中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (9): 1313-1317.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2403
• 人工假体 artificial prosthesis • 下一篇
MAKO机器人辅助后外侧入路全髋关节置换的学习曲线及临床早期效果
崔可赜,郭 祥,韩贵斌,陈元良,刘亦恒,钟海波
- 中南大学湘雅医学院附属海口医院西院(海口骨科与糖尿病医院),海南省海口市 570208
Learning curve and early clinical results of total hip arthroplasty with MAKO robot assisted posterolateral approach
Cui Keze, Guo Xiang, Han Guibin, Chen Yuanliang, Liu Yiheng, Zhong Haibo
- West Hospital (Haikou Orthopedics and Diabetes Hospital), Haikou Hospital, Xiangya School of Medicine, Central South University, Haikou 570208, Hainan Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
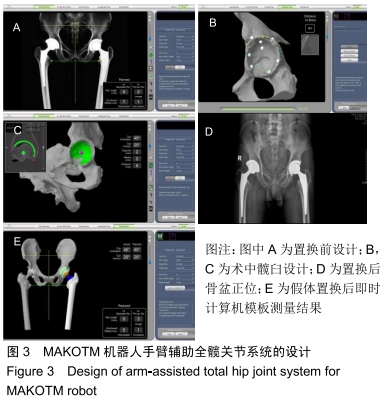
MAKO机器人辅助:是一种半自动手术机器人系统,具有良好的反馈特性,半自动封闭型,主要依靠医生术中操作,术中可根据实际情况随时调整手术计划,髋膝关节置换以及膝关节单髁置换均可操作,是目前世界上应用最广泛的骨科半自动手术机器人系统。
学习曲线:手术医生学习一项新技术,在一定时间内,可以获得的技能或知识的速率,概括来说就是熟能生巧,连续进行有固定方式的手术工作,操作会越来越熟练,完成同样手术操作的工作时间会越来越短,术后的结果更趋于优良。
背景:随着全髋关节置换技术的不断成熟,对手术的精准程度要求越来越高,以期望患者得到更良好的置换结果;MAKO机器人辅助下的关节置换技术使手术的精准程度实现了可能,但该项技术有一定的学习曲线,早期的置换结果及并发症应是关注重点。
目的:分析MAKO机器人辅助下后外侧入路人工髋关节置换的学习曲线及临床早期效果。
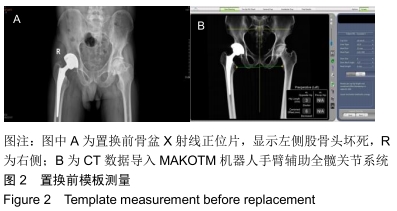
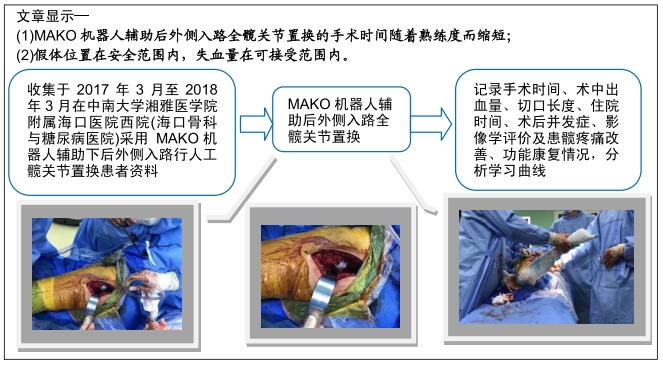
方法:回顾性分析2017年3月至2018年3月中南大学湘雅医学院附属海口医院西院(海口骨科与糖尿病医院)采用MAKO机器人辅助下后外侧入路行人工髋关节置换26例患者的病例资料,其中男12例,女14例。关注学习曲线早期的髋关节置换中易发生的问题及早期临床结果。
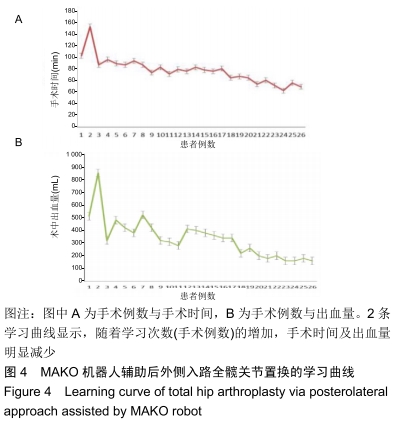
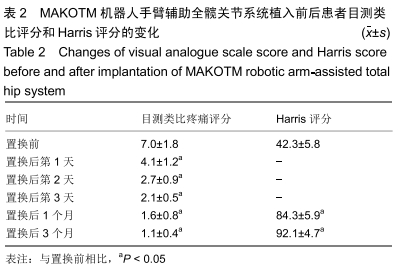
结果与结论:手术时间56-155 min,平均(87.0±16.1)min;显性出血220-850 mL,平均(336±246)mL。髋臼外展角(41.3±2.7)°,髋臼前倾角(16.4±3.4)°,下肢长度差值为(1.0±2.0)mm,股骨偏心距差值为(1.6±0.6)mm。术中股骨距骨折1例,无感染、坐骨神经损伤及伤口相关并发症。置换后弃拐行走时间3-6周,平均(3.8±2.1)周。置换后3个月Harris评分(92.1±4.7)分。提示MAKO机器人辅助下后外侧入路全髋关节置换学习曲线的病例短期内显示疼痛改善,功能康复快,临床结果良好,手术时间随着熟练度而缩短,假体位置均在安全范围内,失血量亦在可接受范围。
ORCID: 0000-0001-7677-1328(崔可赜)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程中图分类号: