中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (32): 5146-5150.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1492
• 数字化骨科 digital orthopedics • 上一篇 下一篇
构建3D椎体模型比较经皮椎体后凸成形与经皮椎体成形治疗胸腰椎压缩性骨折的力学变化
郭大华1,王裕辉1,叶前驱1,刘文豪1,杨 博1,叶林强2
- 1广东医科大学附属第三医院(佛山市顺德区龙江医院),广东省佛山市 528318;2广州中医药大学第一附属医院,广东省广州市 510405
Mechanical changes of percutaneous kyphoplasty and percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of thoracolumbar compressive fractures in three-dimensional vertebral models
Guo Dahua1, Wang Yuhui1, Ye Qianqu1, Liu Wenhao1, Yang Bo1, Ye Linqiang2
- 1Third Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Medical University (Longjiang Hospital of Shunde District of Foshan City), Foshan 528318, Guangdong Province, China; 2First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
.jpg)
文题释义:
胸腰椎压缩性骨折:是老年性骨质疏松常见并发症,由于椎体前缘高度丢失,可导致局部后凸畸形、生理曲线发生改变,进而使椎体前方应力集中,骨折椎体周围应力增大,从而导致邻近椎体再骨折。
经皮椎体后凸成形/经皮椎体成形术后再骨折:已有研究报道,经皮椎体后凸成形较经皮椎体成形手术时间长,骨水泥用量多,术后恢复快,且二者都有一定的术后再骨折发生率。生物力学研究表明,骨水泥弹性模量高于椎体,该差异可能引发刚度增高效应,增加邻近椎体骨折风险,这可能是术后发生再骨折的原因。
摘要
背景:老年人胸腰椎骨折与一般骨折相比有不同的病理变化,多伴有其他全身疾患。较常用的手术方法为经皮椎体成形和经皮椎体后凸成形,不同的术式选择与术后再骨折发生率有关,而如何选择有效的内固定系统及治疗方式对减少老年胸腰椎骨折手术固定失败至关重要。
目的:在3D椎体模型上构建压缩性骨折胸腰椎模型,分析腰椎压缩性骨折的力学变化特点。
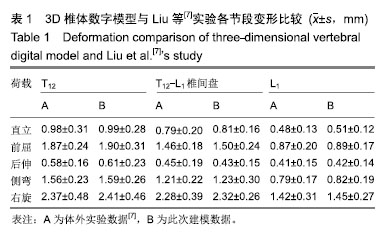
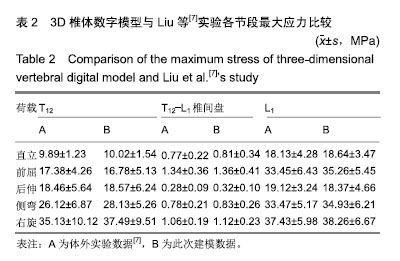
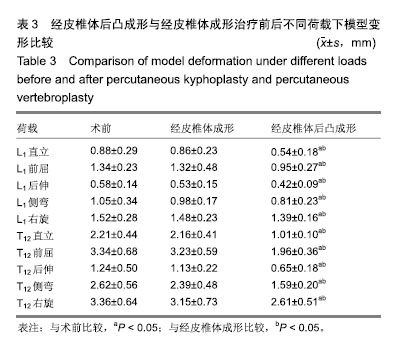
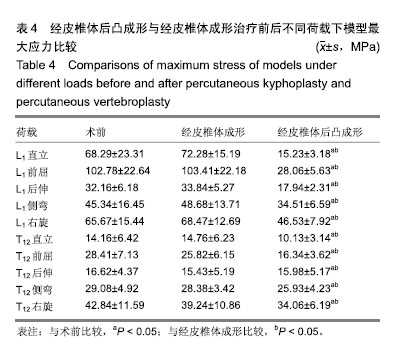
方法:选择1例56岁男性腰痛患者(后确诊为腰肌劳损),椎体形态无明显异常;1例54岁男性由于骨质疏松导致的胸腰椎压缩性骨折患者,2例患者对实验方案知情同意,且得到医院伦理委员会批准,均获取T12-L1节段CT资料。根据腰痛志愿者CT数据,利用Mimics 10.0软件建立椎体3D数字模型,利用三维有限元分析软件Ansys 12.0建立椎体3D实体模型。参照骨折患者资料对正常椎体有限元模型中的L1模拟椎体压缩性骨折,并在此基础上模拟经皮椎体后凸成形和经皮椎体成形手术过程,记录不同载荷下模型各部分Von Mises应力以及变形。
结果与结论:①与其他作者体外生物力学测试实验结果比较,此模型的实验结果与其基本一致(P > 0.05);②经皮椎体后凸成形模型在直立及前屈、后伸、侧弯及右旋荷载下,T12与L1节段变形均显著小于术前及经皮椎体成形模型(P < 0.05);经皮椎体成形模型的骨折节段T12与L1在各种荷载下的脊椎变形与术前差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);③经皮椎体后凸成形模型骨折节段T12与L1在直立及前屈、后伸、侧弯及右旋荷载下的最大应力较术前及经皮椎体成形模型显著减小(P < 0.05);经皮椎体成形模型的骨折节段T12与L1在各种荷载下最大应力与术前差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);④提示经皮椎体后凸成形在直立及前屈、后伸、侧弯及右旋荷载下,T12与L1节段变形及应力均显著小于术前的压缩性骨折模型及经皮椎体成形治疗模型,表明经皮椎体后凸成形可显著增加脊柱胸腰段刚度,经皮椎体成形对于胸腰段刚度无明显影响。
ORCID: 0000-0001-5401-5396(郭大华)
中图分类号:
.jpg)