中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (6): 883-887.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1537
• 组织工程口腔材料 tissue-engineered oral materials • 上一篇 下一篇
牙科烤瓷合金对金黄地鼠颊囊黏膜中凋亡相关蛋白表达的影响
陈 润1,2,邱冰妍3,江 磊1,2,潘 宇1,4,王颖卉1,2,程 辉1,2,4
- 1福建医科大学附属口腔医院修复科,福建省福州市 350002;2福建医科大学口腔医学研究院,福建省福州市 350002;3福建省级机关医院口腔科,福建省福州市 350001;4福建医科大学口腔医学美学与生物力学研究中心,福建省福州市 350002
Effect of dental ceramic alloys on the expression of apoptosis-related signal proteins in the oral buccal mucosa of golden hamsters
Chen Run1, 2, Qiu Bingyan3, Jiang Lei1, 2, Pan Yu1, 4, Wang Yinghui1, 2, Cheng Hui1, 2, 4
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, Hospital of Stomatology, Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou 350002, Fujian Province, China; 3Departmetn of Stomatology, Fujian Provincial Governmental Hospital, Fuzhou 350001, Fujian Province, China; 2Institute of Stomatology, 4Center for Stomatology Aesthetics and Biomechanics, Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou 350002, Fujian Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:

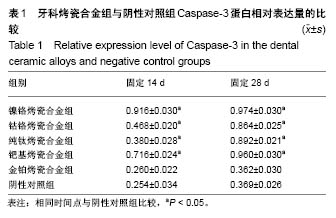
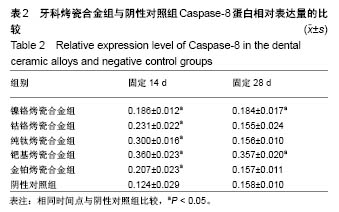
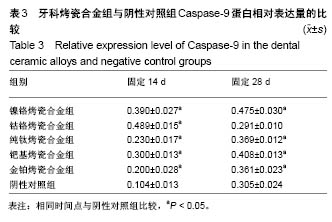
结果与结论:①固定14,28 d时,金铂烤瓷合金组Caspase-3蛋白表达量与阴性对照组比较无明显差异(P > 0.05),其余4种烤瓷合金组Caspase-3蛋白表达量高于阴性对照组(P < 0.05);②固定14 d时,各烤瓷合金组Caspase-8蛋白表达量均高于阴性对照组(P < 0.05);固定28 d时,镍铬烤瓷合金组、钯基烤瓷合金组Caspase-8蛋白表达量高于阴性对照组(P < 0.05),其余烤瓷合金组Caspase-3蛋白表达量与阴性对照组比较无明显差异(P > 0.05);③固定14 d时,各烤瓷合金组Caspase-9蛋白表达量均高于阴性对照组(P < 0.05);固定28 d时,钴铬合金组Caspase-9蛋白表达量与阴性对照组比较无明显差异(P > 0.05),其余烤瓷合金组Caspase-9蛋白表达量均高于阴性对照组(P < 0.05);④结果表明,5种牙科烤瓷合金均不同程度引起凋亡相关信号分子的表达增加。
ORCID: 0000-0002-2601-1205(陈润)
中图分类号:

.jpg)



