中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (32): 5138-5145.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1478
• 骨科植入物 orthopedic implant • 上一篇 下一篇
后外侧支撑固定治疗胫骨平台后外侧髁骨折预后的多元Logistics回归分析
于 健1,徐 刚1,孙 宏2,殷照阳1,盛路新1,厉雷明1,孙 晓1,霍永峰1
- 1连云港市第一人民医院,江苏省连云港市 222002;2江苏省疾病预防控制中心,江苏省南京市 210009
Multivariate Logistic regression analysis of prognosis of posterolateral condylar fractures of tibial plateau treated with posterolateral buttress fixation
Yu Jian1, Xu Gang1, Sun Hong2, Yin Zhaoyang1, Sheng Luxin1, Li Leiming1, Sun Xiao1, Huo Yongfeng1
- 1the First People’s Hospital of Lianyungang, Lianyungang 222002, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Jiangsu Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Nanjing 210009, Jiangsu Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
.jpg)
文题释义:
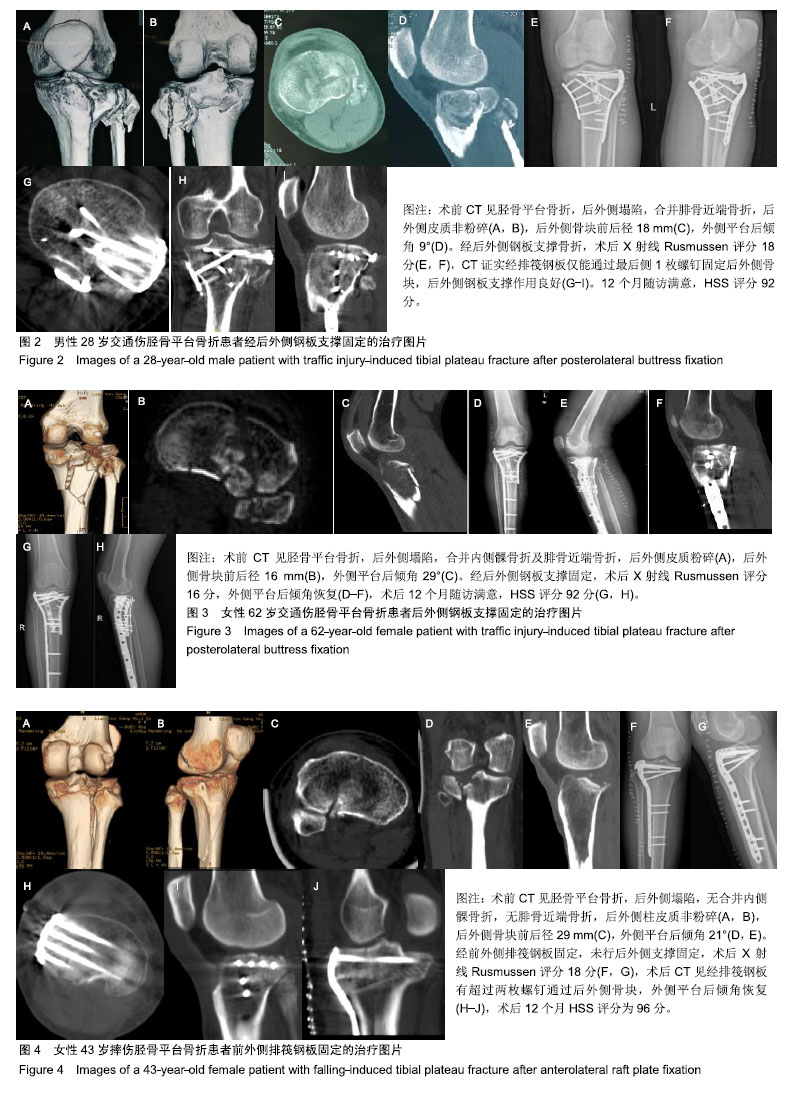
胫骨平台后外侧髁:胫骨平台横截面上看,以腓骨头的前缘水平线为前界,后纵隔为内侧界的胫骨平台区域,该区域在膝关节屈膝后与股骨髁相接触并承受部分压力,显露需解剖后侧的血管神经,风险较高,且操作空间有限。
支撑固定:为骨折内固定术的一种方式,对遭受持续剪切力并有继续移位趋势的干骺端骨折块在侧方加以钢板支撑,对抗骨折移位的趋势及力量的内固定方法。
摘要
背景:累及胫骨平台后外侧髁骨折的治疗一直存在争议,主要集中在后外侧支撑固定的手术指征上,希望此次研究能对该问题的解答提供帮助。
目的:探讨胫骨平台后外侧髁骨折患者采用后外侧支撑固定对其骨折预后的影响。
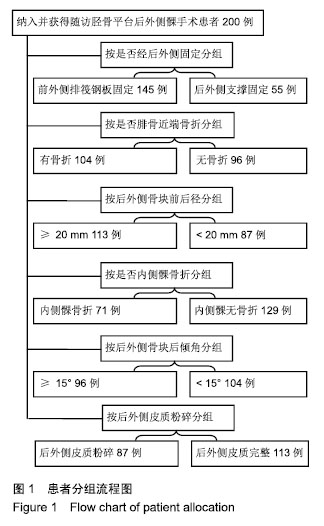
方法:对连云港市第一人民医院2011年1月至2016年12月接受手术治疗的胫骨平台后外侧髁骨折患者进行随访调查。以美国特种外科医院膝关节评分作为观察指标,将患者影像学表现上的后外侧骨块前后径、外侧胫骨平台后倾角、后外侧柱皮质是否粉碎、是否合并腓骨近段骨折、是否合并内侧髁骨折等作为混杂因素,采用多元回归方法进行多因素分析,探讨后外侧支撑固定对患者预后的影响。
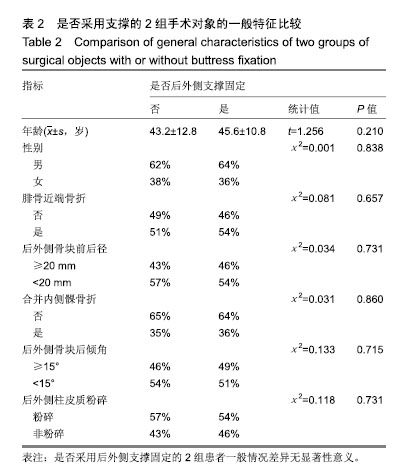
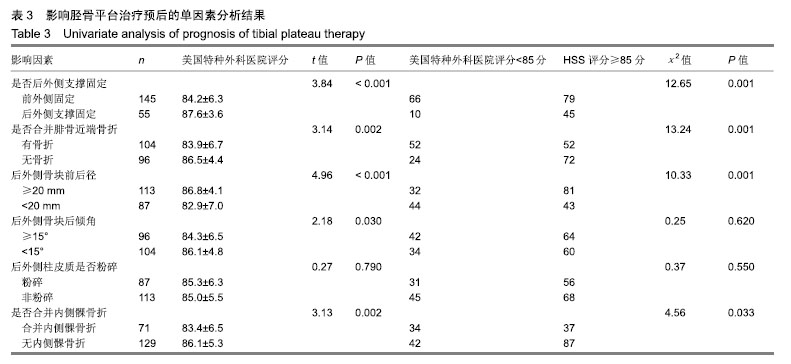
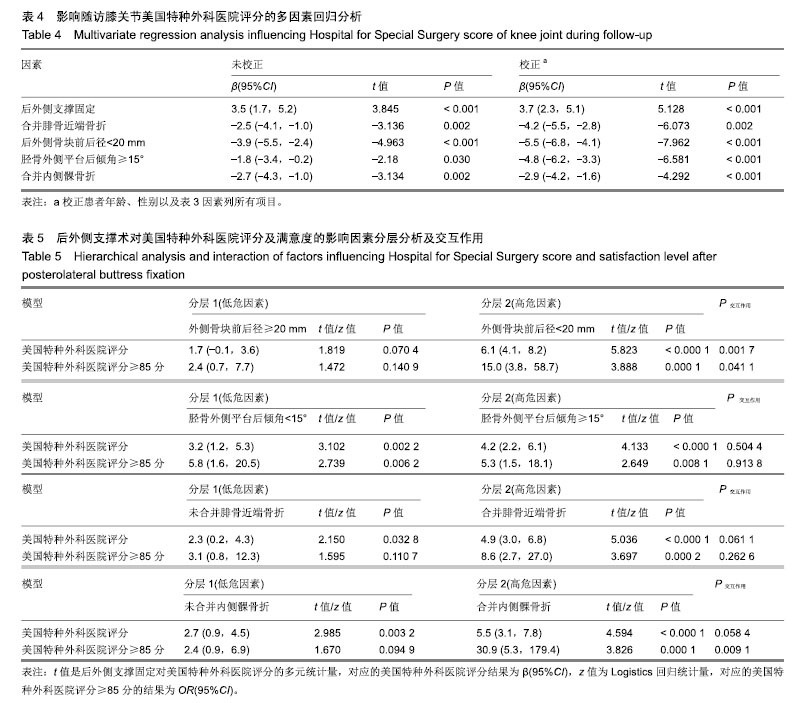
结果与结论:①共随访获得200例患者的完整资料,随访时间12-24个月,末次调查时膝关节美国特种外科医院评分62-95分,平均(85.1±5.8)分;②单因素分析显示,后外侧骨块前后径、外侧胫骨平台后倾角、合并腓骨近段骨折、合并内侧髁骨折、后外侧支撑固定与累及后外侧髁的胫骨平台骨折术后美国特种外科医院评分均具有相关性(P < 0.05);③多因素分层分析进一步确认,后外侧支撑固定可以提高后外侧骨块前后径<20 mm、合并腓骨近段骨折、胫骨外侧平台后倾角≥15°的患者术后1年随访的膝关节美国特种外科医院评分(P < 0.01),但对后外侧骨块前后径≥20 mm患者的膝关节美国特种外科医院评分和满意度的提高无明显影响;④相对于前外侧排筏钢板固定,采用后外侧支撑固定可以大幅提升后外侧骨块前后径<20 mm患者的1年随访美国特种外科医院评分,建议对此类患者采用后外侧支撑固定。对于合并腓骨近端骨折、胫骨外侧平台后倾角≥15°的胫骨平台后外侧髁骨折患者,进行后外侧支撑固定也可以提高术后1年的美国特种外科医院评分优良率,建议作为参考指标。
ORCID: 0000-0001-9741-0281(于健)
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)