中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (18): 2829-2835.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2639
• 数字化骨科 digital orthopedics • 上一篇 下一篇
机器人辅助经皮复位微创内固定治疗Schatzker Ⅱ-Ⅲ型胫骨平台骨折
付雪飞1,张诗剑1,赵保双2,刘其鑫2,吴 磊2,杜博松2,李思源2,祁 超2,杨超群2,翁能源2,张 弢1
- 1天津市天津医院创伤骨科,天津市 300211;2天津医科大学研究生院,天津市 300070
Robot-assisted percutaneous reduction and minimally invasive internal fixation for treating Schatzker II-III tibial plateau fracture
Fu Xuefei1, Zhang Shijian1, Zhao Baoshuang2, Liu Qixin2, Wu Lei2, Du Bosong2, Li Siyuan2, Qi Chao2, Yang Chaoqun2, Weng Nengyuan2, Zhang Tao1
- 1Department of Traumatic Orthopedics, Tianjin Hospital, Tianjin 300211, China; 2Graduate School of Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300070, China
摘要:
文题释义:
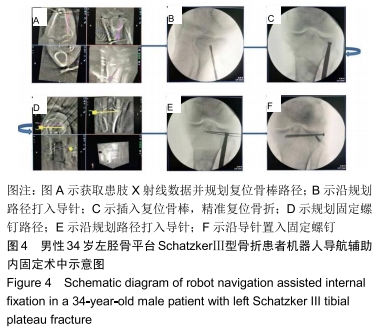
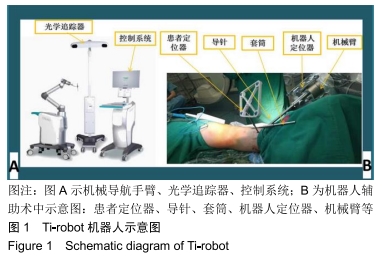
机器人辅助:计算机导航和机器人辅助内固定技术在骨科手术中的应用逐渐开展,应用机器人导航辅助微创治疗骨盆、髋臼、脊柱骨折疗效满意,目前尚无应用机器人辅助经皮复位内固定治疗胫骨平台骨折临床研究相关报道。此次研究应用Ti-Robot(第3代TINAVI骨科手术机器人)辅助定位骨折塌陷位置并规划导航复位路径以微创、精准完成手术。
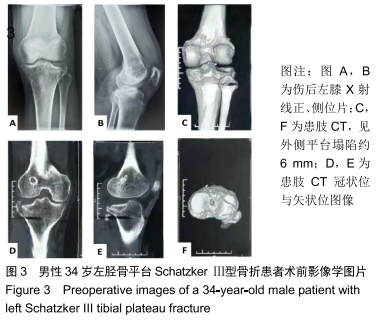
Schatzker Ⅱ-Ⅲ型胫骨平台骨折:SchatzkerⅡ型为胫骨平台外侧裂陷骨折,Schatzker Ⅲ型为外侧平台单纯压缩骨折。SchatzkerⅡ-Ⅲ型骨折共同点是其均存在外侧平台塌陷,其治疗关键在于精准定位并复位塌陷关节面并坚强固定,机器人辅助手术的核心是精准和微创,在复位此类骨折方面优势明显。
背景:精准、微创手术已成为当下外科手术追求的目标,伴随智能机器人的快速发展,骨折的精准、微创治疗也成为了必然趋势。
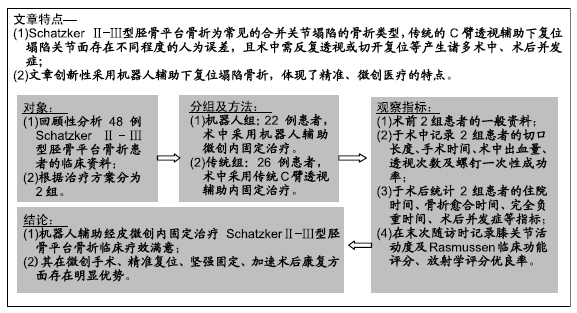
目的:评价机器人辅助经皮复位微创内固定治疗Schatzker Ⅱ-Ⅲ型胫骨平台骨折的临床疗效。
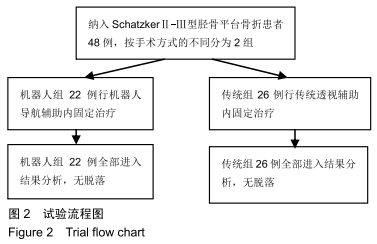
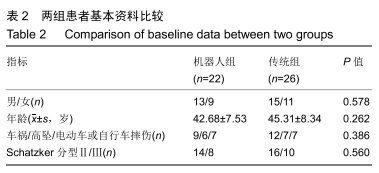
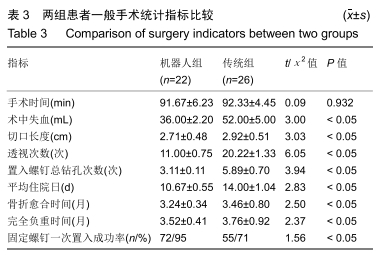
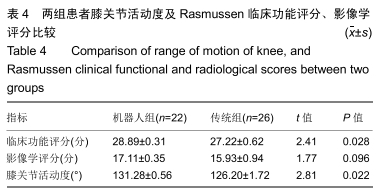
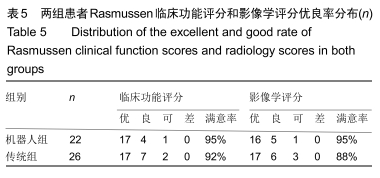
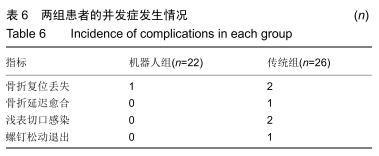
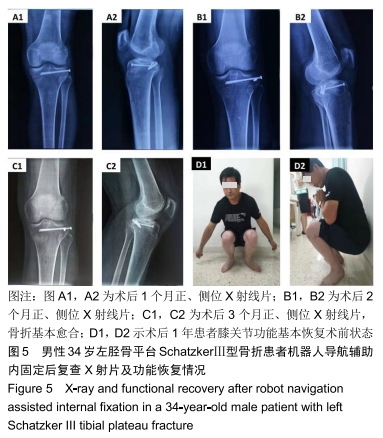
方法:回顾性分析2017年4月至2018年8月在天津市天津医院采用机器人辅助和传统透视辅助内固定治疗单纯Schatzker Ⅱ-Ⅲ型胫骨平台骨折患者的临床资料,其中机器人组22例,传统组26例。所有患者均为单侧、闭合、新鲜胫骨平台骨折。统计2组患者切口长度、手术时间、术中出血量、透视次数、螺钉一次性成功率、住院时间、骨折愈合时间、完全负重时间、术后并发症等指标;并在末次随访时记录膝关节活动度,采用Rasmussen影像学及临床评分评估患者膝关节功能。
结果与结论:①术前2组患者一般资料差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);②与传统组相比,机器人组在术中失血、切口长度、透视次数、置入固定螺钉总钻孔次数、平均住院日、骨折愈合时间、完全负重时间、固定螺钉一次置入成功率等方面均具有优势,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);而2种方式的手术时间相当(P=0.932);③机器人组对比传统组在膝关节活动度及Rasmussen临床功能评分反面亦具有优势(P < 0.05);④另外机器人组术后有更少的并发症;⑤提示机器人辅助经皮微创内固定治疗Schatzker Ⅱ-Ⅲ型胫骨平台骨折临床效果满意,其在微创手术、精准复位、坚强固定、加速术后康复方面存在明显优势。
ORCID: 0000-0003-2656-1001(付雪飞)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: