中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (30): 4855-4863.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0946
• 生物材料综述 biomaterial review • 上一篇 下一篇
羟基磷灰石类陶瓷在骨组织工程中的研究与更广泛应用
毛文文,茹江英
- 扬州市第一人民医院骨科,江苏省扬州市 225000
-
收稿日期:2018-04-09出版日期:2018-10-28发布日期:2018-10-28 -
通讯作者:茹江英,主任医师,扬州大学附属医院骨科,江苏省扬州市 225000 -
作者简介:毛文文,男,1992年生,江苏省扬州市人,汉族,扬州大学医学院在读硕士,主要从事骨关节损伤研究。 -
基金资助:江苏省卫计委面上项目(H201662);江苏省青年医学重点人才项目(QNRC2016356);扬州市“绿扬金凤计划”资助项目(yzlyjfjh2015YB106)
Hydroxyapatite ceramics in bone tissue engineering: research and extensive applications
Mao Wen-wen, Ru Jiang-ying
- Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Yangzhou University (Yangzhou First People’s Hospital), Yangzhou 225000, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2018-04-09Online:2018-10-28Published:2018-10-28 -
Contact:Ru Jiang-ying, Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Yangzhou University (Yangzhou First People’s Hospital), Yangzhou 225000, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Mao Wen-wen, Master candidate, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Yangzhou University (Yangzhou First People’s Hospital), Yangzhou 225000, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:the General Project of Jiangsu Provincial Health and Family Planning Committee, No. H201662; the Key Young Talent Project of Jiangsu Province, No. QNRC2016356; the Green Poplar/Golden Phoenix Plan of Yangzhou Municipality, No. yzlyjfjh2015YB106
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
背景:羟基磷灰石类陶瓷与正常人体骨组织中的结构和化学成分十分相近,具有良好的骨诱导骨传导活性及生物相容性,成为骨组织工程中支架的良好材料之一。 目的:总结羟基磷灰石类陶瓷材料制备方式、特性及作为骨组织代替物的作用机制和临床应用新进展。 方法:以“bioceramics,hydroxylapatite,calcium phosphate,tricalcium phosphate,bone tissue engineering”为检索词,应用计算机检索PubMed数据库2015至2017年发表的相关文献。 结果与结论:羟基磷灰石属于六方晶系,是构成天然骨组织中无机成分的主要组成部分,其中呈六方排列的Ca2+、PO43-、OH-易于被许多阳离子和阴离子取代基替换,从而改变羟基磷灰石的机械强度、溶解速率、生物相容性等一些列理化及生物活性。制备羟基磷灰石陶瓷材料的方法分为湿法和干法两大类,根据实际需要与不同方法的优缺点往往是多种制备方法相结合。羟基磷灰石类陶瓷具备的孔隙结构有利于营养物质和骨生长必要成分的输送,以及细胞代谢废物的排除,并且微小孔隙会引起各种内源性骨生长因子在内孔表面的高度吸附和积累,刺激间充质干细胞分化进入成骨细胞,进一步促进发挥骨诱导活性。近年来虽然生物陶瓷材料在临床上作为植入物涂层、缓释药物的载体、骨移植物代替材料等被应用,但在临床方面广泛运用还面临着许多问题与挑战。
ORCID: 0000-0002-0850-9229(毛文文)
中图分类号:
引用本文
毛文文,茹江英. 羟基磷灰石类陶瓷在骨组织工程中的研究与更广泛应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2018, 22(30): 4855-4863.
Mao Wen-wen, Ru Jiang-ying. Hydroxyapatite ceramics in bone tissue engineering: research and extensive applications[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(30): 4855-4863.

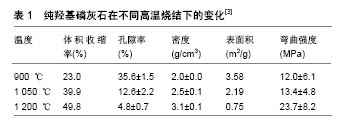
2.3 羟基磷灰石类陶瓷材料的制备及孔隙结构 至今随着生产技术和设备不断的更新换代,羟基磷灰石的制备方法已经达数十余种,其中主要分为湿法和干法两大类。湿法主要有:水热法、沉淀法、溶胶-凝胶法等。干法主要有:烧结法、喷雾法、超声波法、仿生合成法等。根据植入的环境需要,很多时候是两种或多种制备方法相结合,来生产出满足需要的陶瓷类植入材料。每种方法优缺点也各有不同,如沉淀法,生产过程简单,操作温度低,以合理的成本达到高产率,但有时不完全的反应和沉淀,导致化学计量学变化,导致混入不需要的杂质。溶胶-凝胶法可将各种分子均匀混合,与其他方法相比可较好地产出纳米尺寸的颗粒,但起始材料非常昂贵,而且形成的前体通常对湿度极其敏感,增添了生产的难度[22]。不同方法制造出的陶瓷支架,其孔隙率、孔径结构、比表面积、致密化行为、材料的收缩和形态等也不同,这直接影响到了生物活性的表达和具体适用范围。如烧结法的优势是在烧结后压缩更多的空间,得到较高的孔隙率,但孔径和孔与孔间的互相连通性(大部分孔径小于10 μm以下的微孔,在烧结温度在1 200 ℃或以上时关闭,这也是大多经高温烧结法制备的磷酸钙多孔陶瓷不能诱导异位骨形成的主要原因),产物的尺寸难以掌控[23]。对于纯羟基磷灰石,烧结温度在900,1 050,1 200 ℃时,随着温度升高(β-磷酸三钙相逐渐增加),晶粒明显生长,致使其体积逐步扩大,平均晶粒尺寸约800 nm,孔隙率、表面积、弯曲强度变化见表1[3,12]。
| [1] Capanema NSV,Mansur AAP,Carvalho SM,et al.Niobium-Doped Hydroxyapatite Bioceramics: Synthesis, Characterization and In Vitro Cytocompatibility. Materials(Basel).2015;8(7): 4191-4209.[2] Tamaddon M,Samizadeh S,Wang L,et al.Intrinsic Osteoinductivity of Porous Titanium Scaffold for Bone Tissue Engineering.Int J Biomater. 2017.2017:5093063.[3] Fuh LJ,Huang YJ,Chen WC,et al.Preparation of micro-porous bioceramic containing silicon-substituted hydroxyapatite and beta-tricalcium phosphate.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;75: 798-806.[4] Vollmer NL,Spear JR,Ayers RA.Antimicrobial activity and biologic potential of silver-substituted calcium phosphate constructs produced with self-propagating high-temperature synthesis.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2016;27(6):104.[5] Gomes S,Kaur A,Grenèche JM,et al.Atomic scale modeling of iron-doped biphasic calcium phosphate bioceramics.Acta Biomater. 2017;50:78-88.[6] Blum C,Brückner T,Ewald A,et al.Mg:Ca ratio as regulating factor for osteoclastic in vitro resorption of struvite biocements. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;73:111-119.[7] Ke D,Dernell W,Bandyopadhyay A,et al.Doped tricalcium phosphate scaffolds by thermal decomposition of naphthalene: Mechanical properties and in vivo osteogenesis in a rabbit femur model.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2015;103(8):1549-1559.[8] Schumacher TC,Treccani L,Rezwan K.Effect of silica on porosity, strength, and toughness of pressureless sintered calcium phosphate–zirconia bioceramics.Biomed Mater. 2015;10(4):045020.[9] Denry I,Kuhn LT.Design and characterization of calcium phosphate ceramic scaffolds for bone tissue engineering.Dent Mater. 2016;32(1): 43-53.[10] Mbarki M,Sharrock P,Fiallo M,et al.Hydroxyapatite bioceramic with large porosity. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;76:985-990.[11] Yatongchai C,Placek LM,Curran DJ,et al.Investigating the addition of SiO2–CaO–ZnO–Na2O–TiO2 bioactive glass to hydroxyapatite: Characterization, mechanical properties and bioactivity. J Biomater Appl.2015;30(5):495-511.[12] Lindner M,Bergmann C,Telle R,et al.Calcium phosphate scaffolds mimicking the gradient architecture of native long bones.J Biomed Mater Res A.2014;102(10):3677-3684.[13] Philippart A,Boccaccini AR,Fleck C,et al.Toughening and functionalization of bioactive ceramic and glass bone scaffolds by biopolymer coatings and infiltration: a review of the last 5 years.Expert Rev Med Devices.2015;12(1):93-111.[14] Duan S,Feng P,Gao C,et al.Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties Improvement in Liquid-Phase-Sintered Hydroxyapatite by Laser Sintering.Materials(Basel). 2015;8(3):1162-1175.[15] Yao MZ,Huang-Fu MY,Liu HN,et al.Fabrication and characterization of drug-loaded nano-hydroxyapatite/polyamide 66 scaffolds modified with carbon nanotubes and silk fibroin. Int J Nanomedicine. 2016;11: 6181-6194.[16] Kunert-Keil C,Scholz F,Gedrange T,et al.Comparative study of biphasic calcium phosphate with beta-tricalcium phosphate in rat cranial defects--A molecular-biological and histological study. Ann Anat.2015;199:79-84.[17] Xie L,Yu H,Deng Y,et al.Preparation, characterization and in vitro dissolution behavior of porous biphasic alpha/beta-tricalcium phosphate bioceramics. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016;59: 1007-1015.[18] de Wild M,Amacher F,Bradbury CR,et al.Investigation of structural resorption behavior of biphasic bioceramics with help of gravimetry, muCT, SEM, and XRD.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2016; 104(3):546-553.[19] Lu J,Descamps M,Dejou J,et al.The biodegradation mechanism of calcium phosphate biomaterials in bone.J Biomed Mater Res. 2002; 63(4):408-412.[20] Roldán JC,Klünter T,Schulz P,et al.Bone Morphogenetic Protein-7 Enhances Degradation of Osteoinductive Bioceramic Implants in an Ectopic Model. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2017;5(6):e1375.[21] Bouler JM,Pilet P,Gauthier O,et al.Biphasic calcium phosphate ceramics for bone reconstruction: A review of biological response.Acta Biomater.2017;53:1-12.[22] Ghosh R,Sarkar R.Synthesis and characterization of sintered beta-tricalcium phosphate: A comparative study on the effect of preparation route.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016;67:345-352.[23] Wang J,Chen Y,Zhu X,et al.Effect of phase composition on protein adsorption and osteoinduction of porous calcium phosphate ceramics in mice.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2014;102(12):4234-4243.[24] Despang F,Bernhardt A,Lode A,et al.Synthesis and physicochemical, in vitro and in vivo evaluation of an anisotropic, nanocrystalline hydroxyapatite bisque scaffold with parallel-aligned pores mimicking the microstructure of cortical bone.J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2015; 9(12):E152-166.[25] Feng P,Deng Y,Duan S,et al.Liquid phase sintered ceramic bone scaffolds by combined laser and furnace.Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(8): 14574-14590.[26] Civinini R,Capone A,Carulli C,et al.The kinetics of remodeling of a calcium sulfate/calcium phosphate bioceramic.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2017;28(9):137.[27] Rabadan-Ros R,VelásquezPA,Meseguer-Olmo L,et al.Morphological and Structural Study of a Novel Porous Nurse's A Ceramic with Osteoconductive Properties for Tissue Engineering. Materials (Basel). 2016;9(6).pii: E474. doi: 10.3390/ma9060474.[28] Sun H,Yang HL.Calcium phosphate scaffolds combined with bone morphogenetic proteins or mesenchymal stem cells in bone tissue engineering.Chin Med J (Engl). 2015;128(8):1121-1127.[29] Maté Sánchez de Val JE,Calvo-Guirado JL,Gómez-Moreno G,et al.Influence of hydroxyapatite granule size, porosity, and crystallinity on tissue reaction in vivo. Part A: synthesis, characterization of the materials, and SEM analysis.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2016;27(11): 1331-1338.[30] Ros-Tárraga P, Mazón P, Rodríguez MA,et al.Novel Resorbable and Osteoconductive Calcium Silicophosphate Scaffold Induced Bone Formation. Materials(Basel). 2016;9(9).pii: E785. doi:10.3390/ma9090785. [31] Maji K,Dasgupta S,Kundu B,et al.Development of gelatin-chitosan- hydroxyapatite based bioactive bone scaffold with controlled pore size and mechanical strength.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed.2015;26(16): 1190-1209.[32] Rustom LE,Boudou T,Lou S,et al.Micropore-induced capillarity enhances bone distribution in vivo in biphasic calcium phosphate scaffolds.Acta Biomater.2016;44:144-154.[33] Bianchi M,Urquia Edreira ER,Wolke JG,et al.Substrate geometry directs the in vitro mineralization of calcium phosphate ceramics.Acta Biomater.2014;10(2):661-669.[34] Lobo SE,Glickman R,da Silva WN,et al.Response of stem cells from different origins to biphasic calcium phosphate bioceramics.Cell Tissue Res.2015;361(2):477-495.[35] Yu X,Tang X1,Gohil SV,et al.Biomaterials for Bone Regenerative Engineering.Adv Healthc Mater. 2015;4(9):1268-1285.[36] Roohani-Esfahani SI,No YJ,Lu Z,et al.A bioceramic with enhanced osteogenic properties to regulate the function of osteoblastic and osteocalastic cells for bone tissue regeneration. Biomed Mater.2016; 11(3):035018.[37] He F,Zhang J,Yang F,et al.In vitro degradation and cell response of calcium carbonate composite ceramic in comparison with other synthetic bone substitute materials.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2015;50:257-265.[38] Cushnie EK,Ulery BD,Nelson SJ,et al.Simple Signaling Molecules for Inductive Bone Regenerative Engineering.PLoS One. 2014;9(7): e101627.[39] Harada N,Watanabe Y,Sato K,et al.Bone regeneration in a massive rat femur defect through endochondral ossification achieved with chondrogenically differentiated MSCs in a degradable scaffold. Biomaterials.2014;35(27):7800-7810.[40] Huang X,Bai S,Lu Q,et al.Osteoinductive-nanoscaled silk/HA composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering application. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2015;103(7):1402-1414.[41] Tian J,Qi W,Zhang Y,et al.Bioaggregate Inhibits Osteoclast Differentiation, Fusion, and Bone Resorption In Vitro.J Endod. 2015; 41(9):1500-1506.[42] Tae Young A,Kang JH,Kang DJ,et al.Interaction of stem cells with nano hydroxyapatite-fucoidan bionanocomposites for bone tissue regeneration.Int J Biol Macromol. 2016;93(PtB):1488-1491.[43] Arcos D,Vallet-Regí M.Bioceramics for drug delivery.Acta Materialia. 2013;61(3):890-911.[44] Parent M,Baradari H,Champion E,et al.Design of calcium phosphate ceramics for drug delivery applications in bone diseases: A review of the parameters affecting the loading and release of the therapeutic substance.J Control Release. 2017;252:1-17.[45] Zhu M,Li K,Zhu Y,et al.3D-printed hierarchical scaffold for localized isoniazid/rifampin drug delivery and osteoarticular tuberculosis therapy. Acta Biomater.2015;16:145-55.[46] Feng DS,Shi J,Wang XJ,et al.Hollow hybrid hydroxyapatite microparticles with sustained and pH-responsive drug delivery properties. RSC Adv.2013;3(47):24975.[47] Guimond-Lischer S,Ren Q,Braissant O,et al.Vacuum plasma sprayed coatings using ionic silver doped hydroxyapatite powder to prevent bacterial infection of bone implants. Biointerphases. 2016;11(2): 011012.[48] Brooks BD,Sinclair KD,Davidoff SN,et al.Molded polymer-coated composite bone void filler improves tobramycin controlled release kinetics.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2014;102(5): 1074-1083.[49] Zheng X,Shi Y,Chen Y,et al.Novel impurity-free hexagonal hydroxyapatite nanotubes for local delivery of antibiotics in orthopedic surgery: in vitro release validation.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(2): 2628-2634.[50] Chia HN,Wu BM.Recent advances in 3D printing of biomaterials.J Biol Eng.2015;9:4. |
| [1] | 刘江锋. 纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66复合材料联合锁定钢板治疗股骨骨纤维异常增殖症[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(4): 542-547. |
| [2] | 吴子健, 胡昭端, 谢有琼, 王 峰, 李 佳, 李柏村, 蔡国伟, 彭 锐. 3D打印技术与骨组织工程研究文献计量及研究热点可视化分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [3] | 李 黎, 马 力. 磁性壳聚糖微球固定化乳糖酶及其酶学性质[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(4): 576-581. |
| [4] | 李晓壮, 段 浩, 王伟舟, 唐志宏, 王旸昊, 何 飞. 骨组织工程材料治疗骨缺损疾病在体内实验中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [5] | 刘 鋆, 杨 龙, 王伟宇, 周玉虎, 吴 颖, 卢 涛, 舒莉萍, 马敏先, 叶 川. 聚3-羟基丁酸酯4-羟基丁酸酯/聚乙二醇/氧化石墨烯组织工程支架的制备和性能评价[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(22): 3466-3472. |
| [6] | 李鑫平, 崔秋菊, 曾曙光, 冉高英, 张兆强, 刘显文, 方 炜, 徐帅妹. β-磷酸三钙/壳聚糖水凝胶改性对牙髓干细胞生长与矿化的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(22): 3493-3499. |
| [7] | 何 林, 吴 稀, 何 淞, 杨 森. 经聚多巴胺涂层的羟基磷灰石生物陶瓷具有亲水性与细胞黏附性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(22): 3540-3544. |
| [8] | 周安琪, 唐渝菲, 吴秉峰, 向 琳. 骨膜组织工程设计:共性与个性的结合[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(22): 3551-3557. |
| [9] | 陈 崧, 何远丽, 谢雯佳, 钟林娜, 王 剑. 磷酸钙纳米颗粒药物递送系统在骨组织工程研究与应用中的优势[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(22): 3565-3570. |
| [10] | 张振华, 刘姿辰, 禹宝庆. 聚己内酯及其复合材料在组织工程骨构建中的地位与问题[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(22): 3571-3577. |
| [11] | 郎丽敏, 何 生, 姜增誉, 胡奕奕, 张智星, 梁敏茜. 导电复合材料在心肌梗死组织工程治疗领域的应用进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(22): 3584-3590. |
| [12] | 许 辉, 康冰心, 钟 声, 高晨鑫, 赵 翅, 邱国伟, 孙松涛, 解 骏, 肖涟波, 施 杞. 点按局部腧穴与坐位调膝法联用治疗膝关节骨关节炎:随机对照研究[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(2): 216-221. |
| [13] | 汪 鎏, 宋东哲, 黄定明. 骨形态发生蛋白9调控干细胞分化与骨再生[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(19): 3064-3070. |
| [14] | 王任先, 曹晶晶, 王宏刚, 万 奔, 刘巍峰. 几种分散剂对纳米羟基磷灰石团聚、细胞内分布和细胞增殖的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(16): 2500-2505. |
| [15] | 王宏远, 王 薇, 杨树青, 窦丽鑫, 刘利军. 多孔氮氧生物玻璃骨修复支架的制备及性能[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(16): 2521-2527. |
1.1 资料来源 以“bioceramics,hydroxylapatite,calcium phosphate,tricalcium phosphate,bone tissue engineering”为检索词,应用计算机检索PubMed数据库2015至2017年发表的相关文献。
1.3 文献质量评价 初步检索得到英文文献1 397篇,排除与研究相关性低、研究内容陈旧及重复性文献,最终纳入50篇符合标准的文献。
.jpg)
虽然生物陶瓷材料具有诸多好处,但仍有许多问题等待去解决,如:具有生长因子的CaP涂层技术,涂料与基材之间整合的高成本限制了这个技术在商业规模上广泛应用;在对应的不同植入部位及所需目的上,陶瓷制作的孔径大小及孔隙度尚未有统一标准;作为骨移植代替材料,尽管可联合的聚合物或其他添加剂种类有很多,但是相当一部分处于试验阶段,即使是应用于临床阶段的产品,仍缺乏长期临床随访来评测其远期的预后;还有3D打印技术虽有其优势,但是降低生产成本也是眼下需要解决的问题。具有药物递送能力的支架仍在研究中,以便针对特定情况的应用(特定生物活性分子,治疗类型,手术类型,患者的特定需求,抗生素和生长因子的双重递送)开发优化的载体。除此之外支架在体内或体外支架植入时,还要考虑所用聚合物降解,弥合临床应用与基础研究的差距。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||