| [1]Li Y,Qing Y,Zhang Z,et al.Clinical efficacy of percutaneous vertebroplasty combined with intensity-modulated radiotherapy for spinal metastases in patients with NSCLC. Onco Targets Ther. 2015; 8:2139-2145.[2]Yang Z,Tan J,Zhao R,et al.Clinical Investigations on the Spinal Osteoblastic Metastasis Treated by Combination of Percutaneous Vertebroplasty and 125I Seeds Implantation Versus Radiotherapy. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2013; 28(1):58-64.[3]Mansoorinasab M,Abdolhoseinpour H.A review and update of vertebral fractures due to metastatic tumors of various sites to the spine: Percutaneous vertebroplasty.Interv Med Appl Sci. 2018;10(1): 1-6. [4]Liu Y,Wang Y,Zhao L,et al.Effectiveness and safety of percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of spinal metastatic tumor.Pak J Med Sci.2017;33(3):675-679.[5]Gu YF,Tian QH,Li YD,et al.Percutaneous vertebroplasty and interventional tumor removal for malignant vertebral compression fractures and/or spinal metastatic tumor with epidural involvement: a prospective pilot study.J Pain Res. 2017;10:211-218.[6]Su Y,Sun ZZ,Shen LX,et al.Comparison of percutaneous vertebroplasty with and without interventional tumor removal for spinal metastatic tumor without epidural involvement.J Bone Oncol.2017;6:1-7.[7]Qi L,Li C,Wang N,et al.Efficacy of percutaneous vertebroplasty treatment of spinal tumors: A meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore).2018;97(3):e9575.[8]闫光华,葛顺杰,仇继任,等.经皮椎体成形骨水泥渗漏的治疗与预防[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(26):4241-4246.[9]Martins PC,Couto TE,Gama AC.Auditory perceptual evaluation of the degree vocal deviation: correlation between the Visual Analogue Scale and Numerical Scale.Codas. 2015; 27(3):279-284.[10]Monticone M,Baiardi P,Vanti C,et al.Responsiveness of the Oswestry Disability Index and the Roland Morris Disability Questionnaire in Italian subjects with sub-acute and chronic low back pain.Eur Spine J.2012;21(1):122-129.[11]Masala S,Anselmetti GC,Muto M,et al.Percutaneous Vertebroplasty Relieves Pain in Metastatic Cervical Fractures.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2011;469(3):715-722.[12]Jansson KA,Bauer HC.Survival,complications and outcome in 282 patients operated for neurological deficit due to thoracic or lumbar spinal metastases.Eur Spine J.2006;15(2):196-202. [13]Polastri M,Gasbarrini A.Vertebroplasty in patients with tumour-related vertebral fractures: is rehabilitation needed? Asian Spine J.2013;7(3):248-252.[14]Ma XL,Xing D,Ma JX,et al.Balloon kyphoplasty versus percutaneous vertebroplasty in treating osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: grading the evidence through a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur Spine J. 2012;21(9): 1844-1859.[15]杨学刚,吴戈,李政文,等.骨填充网袋辅助经皮椎体成形术治疗伴椎体后壁破损的脊柱转移瘤[J].介入放射学杂志, 2017,26(9): 803-806.[16]De la Garza-Ramos R,Benvenutti-Regato M,Caro-Osorio E.Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty for cervical spine metastases: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Spine Surg.2016;10:7. [17]Sadeghi-Naini M,Aarabi S,Shokraneh F,et al.Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty for Metastatic Spinal Lesions:A Systematic Review.Clin Spine Surg.2018;31(5):203-210. [18]王伟军.高黏度与低黏度骨水泥椎体成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折有效性的Meta分析[J].中华创伤杂志, 2018,34(9): 806-812.[19]陈秋洪,胡炳树,李杰,等.经皮椎体成形术治疗脊柱转移瘤的疗效评估[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2018,12(9):681-686.[20]Farrokhi M,Nouraei H,Kiani A.The Efficacy of Percutaneous Vertebroplasty in Pain Relief in Patients with Pathological Vertebral Fractures due to Metastatic Spinal Tumors.Iran Red Crescent Med J.2012;14(9):523-530.[21]Liang L,Chen X,Jiang W, et al.Balloon kyphoplasty or percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture? An updated systematic review and meta-analysis.Ann Saudi Med.2016;36(3):165-174.[22]He Z,Zhai Q,Hu M,et al.Bone cements for percutaneous vertebroplasty and balloon kyphoplasty: Current status and future developments.J Orthop Translat.2015;3(1):1-11.[23]Liu W,Zhou S,Wang S.Application of percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of multiple thoracic metastases. Oncol Lett.2015;9(6):2775-2780.[24]Guo D,Cai J,Zhang S,et al.Treating osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures with intraosseous vacuum phenomena using high-viscosity bone cement via bilateral percutaneous vertebroplasty. Medicine(Baltimore).2017;96(14):e6549.[25]Ate? A,Gemalmaz HC,Deveci MA,et al.Comparison of effectiveness of kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty in patients with osteoporotic vertebra fractures.Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc.2016;50(6):619-622.[26]张伟,杨金华,黄开,等.PKP与高粘度骨水泥PVP治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的疗效比较[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2017, 32(11):1138-1140.[27]曾森炎,季卫锋,董玉鹏,等.高粘度与低粘度骨水泥PVP治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨的Meta分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2018,33(3):240-243.[28]徐敏,张鸿升,王继,等.高黏度与低黏度骨水泥经皮椎体成形治疗骨质疏松椎体压缩性骨折的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究, 2017,21(34):5571-5576.[29]唐冲,吴四军,刘正,等.高粘度骨水泥经皮椎体成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的疗效分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2017, 27(8):720-726.[30]Yuan WH, Hsu HC,Lai KL.Vertebroplasty and balloon kyphoplasty versus conservative treatment for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: A meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore).2016;95(31):e4491.[31]Zeng TH,Wang YM,Yang XJ,et al.The clinical comparative study on high and low viscosity bone cement application in vertebroplasty.Int J Clin Exp Med.2015;8(10):18855-18860. |
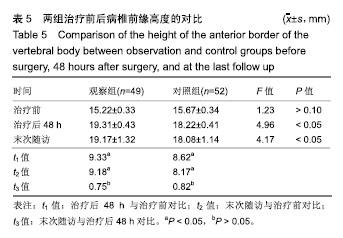
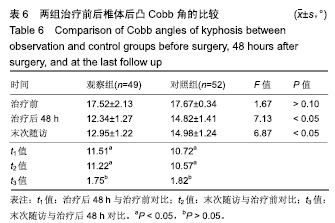
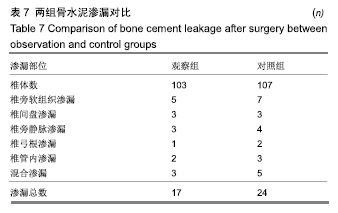
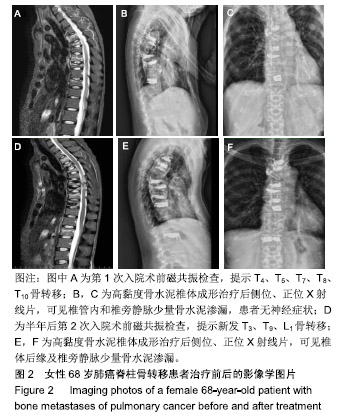
.jpg)
.jpg)