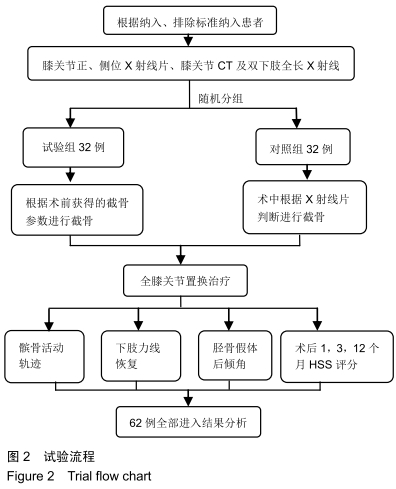
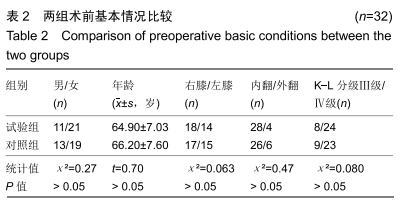
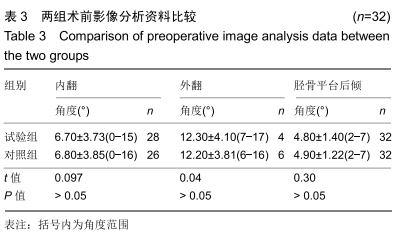
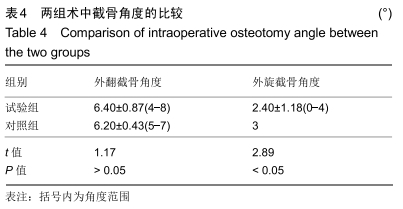
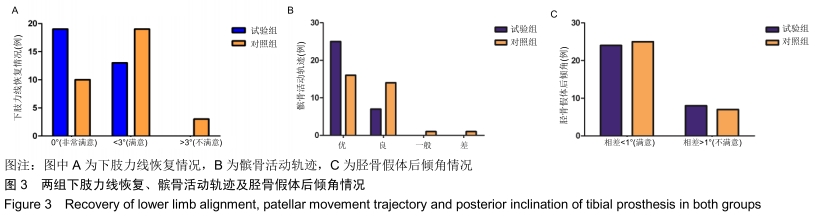
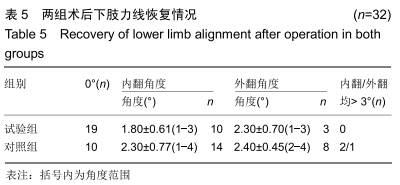
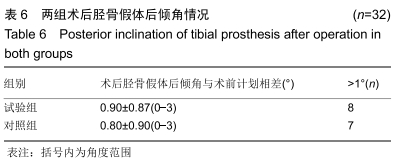
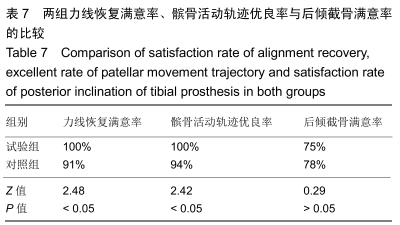
[1] SHARKEY PF, HOZACK WJ, ROTHMAN RH, et al. Insall Award paper. Why are total knee arthroplasties failing today? Clin Orthop Rel Res.2002;(404):7-13.
[2] LEE SY, LIM HC, JANG KM, et al.What Factors Are Associated With Femoral Component Internal Rotation in TKA Using the Gap Balancing Technique?Clin Orthop Relat Res.2017;475(8):1999-2010.
[3] KIA M, WRIGHT TM, CROSS MB, et al.Femoral Component External Rotation Affects Knee Biomechanics: A Computational Model of Posterior-stabilized TKA.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2018; 476(1):113-123.
[4] HEYSE TJ, EL-ZAYAT BF, CORTE RD, et al.Internal femoral component malrotation in TKA significantly alters tibiofemoral kinematics.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2018;26(6): 1767-1775.
[5] NEDOPIL AJ, HOWELL SM, HULL ML.Does Malrotation of the Tibial and Femoral Components Compromise Function in Kinematically Aligned Total Knee Arthroplasty?Orthop Clin North Am.2016;47(1):41-50.
[6] 朱诗白,陈曦,钱文伟,等.浅谈全膝关节置换术中的冠状位下肢力线[J].中华外科杂志, 2018,56(9):665-669.
[7] 贾卫斗,贾薇薇,杨飞,等.PACS在颈椎后方结构测量及其临床意义[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2010,28(3):294-298.
[8] 何家维,严志汉,虞志康,等.PACS工作站上Cobb角测量的可靠性研究[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2006,16(10):732-734.
[9] 杨波,黄向辉,凌鸣,等.全膝关节置换术治疗膝骨性关节炎的临床效果[J].临床骨科杂志,2018,21(4):459-462.
[10] HETAIMISH BM, KHAN MM, SIMUNOVIC N, et al. Meta-analysis of navigation vs conventional total knee arthroplasty.J Arthroplasty. 2012;27(6):1177-1182.
[11] 王本超,陈森,方洪松,等.股骨畸形对TKA术后下肢力线及膝关节线的影响[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2018,33(12):1247-1250.
[12] INNOCENTI B, BELLEMANS J, CATANI F, et al.Deviations From Optimal Alignment in TKA: Is There a Biomechanical Difference Between Femoral or Tibial Component Alignment? J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(1):295-301.
[13] LEE BS, CHO HI, BIN SI, et al.Femoral Component Varus Malposition is Associated with Tibial Aseptic Loosening After TKA.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2018;476(2):400-407.
[14] 刘帅,姚庆强,周进,等.计算机辅助设计与3D打印个性化截骨导板辅助人工全膝关节置换术的精准度研究[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2017,32(6):580-584.
[15] ZAPATA G, SANZ-PENA I, VERSTRAETE M, et al.Effects of femoral component placement on the balancing of a total knee at surgery.J Biomech.2019;(86):117-124.
[16] CONN KS, CLARKE MT, HALLETT JP.A simple guide to determine the magnification of radiographs and to improve the accuracy of preoperative templating.J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002; 84(2):269-272.
[17] ARORA J, SHARMA S, BLYTH M.The role of pre-operative templating in primary total knee replacement.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.2005;13(3):187-189.
[18] ELSON DW, PETHERAM TG, DAWSON MJ.High reliability in digital planning of medial opening wedge high tibial osteotomy, using Miniaci’s method.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2015;23(7):2041-2048.
[19] HSU AR, KIM JD, BHATIA S, et al.Effect of Training Level on Accuracy of Digital Templating in Primary Total Hip and Knee Arthroplasty.Orthopedics.2012;35(2):e179-83.
[20] 马路遥,郭万首,马金辉,等.全膝关节置换术中固定角度外翻截骨会影响置换后下肢力线吗?[J].中国组织工程研究, 2017,21(11): 1658-1663.
[21] 朱琪琪,许杰,翁健豪,等.全膝关节置换术假体型号预测模型的初步探讨[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2015,9(5):561-564.
[22] 张强,杨惠光.膝关节置换中股骨假体大小的测量及其对疗效影响[J].现代医学,2011,39(3):381-384.
[23] LEVINE B, FABI D, DEIRMENGIAN C.Digital templating in primary total hip and knee arthroplasty. Orthopedics. 2010;33(11): 797.
[24] SCHOTANUS MGM, SCHOENMAKERS DAL, SOLLIE R, et al. Patient-specific instruments for total knee arthroplasty can accurately predict the component size as used peroperative.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017;25(12):3844-3848.
[25] 杨硕,冯硕,徐崇俊,等.全膝关节置换后下肢力线及假体力线与疗效和假体松动率的关系[J].中国组织工程研究, 2019,23(24): 3780-3785.
[26] 余进伟,郭甲瑞,陈旭,等.3D打印模板辅助关节置换治疗膝骨关节炎的前瞻性研究[J].实用骨科杂志,2018,24(9):782-785,836.
[27] 赵辉,吴宇黎,吴海山,等.两种不同股骨假体旋转设计对全膝关节置换术后髌骨轨迹的影响[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2011,5(6): 687-692.
[28] 谢军,刘巍,袁凤来.股骨假体旋转角对全膝关节置换后膝关节功能恢复影响的3年随访[J].中国组织工程研究, 2017,21(27):4283-4287.
[29] 王戟森,陈坚锋,潘耀成,等.人工膝关节置换术中的胫骨平台后倾角[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2016,24(9):826-831.
[30] 符得红,戴祝.全膝关节置换术中间隙平衡技术的应用进展[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2018,33(4):446-448.
[31] 王伟刚,张勇.全膝关节置换挛缩问题的处理与术后效果[J].中国骨与关节外科, 2017,10(2):104-108.
[32] ZHANG Y, WANG J, XIAO J, et al. Measurement and comparison of tibial posterior slope angle in different methods based on three-dimensional reconstruction.Knee. 2014;21(3):694-698.
|