中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (20): 3268-3274.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1190
• 骨与关节循证医学 evidence-based medicine of the bone and joint • 上一篇 下一篇
跟骨骨折手术中静脉注射氨甲环酸:疗效与安全性的Meta分析
张 帅,葛文龙,李 昌,韩世翀,王 刚,任文军
- 吉林大学中日联谊医院,吉林省长春市 130033
Efficacy and safety of intravenous tranexamic acid in the operative treatment of calcaneal fractures: a meta-analysis
Zhang Shuai, Ge Wenlong, Li Chang, Han Shichong, Wang Gang, Ren Wenjun
- China-Japan Union Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun 130033, Jilin Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
氨甲环酸:是一种抑制纤维蛋白溶解的赖氨酸衍生物,通过与纤维蛋白的赖氨酸结合位点结合,竞争性抑制纤溶酶与纤维蛋白的结合,阻断纤维蛋白的溶解,从而达到止血目的,减少术中出血、术后引流量。目前,氨甲环酸已被广泛用于髋、膝关节置换中,并被证实有效、安全。
跟骨骨折术后切口并发症:由于跟骨手术切口周围的血供及解剖特点,使跟骨骨折术后切口并发症发生率较高,其与跟骨术后切口肿胀、切口下血肿和切口长期渗血有关。切口并发症的出现意味着更长的住院时间、更多的费用和更多的痛苦。
摘要
背景:跟骨骨折手术中使用氨甲环酸能减少术中及术后的失血量、降低切口并发症发生率并且不增加深静脉血栓等的风险,但目前国内外对氨甲环酸用于跟骨骨折治疗的相关研究较少,受样本量、研究水平等因素的影响,使研究结果存在差异和较低的可信度。
目的:通过Meta分析系统评价氨甲环酸静脉注射用于跟骨骨折手术的有效性及安全性。
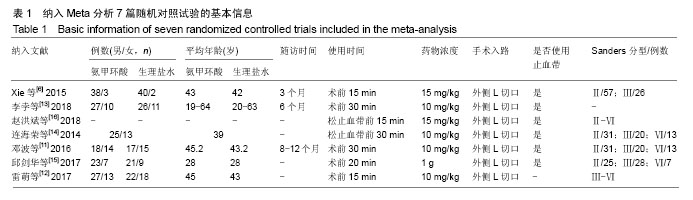
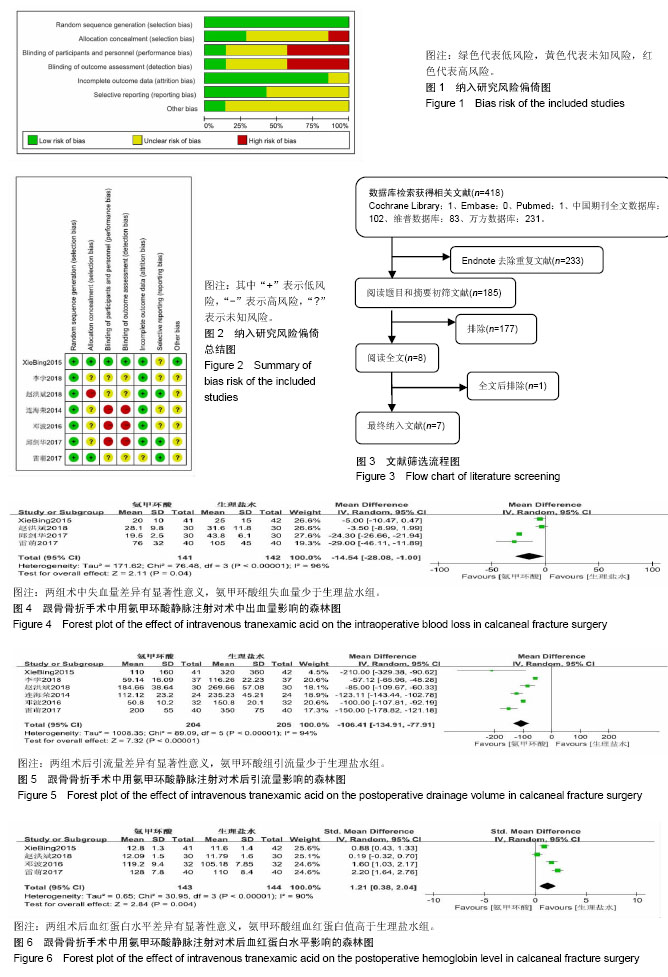
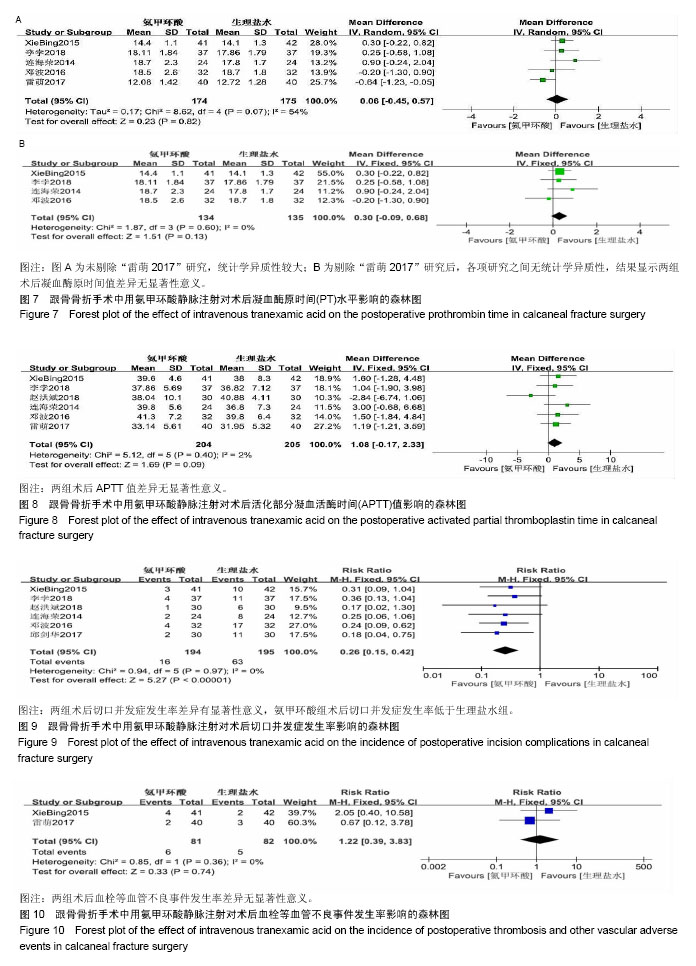
方法:计算机检索Cochrane Library、Embase、PubMed、中国期刊全文数据库(CNKI)、维普数据库(CQVIP)和万方数据库(CECDB),收集采用静脉注射氨甲环酸在跟骨骨折手术中应用的高质量前瞻性随机对照研究,对纳入文献进行质量评价、提取数据,采用Cochrane系统提供的RevMan5.3软件对氨甲环酸组与生理盐水组的术中失血量、术后引流量、术后血红蛋白值、术后凝血功能(凝血酶原时间及活化部分凝血活酶时间)、切口并发症及血管不良事件等进行Meta分析。
结果与结论:共纳入7篇随机对照试验,包括1篇英文文献,6篇中文文献,共纳入469例跟骨骨折患者,其中氨甲环酸组234例,生理盐水组235例。Meta分析结果显示:①氨甲环酸组术中出血量及术后引流量低于生理盐水组[MD=-14.54,95%CI(-25.08,-1.00),P=0.04;MD=-106.41,95%CI(-134.91,-77.91),P < 0.000 01];②氨甲环酸组术后血红蛋白值明显高于生理盐水组[SMD=1.21,95%CI(0.38,2.24),P=0.004];③在术后凝血功能方面,两组的术后凝血酶原时间及活化部分凝血活酶时间值比较差异无统计学意义[MD=0.30,95%CI(-0.09,0.68),P=0.13;MD=1.08,95%CI(-0.17,2.33),P=0.09];④氨甲环酸组术后切口并发症的发生率低于生理盐水组[RR=0.26,95%CI(0.15,0.42),P < 0.000 01],两组术后胃肠道出血、深静脉血栓、急性冠脉综合征等血管不良事件的发生率比较差异无统计学意义[RR=1.22,95%CI(0.39,3.83),P=0.74]。结果提示:氨甲环酸能有效减少跟骨骨折的手术失血量,降低跟骨骨折术后切口并发症,且氨甲环酸对患者凝血功能无影响,不增加血栓形成的风险,也并未增加相关血管不良事件的发生率,因此在跟骨骨折手术中应用氨甲环酸是安全有效的。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-5663-5369(张帅)
中图分类号:
.jpg)