中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (32): 5170-5174.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1466
• 骨与关节生物力学 bone and joint biomechanics • 上一篇 下一篇
臀中肌主动响应对老年骨质疏松股骨颈骨折的有限元断裂力学分析
孙文涛1,林梓凌2,李 凡3,洪定刚1,周建飞1,庞向华1,韦怀籍1,徐攀峰1,王小芃1
- 1柳州市中医医院,广西壮族自治区柳州市 545000;2广州中医药大学第一附属医院,广东省广州市 510405;3湖南大学汽车车身先进设计制造国家重点实验室,湖南省长沙市 410082
Finite element fracture mechanics analysis of gluteus medius muscle active response to osteoporotic femoral neck fracture
Sun Wentao1, Lin Ziling2, Li Fan3, Hong Dinggang1, Zhou Jianfei1, Pang Xianghua1, Wei Huaiji1, Xu Panfeng1, Wang Xiaopeng1
- 1Liuzhou Chinese Medicine Hospital, Liuzhou 545000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China; 3State Key Laboratory of Advanced Design Manufacture for Vehicle Body, Hunan University, Changsha 410082, Hunan Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
主动响应:当人预感到一个压力源存在时,常以交感神经系统兴奋为主,做出“战或逃”的反应,表现为呼吸变浅、瞳孔散大、心率加快和肌肉紧张。以人体跌倒为例,跌倒时臀部肌肉主动反射收缩,对下跌重力做出对抗抵消响应,改变下跌方向,使髋部的直接撞击损伤减少到最低,从而保护人体的损伤,这个过程就被称作“肌肉的主动响应”。
断裂力学:它是固体力学的一个分支,主要研究裂纹在固体材料中的传播和扩展规律,以预测、防止和控制断裂行为的发生。断裂力学运用到骨科研究中,可以预测骨骼的骨折断裂行为,为临床提供理论支持。
摘要
背景:老年患者肌肉应激保护性动作响应同样是髋部骨折重要影响因素,相关报道较少。
目的:运用有限元断裂力学方法研究臀中肌对老年骨质疏松股骨颈骨折的作用机制。
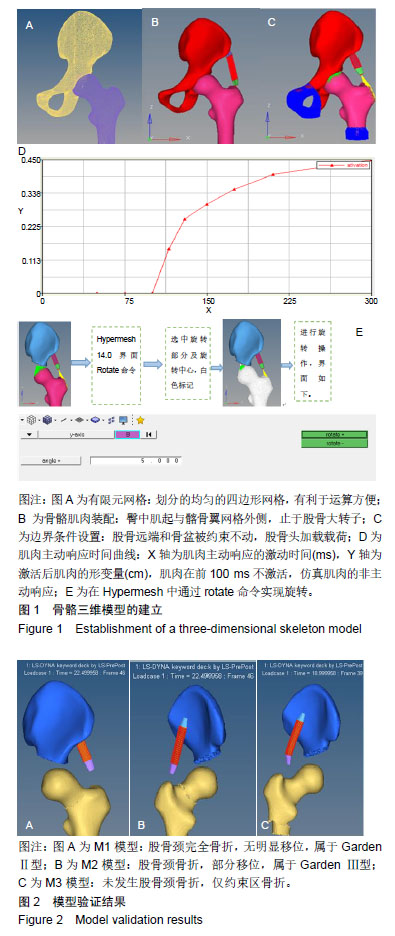
方法:选取1例87岁在广州中医药大学第一附属医院诊断为股骨颈骨折老年女性患者,重建髋部骨骼与臀中肌的三维有限元模型,对材料赋值进行仿真模拟,分别模拟以下3种不同状态:肌肉激活前,M1模型:股骨头与矢状位呈20°夹角,自上而下施加500 N载荷;肌肉激活后,M2模型:在M1模型的基础上使髋关节外展外旋各5°;M3模型:在M1模型的基础上使髋关节外展内旋各5°,将3个模型导入有限元后处理软件LS-DYNA中计算,得到臀中肌主动响应前后基于应力-应变曲线关系的股骨颈骨折断裂模型,对比分析3种有限元断裂模型前后的骨折裂纹。
结果与结论:①臀中肌主动响应后的M2、M3模型对比:M3模型在髋关节外展内旋5°后未见股骨颈骨折,而是在股骨约束区域发生骨折,M2模型在髋关节外展外旋5°后仍然发生了股骨颈骨折;②对比M1、M2模型:两者均发生股骨颈骨折,发生股骨颈骨折的时间均为T=22.5 ms,按照骨折移位程度M1模型骨折裂纹为GardenⅡ型,M2模型骨折裂纹为Garden Ⅲ型,较M1模型移位更加严重;③上述结果提示,臀中肌主动响应后,肌肉收缩引起髋关节跌倒姿势改变可能是影响老年股骨颈骨折裂纹的因素。
ORCID: 0000-0002-6116-8080(孙文涛)
中图分类号:
.jpg)