| [1] Myers SR, Eijer H, Ganz R.Anterior femoroacetabular impingement after periacetabular osteotomy. Clin Orthop Relat Res.1999;(363):93-99.[2] Eijer H, Myers SR, Ganz R.Anterior femoroacetabular impingement after femoral neck fractures.J Orthop Trauma. 2001;15(7): 475-481.[3] Ganz R,Parvizi J,Beck M,et al.Femoroacetabular impingement: a cause for osteoarthritis of the hip.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2003;(417):112-120.[4] Sangal RB, Waryasz GR, Schiller JR.Femoroacetabular impingement: a review of current concepts.R I Med J (2013). 2014;97(11):33-38.[5] Amanatullah DF, Antkowiak T, Pillay K, et al. Femoroacetabular impingement: current concepts in diagnosis and treatment. Orthopedics.2015l38(3):185-199.[6] Khan M, Bedi A, Fu F, Karlsson J, et al.New perspectives on femoroacetabular impingement syndrome.Nat Rev Rheumatol.2016;12(5):303-310.[7] Monazzam S, Bomar JD, Dwek JR,et al.Development and prevalence of femoroacetabular impingement-associated morphology in a paediatric and adolescent population: a CT study of 225 patients.Bone Joint J.2013;95-B(5): 598-604.[8] Ramachandran M, Azegami S, Hosalkar HS.Current concepts in the treatment of adolescent femoroacetabular impingement. J Child Orthop.2013;7(2):79-90.[9] Swenson KM, Erickson J, Peters C, et al.Hip pain in young adults: diagnosing femoroacetabular impingement. JAAPA. 2015;28(9):39-45.[10] Pathy R, Sink EL.Femoroacetabular impingement in children and adolescents. Curr Opin Pediatr.2016;28(1): 68-78.[11] Chaudhry H, Ayeni OR. The etiology of femoroacetabular impingement: what we know and what we don't. Sports Health.2014;6(2):157-161.[12] Leunig M, Beaule PE, Ganz R, et al. The concept of Femoroacetabular Impingement: Current status and future perspectives. Clin Orthop Relat Res.2009;467(3):616-622.[13] Hartofilakidis G, Bardakos NV, Babis GC, et al. An examination of the association between different morphotypes of femoroacetabular impingement in asymptomatic subjects and the development of osteoarthritis of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011;93(5):580-586.[14] Papalia R, Del Buono A, Franceschi F, et al. Femoroacetabular impingement syndrome management: arthroscopy or open surgery? Int Orthop.2012;36(5):903-914.[15] Collins JA, Ward JP, Youm T. Is prophylactic surgery for femoroacetabular impingement indicated? A systematic review.Am J Sports Med.2014;42(12):3009-3015.[16] Kuhns BD, Weber AE, Levy DM, et al.The Natural History of Femoroacetabular Impingement.Front Surg.2015;2:58.[17] Packer JD, Safran MR.The etiology of primary femoroacetabular impingement: genetics or acquired deformity? J Hip Preserv Surg.2015;2(3):249-257.[18] Zadpoor AA.Etiology of Femoroacetabular Impingement in Athletes: A Review of Recent Findings. Sports Med. 2015; 45(8):1097-1106.[19] Nepple JJ, Clohisy JC•ANCHOR Study Group Members. Evolution of Femoroacetabular Impingement Treatment: The ANCHOR Experience.Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2017; 46(1): 28-34.[20] Siebenrock KA, Fiechter R, Tannast M, et al.Experimentally induced cam impingement in the sheep hip. J Orthop Res. 2013;31(4):580-587.[21] Adolphe M, Parodi AL Ethical issues in animal experimentation. Bull Acad Natl Med. 2009;193(8):1803-1804.[22] Beck M, Kalhor M, Leunig M, et al.Hip morphology influences the pattern of damage to the acetabular cartilage: femoroacetabular impingement as a cause of early osteoarthritis of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87(7): 1012-1018.[23] Mankin HJ.The reaction of articular cartilage to injury and osteoarthritis (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1974;291(24): 1285-1292.[24] Mankin HJ.The reaction of articular cartilage to injury and osteoarthritis (second of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1974;291 (25):1335-1340.[25] van der Sluijs JA, Geesink RG, van der Linden AJ, et al.The reliability of the Mankin score for osteoarthritis.J Orthop Res. 1992;10(1): 58-61.[26] Pollard TC, Villar RN, Norton MR, et al. Genetic influences in the aetiology of femoroacetabular impingement: a sibling study. J Bone Joint Surg Br.2010; 92(2):209-216.[27] Leunig M, Slongo T, Ganz R. Subcapital realignment in slipped capital femoral epiphysis: surgical hip dislocation and trimming of the stable trochanter to protect the perfusion of the epiphysis. Instr Course Lect.2008;57:499-507.[28] Banerjee P, McLean CR. Femoroacetabular impingement:a review of diagnosis and management. Curr Rev Musculosketlet Med. 2011;(1):23-32.[29] Fraitzl CR, Nelitz M, Cakir B, et al. Transfixation in slipped capital femoral epiphysis: long-term evidence for femoroacetabular impingement. Z Orthop Unfall. 2009;147(3): 334-340.[30] Laborie LB, Lehmann TG, Engesæter IØ, et al. Prevalence of radiographic findings thought to be associated with femoroacetabular impingement in a population-based cohort of 2081 healthy young adults. Radiology. 2011;260(2): 494-502.[31] Ramachandran M, Azegami S,Hosalkar HS. Current concepts in treatment of adolescent femoroacetabular impingement. J Child Orthop. 2013;7(2):79-90.[32] Tannast M, Goricki D, Beck M, et al.Hip damage occurs at the zone of femoroacetabular impingement. Clin Orthop Relat Res.2008;466(2): 273-280.[33] Crespo Rodríguez AM, de Lucas Villarrubia JC, Pastrana Ledesma MA, et al.Diagnosis of lesions of the acetabular labrum, of the labral-chondral transition zone, and of the cartilage in femoroacetabular impingement: Correlation between direct magnetic resonance arthrography and hip arthroscopy.Radiologia. 2015;57(2):131-141.[34] Meermans G, Konan S, Haddad FS, et al.Prevalence of acetabular cartilage lesions and labral tears in femoroacetabular impingement.Acta Orthop Belg. 2010;76(2): 181-188.[35] Flannelly J, Chambers MG, Dudhia J, et al.Metalloproteinase and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase expression in the murine STR/ort model of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2002;10(9):722-733.[36] Staines KA, Madi K, Mirczuk SM,et al.Endochondral Growth Defect and Deployment of Transient Chondrocyte Behaviors Underlie Osteoarthritis Onset in a Natural Murine Model. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016;68(4):880-891.[37] Akagi R, Sasho T, Saito M, Yet al.Effective knock down of matrix metalloproteinase-13 by an intra-articular injection of small interfering RNA (siRNA) in a murine surgically-induced osteoarthritis model.J Orthop Res. 2014;32(9):1175-1180.[38] Ferrell WR, Kelso EB, Lockhart JC, et al.Protease-activated receptor 2: a novel pathogenic pathway in a murine model of osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis.2010;69(11):2051-2054.[39] Lim NH, Meinjohanns E, Meldal M, et al.In vivo imaging of MMP-13 activity in the murine destabilised medial meniscus surgical model of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2014;22(6):862-868.[40] Botter SM,van Osch GJ,Waarsing JH,et al.Quantification of subchondral bone changes in a murine osteoarthritis model using micro-CT. Biorheology.2006;43(3-4):379-388.[41] Haque Bhuyan MZ,Tamura Y,Sone E,et al.The intra-articular injection of RANKL-binding peptides inhibits cartilage degeneration in a murine model of osteoarthritis. J Pharmacol Sci.2017;134(2):124-130.[42] Leunig M, Beck M, Kalhor M, et al. Fibrocystic changes at anterosuperior femoral neck: prevalence in hips with femoroacetabular impingement. Radiology. 2005;236(1): 237-246.[43] Dimmick S, Stevens KJ, Brazier D, et al. Femoroacetabular impingement. Radiol Clin North Am. 2013;51(3):337-352. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
股骨髋臼撞击症(femoroacetabular impingement,FAI):是近年来认识的因股骨头、颈或髋臼较细微结构异常引起的一类疾病。现已表明,所谓原发性髋关节骨性关节炎其中有相当比例是因FAI引起的。股骨颈部骨性突出或髋臼边缘异常,在髋关节旋转活动时(特别是屈髋与内旋的终末)引起反复的微创,最终导致髋臼盂唇和关节软骨损伤而引起退行性关节炎。
髋臼:髋骨(acetabulum)是人身体的一个骨头,由髂、坐、耻三骨组的体合成。窝内半月形的关节面称月状面(lunate surface)。窝的中央未形成关节面的部分,称髋臼窝。髋臼边缘下部的缺口称髋臼切迹。
文题释义:
股骨髋臼撞击症(femoroacetabular impingement,FAI):是近年来认识的因股骨头、颈或髋臼较细微结构异常引起的一类疾病。现已表明,所谓原发性髋关节骨性关节炎其中有相当比例是因FAI引起的。股骨颈部骨性突出或髋臼边缘异常,在髋关节旋转活动时(特别是屈髋与内旋的终末)引起反复的微创,最终导致髋臼盂唇和关节软骨损伤而引起退行性关节炎。
髋臼:髋骨(acetabulum)是人身体的一个骨头,由髂、坐、耻三骨组的体合成。窝内半月形的关节面称月状面(lunate surface)。窝的中央未形成关节面的部分,称髋臼窝。髋臼边缘下部的缺口称髋臼切迹。.jpg) 文题释义:
股骨髋臼撞击症(femoroacetabular impingement,FAI):是近年来认识的因股骨头、颈或髋臼较细微结构异常引起的一类疾病。现已表明,所谓原发性髋关节骨性关节炎其中有相当比例是因FAI引起的。股骨颈部骨性突出或髋臼边缘异常,在髋关节旋转活动时(特别是屈髋与内旋的终末)引起反复的微创,最终导致髋臼盂唇和关节软骨损伤而引起退行性关节炎。
髋臼:髋骨(acetabulum)是人身体的一个骨头,由髂、坐、耻三骨组的体合成。窝内半月形的关节面称月状面(lunate surface)。窝的中央未形成关节面的部分,称髋臼窝。髋臼边缘下部的缺口称髋臼切迹。
文题释义:
股骨髋臼撞击症(femoroacetabular impingement,FAI):是近年来认识的因股骨头、颈或髋臼较细微结构异常引起的一类疾病。现已表明,所谓原发性髋关节骨性关节炎其中有相当比例是因FAI引起的。股骨颈部骨性突出或髋臼边缘异常,在髋关节旋转活动时(特别是屈髋与内旋的终末)引起反复的微创,最终导致髋臼盂唇和关节软骨损伤而引起退行性关节炎。
髋臼:髋骨(acetabulum)是人身体的一个骨头,由髂、坐、耻三骨组的体合成。窝内半月形的关节面称月状面(lunate surface)。窝的中央未形成关节面的部分,称髋臼窝。髋臼边缘下部的缺口称髋臼切迹。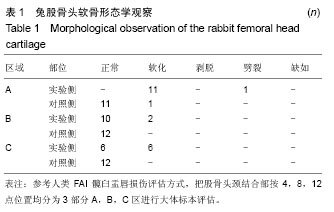
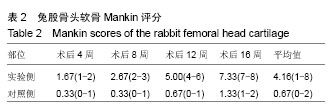
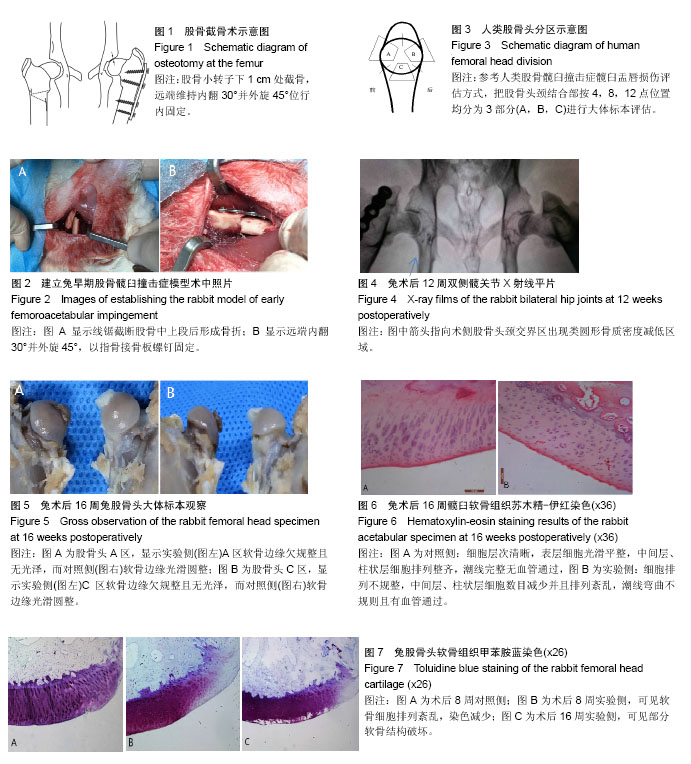
.jpg) 文题释义:
股骨髋臼撞击症(femoroacetabular impingement,FAI):是近年来认识的因股骨头、颈或髋臼较细微结构异常引起的一类疾病。现已表明,所谓原发性髋关节骨性关节炎其中有相当比例是因FAI引起的。股骨颈部骨性突出或髋臼边缘异常,在髋关节旋转活动时(特别是屈髋与内旋的终末)引起反复的微创,最终导致髋臼盂唇和关节软骨损伤而引起退行性关节炎。
髋臼:髋骨(acetabulum)是人身体的一个骨头,由髂、坐、耻三骨组的体合成。窝内半月形的关节面称月状面(lunate surface)。窝的中央未形成关节面的部分,称髋臼窝。髋臼边缘下部的缺口称髋臼切迹。
文题释义:
股骨髋臼撞击症(femoroacetabular impingement,FAI):是近年来认识的因股骨头、颈或髋臼较细微结构异常引起的一类疾病。现已表明,所谓原发性髋关节骨性关节炎其中有相当比例是因FAI引起的。股骨颈部骨性突出或髋臼边缘异常,在髋关节旋转活动时(特别是屈髋与内旋的终末)引起反复的微创,最终导致髋臼盂唇和关节软骨损伤而引起退行性关节炎。
髋臼:髋骨(acetabulum)是人身体的一个骨头,由髂、坐、耻三骨组的体合成。窝内半月形的关节面称月状面(lunate surface)。窝的中央未形成关节面的部分,称髋臼窝。髋臼边缘下部的缺口称髋臼切迹。