in Older Men: The Concord Health and Ageing in Men Project.J Bone Miner Res.2017;32(3):575- 583.
[47] WANG X, YAN S, LIU C, et al. Fracture risk and bone mineral density levels in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus:a systematic review and meta-analysis.Osteoporos Int.2016;27(4):1413-1423.
[48] NEGREIROS CC,BERIGO MG,DOMINONI RL,et al.Asymptomatic vertebral fractures in patients with low bone mineral density.Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992).2016;62(2):145-150.
[49] 陈恒亭,马剑雄,卢斌,等.骨量-肌量减少性肥胖综合征与骨折关系的研究进展[J].中华老年医学杂志, 2018,37(3):347-350.
[50] PLIATSIKA P, ANTONIOU A, ALEXANDROU A, et al. Serum lipid levels and bone mineral density in Greek postmenopausal women. Gynecol Endocrinol.2012;28(8):655-660.
[51] HYDER JA, ALLISON MA, BARRETT-CONNOR E, et al.Bone mineral density and atherosclerosis: the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis, Abdominal Aortic Calcium Study. Atherosclerosis.2010;209(1):283-289.
[52] KOTANI K, YAMADA S, UURTUYA S, et al.The association between blood glucose and oxidized lipoprotein(a) in healthy young women. Lipids Health Dis.2010;9(1):103.
[53] ALMEIDA M, AMBROGINI E, HAN L, et al. Increased lipid oxidation causes oxidative stress, increased peroxisome proliferator activated receptor- gamma expression, and diminished pro-osteogenic Wnt signaling in the skeleton.J Biol Chem.2009;284(40):27438- 27448.
[54] KIM TN, CHOI KM.The implications of sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity on cardiometa- bolic disease.J Cell Biochem.2015;116(7): 1171-1178.
[55] BAEK SJ, NAM GE, HAN KD, et al.Sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity and their association with dyslipidemia in Korean elderly men: the 2008-2010 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey.J Endocrinol Invest.2014;37(3):247-260.
[56] 王丽娟,汪明芳,李晓琳,等.中青年人群少肌症肥胖与血脂异常的相关性研究[J].中华健康管理学杂志,2015,8(3):186-190.
[57] JORNAYVAZ FR, SAMUEL VT, SHULMAN GI.The Role of Muscle Insulin Resistance in the Pathogenesis of Atherogenic Dyslipidemia and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Associated with the Metabolic Syndrome.Annu Rev Nutr. 2010;30:273-290.
[58] RUSSELL-JONES D, KHAN R.Insulin-associated weight gain in diabetes- causes, effects and coping strategies.Diabetes Obes Metab . 2007;9(6): 799-812.
[59] DeMarco VG, Aroor AR, Sowers JR.The pathophysiology of hypertension in patients with obesity.Nat Rev Endocrinol.2014;10(6):364-376.
[60] KELLY OJ, GILMAN JC, KIM Y, et al. Macronutrient Intake in the Etiology, Prevention and Treatment of Osteosarcopenic Obesity.Curr Aging Sci.2016;9(4):260-278.
[61] INGLIS JE, JAFARINASABIAN P, GILMAN JC, et al. Possible nutritional etiology of osteosarcopenic obesity syndrome.FASEB J.2016;30(1):1156.8.
[62] PRICE CT, LANGFORD JR, LIPORACE FA.Essential Nutrients for Bone Health and a Review of their Availability in the Average North American Diet.Open Orthop J.2012;6(1):143-149.
[63] KIM J, LEE Y, KYE S, et al.Diet quality and osteosarcopenic obesity in community-dwelling adults 50 years and older.Maturitas.2017;104:73-79.
[64] ANDERSSON DC, BETZENHAUSER MJ, REIKEN S, et al. Ryanodine receptor oxidation causes intracellular calcium leak and muscle weakness in aging.Cell Metab.2011;14(2):196-207.
[65] ZEMEL MB, SHI H, GREER B, et al.Regulation of adiposity by dietary calcium.FASEB J.2000;14(9):1132-1138.
[66] BOOTH FW, GORDON SE, CARLSON CJ, et al.Waging war on modern chronic diseases: primary prevention through exercise biology. J Appl Physiol.2000;88(2):774-787.
[67] HUGHES VA, FRONTERA WR, WOOD M, et al.Longitudinal muscle strength changes in older adults: influence of muscle mass, physical activity, and health.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci.2001;56(5):B209-B217.
[68] KELLY OJ, GILMAN JC.Can Unconventional Exercise be Helpful in the Treatment, Management and Prevention of Osteosarcopenic Obesity?. Curr Aging Sci.2017;10(2): 106-121.
[69] GARBER CE, BLISSMER B, DESCHENES MR, et al.American College of Sports Medicine. Quantity and quality of exercise for developing and maintaining cardiorespiratory, musculoske- letal, and neuromotor ftness in apparently healthy adults: guidance for prescribing exercise.Med Sci Sports Exerc.2011;43(7):1334-1359.
[70] FRANCO MR, PEREIRA LS, FERREIRA PH. Exercise interventions for preventing falls in older people living in the community.Br J Sports Med.2014;48(10):867-868.
[71] TARANTINO U, BALDI J, SCIMECA M, et al.The role of sarcopenia with and without fracture.Injury. 2016;47(Suppl 4):S3-S10.
|