| [1]Mo Z, Li Q, Jia Z, et al. Biomechanical consideration of prosthesis selection in hybrid surgery for bi-level cervical disc degenerative diseases. Eur Spine J. 2017;26(4):1181-1190.[2]Zhu Y, Tian Z, Zhu B, et al. Bryan cervical disc arthroplasty versus anterior cervical discectomy and fusion for treatment of cervical disc diseases: a meta-analysis of prospective, randomized controlled trials. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2016;41(12):E733-E741.[3]Chung TT, Hueng DY, Lin SC. Hybrid strategy of two-level cervical artificial disc and intervertebral cage: biomechanical effects on tissues and implants. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015;94(47):e2048.[4]Pandey PK, Pawar I, Gupta J, et al. Comparison of outcomes of single-level anterior cervical discectomy with fusion and single-level artificial cervical disc replacement for single-level cervical degenerative disc disease. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2017; 42(1):E41-E49.[5]Chen J, Xu L, Jia YS, et al. Cervical anterior hybrid technique with bi-level Bryan artificial disc replacement and adjacent segment fusion for cervical myelopathy over three consecutive segments. J Clin Neurosci. 2016;27:59-62.[6]Kang L, Lin D, Ding Z, et al. Artificial disk replacement combined with midlevel ACDF versus multilevel fusion for cervical disk disease involving 3 levels. Orthopedics. 2013;36(1):e88-e94.[7]段硕,朱震奇,钱亚龙,等. 颈椎前路椎间融合术与人工椎间盘置换术联合椎间融合术治疗连续双节段颈椎病的中长期疗效对比[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2017,27(11):1004-1012.[8]Wu TK, Wang BY, Deng MD, et al. A comparison of anterior cervical discectomy and fusion combined with cervical disc arthroplasty and cervical disc arthroplasty for the treatment of skip-level cervical degenerative disc disease: A retrospective study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(41):e8112.[9]Wu TK, Wang BY, Cheng D, et al. Clinical and radiographic features of hybrid surgery for the treatment of skip-level cervical degenerative disc disease: A minimum 24-month follow-up. J Clin Neurosci. 2017;40:102-108.[10]Bisson EF, Samuelson MM, Apfelbaum RI. Intermediate segment degeneration after noncontiguous anterior cervical fusion. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2011;153(1):123-127,128.[11]Qizhi S, Lei S, Peijia L, et al. A comparison of zero-profile devices and artificial cervical disks in patients with 2 noncontiguous levels of cervical spondylosis. Clin Spine Surg. 2016;29(2):E61-E66.[12]Suzuki A, Daubs MD, Inoue H, et al. Prevalence and motion characteristics of degenerative cervical spondylolisthesis in the symptomatic adult. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013;38(17): E1115-E1120.[13]Yamaguchi S, Mitsuhara T, Abiko M, et al. Epidemiology and overview of the clinical spectrum of degenerative cervical myelopathy. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2018;29(1):1-12.[14]Kopperdahl DL, Morgan EF, Keaveny TM. Quantitative computed tomography estimates of the mechanical properties of human vertebral trabecular bone. J Orthop Res. 2002;20(4):801-805.[15]樊黎霞,丁光兴,费王华,等.基于CT图像的长管骨有限元材料属性研究及实验验证[J].医用生物力学,2012,27(1):102-108.[16]Panjabi MM, Crisco JJ, Vasavada A, et al. Mechanical properties of the human cervical spine as shown by three-dimensional load-displacement curves. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(24): 2692-2700.[17]Shang Z, Zhang Y, Zhang D, et al. Clinical and radiological analysis of bryan cervical artificial disc replacement for "skip" multi-segment cervical spondylosis: long-term follow-up results. Med Sci Monit. 2017;23:5254-5263.[18]Matsumoto M, Okada E, Ichihara D, et al. Anterior cervical decompression and fusion accelerates adjacent segment degeneration: comparison with asymptomatic volunteers in a ten-year magnetic resonance imaging follow-up study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010;35(1):36-43.[19]Zheng B, Hao D, Guo H, et al. ACDF vs TDR for patients with cervical spondylosis - an 8 year follow up study. BMC Surg. 2017;17(1):113.[20]Cho SK, Riew KD. Adjacent segment disease following cervical spine surgery. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2013;21(1):3-11.[21]Joaquim AF, Makhni MC, Riew KD. Evidence-based use of arthroplasty in cervical degenerative disc disease. Int Orthop. 2019.[22]Hung CW, Wu MF, Yu GF, et al. Comparison of sagittal parameters for anterior cervical discectomy and fusion, hybrid surgery, and total disc replacement for three levels of cervical spondylosis. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2018;168:140-146.[23]Wang KF, Duan S, Zhu ZQ, et al. Clinical and radiologic features of 3 reconstructive procedures for the surgical management of patients with bilevel cervical degenerative disc disease at a minimum follow-up period of 5 years: a comparative study. World Neurosurg. 2018;113:e70-e76.[24]Zhang Z, Li Y, Jiang W. A comparison of zero-profile anchored spacer (ROI-C) and plate fixation in 2-level noncontiguous anterior cervical discectomy and fusion- a retrospective study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018;19(1):119.[25]王亦璁.骨与关节损伤[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2012.[26]Nunley PD, Coric D, Frank KA, et al. Cervical disc arthroplasty: current evidence and real-world application. Neurosurgery. 2018;83(6):1087-1106.[27]Kepler CK, Brodt ED, Dettori JR, et al. Cervical artificial disc replacement versus fusion in the cervical spine: a systematic review comparing multilevel versus single-level surgery. Evid Based Spine Care J. 2012;3(S1):19-30.[28]Ganbat D, Kim K, Jin YJ, et al. Heterotopic ossification in cervical total disk replacement: a finite element analysis. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2014;228(2):200-205.[29]赖宪良,王萧枫,陈鸥,等.Hybrid手术对多节段颈椎退行性病变椎体的生物力学影响[J].中华全科医学,2018,16(2):196-199.[30]McDonald CP, Chang V, McDonald M, et al. Three-dimensional motion analysis of the cervical spine for comparison of anterior cervical decompression and fusion versus artificial disc replacement in 17 patients: clinical article. J Neurosurg Spine. 2014;20(3):245-255. |
.jpg)
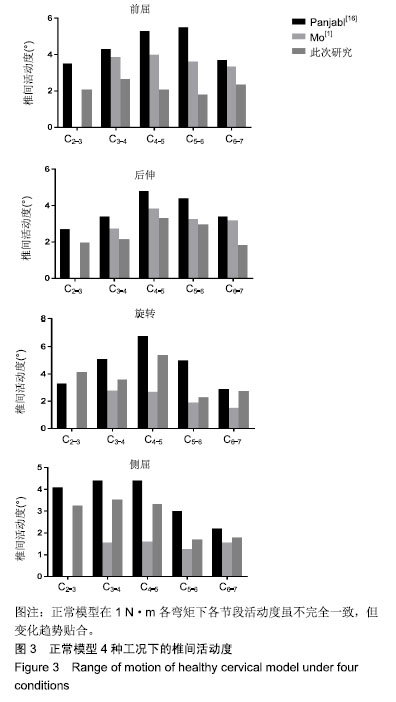
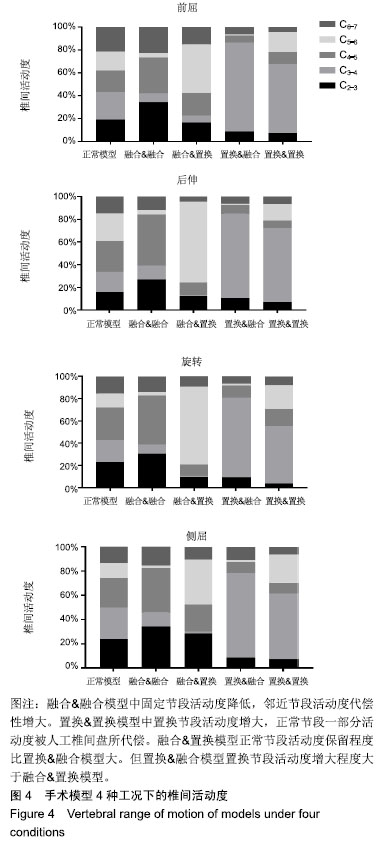
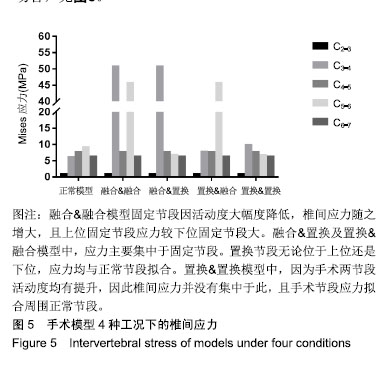

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)