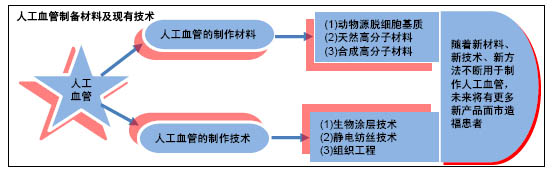
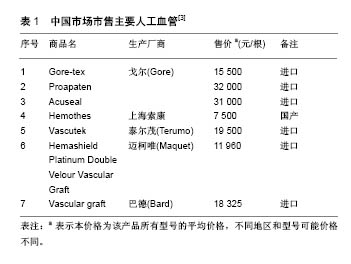
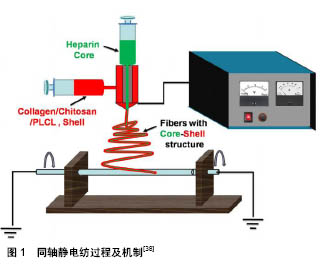
| [1] 王维慈,欧阳晨曦,周飞,等.高分子材料小口径人工血管的相关研究[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2008,12(1):125-128.[2] 张家庆,王武军,闫玉生.小口径人工血管材料应用进展[J].实用医学杂志,2014,130(21):3520-3521.[3] Begovac PC,Thomson RC,Fisher JL,et al.Improvements in GORE-TEX1 vascular graft performance by Carmeda1 bioactive surface heparin immobilization.Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2003; 25:432-437.[4] McClurken ME,McHaney JM,Colone W.Physical Properties and Test Methods for Expanded Polytetra fluoroethylene (PTFE) Grafts.Vascular Graft Update: Safety and Performance.ASTM STP 898,1986.[5] Twine CP,McLain AD.Graft type for femoro-popliteal bypass surgery (review). Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010;5: CD001487.[6] Lösel-Sadée H,Alefelder C.Heparin-bonded expanded polytetrafluoroethylene graft for infragenicular bypass: five-year results.J Cardiovasc Surg.2009;50(3):339-343.[7] Kirkwood ML,Wang GJ,Jackson BM,et al.Lower limb revascularization for PAD using a heparin-coated PTFE conduit.Vasc Endovasc Surg.2011;45(4):329-334.[8] Pulli R,Dorigo W,Castelli P,et al.Propaten Italian Registry Group. Midterm results from a multicenter registry on the treatment of infrainguinal critical limb ischemia using a heparin- bonded ePTFE graft.J Vasc Surg. 2010;51(5):1167-1177.[9] 涂秋芬,张怡,陈槐卿,等.以脱细胞犬动脉为基质的血管支架体外再细胞化[J].航天医学与医学工程,2007,20(5):358-363.[10] 冉峰,刘长建,周敏,等.脱细胞支架复合兔骨髓间充质干细胞构建组织工程血管[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2009,13(47): 9226-9230.[11] 武欣,谷涌泉,段红永,等.利用脱细胞血管基质体外构建小口径组织工程血管[J].中国实验动物学报,2010,18(5):377-382.[12] Nagai N,Nakayama Y,Zhou YM,et al.Development of salmon collagen vascular graft: Mechanical and biological properties and preliminary implantation study.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2008;87(2):432-439.[13] 虞希高.明胶基电纺小直径人造血管的制备及性能研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2011.[14] 王叶香,闫星儒,王璐,等.人工血管用海藻酸钠-聚丙烯酰胺水凝胶的制备及性能[J].东华大学学报(自然科学版),2016,42(5):647-653.[15] 孔晓颖,韩宝芹,王海霞,等.可降解性壳聚糖基小口径人工血管的生物安全性[J].青岛大学医学院学报, 2012,48(4):334-336.[16] He C,Xu X,Zhang F,et al.Fabrication of fibrinogen/P (LLA‐CL) hybrid nanofibrous scaffold for potential soft tissue engineering applications.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2011,97(3):339-347.[17] 唐景梁,沈雳,吴轶喆,等.壳聚糖/肝素层层自组装涂层与CD133+内皮祖细胞生物相容性的实验研究[J].中国分子心脏病学杂志, 2009, 9(6):342-347.[18] Thein-Han WW,Misra RDK.Biomimetic chitosan– nanohydroxyapatite composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering.Acta Biomaterialia.2009;5(4):1182-1197.[19] 刘涛.壳聚糖—硫酸化丝素蛋白小口径人工血管动物实验研究[D]. 北京: 首都医科大学,2016.[20] 湛权.涤纶人造血管材料表面改性及其性能研究[D].上海:东华大学, 2012.[21] 张明,刘长建,刘晨,等.膨体聚四氟乙烯人工血管表面肝素固化替代犬下腔静脉的表面抗凝血性能[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,15(47):8833-8836.[22] 周飞,徐卫林,欧阳晨曦,等.小口径微孔聚氨酯人造血管生物力学性能研究[J].医用生物力学,2008, 23(4):270-274.[23] Zheng W,Wang Z,Song L,et al.Endothelialization and patency of RGD-functionalized vascular grafts in a rabbit carotid artery model.Biomaterials.2012;33(10):2880.[24] Bastijanic JM,Kligman FL,Marchant RE,et al.Dual biofunctional polymer modifications to address endothelialization and smooth muscle cell integration of ePTFE vascular grafts.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2016;104(1):71-81.[25] Hoshi RA,Van Lith R,Jen MC,et al.The blood and vascular cell compatibility of heparin-modified ePTFE vascular grafts. Biomaterials.2013;34(1):30-41.[26] Khorasani MT,Shorgashti S.Fabrication of microporous thermoplastic polyurethane for use as small‐diameter vascular graft material. I. Phase-inversion method.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2006;76(1):41-48.[27] Miyamoto K,Sugimoto T,Okada M,et al.Usefulness of polyurethane for small-caliber vascular prostheses in comparison with autologous vein graft.J Artif Organs. 2002;5(2):113-116.[28] Wang Z,Cui Y,Wang J,et al.The effect of thick fibers and large pores of electrospun poly (ε-caprolactone) vascular grafts on macrophage polarization and arterial regeneration.Biomaterials. 2014;35(22):5700-5710.[29] Aldenhoff YB,van Der Veen FH,ter Woorst J,et al.Performance of a polyurethane vascular prosthesis carrying a dipyridamole (Persantin®) coating on its lumenal surface.J Biomed Mater Res. 2001;54(2):224-233.[30] Zhang K,Liu T,Li JA,et al.Surface modification of implanted cardiovascular metal stents: from antithrombosis and antirestenosis to endothelialization.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2014;102(2):588-609. [31] Natterodt JC,Petri-Fink A,Weder C,et al.Cellulose Nanocrystals: Surface Modification, Applications and Opportunities at Interfaces.Chimia(Aarau). 2017;71(6):376-383. [32] Liu T,Hu Y,Tan J,et al.Surface biomimetic modification with laminin-loaded heparin/poly-l-lysine nanoparticles for improving the biocompatibility.Mater Sci Eng C. 2017;71:929-936.[33] Tang C,Kligman F,Larsen CC,et al.Platelet and endothelial adhesion on fluorosurfactant polymers designed for vascular graft modification.J Biomed Mater Res A.2009;88(2):348-358.[34] Walluscheck KP,Steinhoff G,Kelm S,et al.Improved endothelial cell attachment on ePTFE vascular grafts pretreated with synthetic RGD-containing peptides.Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 1996;12(3): 321-330.[35] Liu T,Liu Y,Chen Y,et al,Immobilization of heparin/ poly-L-lysine nanoparticles on dopamine-coated surface to create a heparin density gradient for selective direction of platelet and vascular cells behavior.Acta Biomaterialia.2014;10:1940-1954.[36] Catto V,Fare S,Cattaneo I,et al.Small diameter electrospun silk fibroin vascular grafts: Mechanical properties, in vitro biodegradability, and in vivo biocompatibility.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2015; 54:101-111. [37] Yin A,Luo R,Li J,et al.Coaxial electrospinning multicomponent functional controlled-release vascular graft: Optimization of graft properties.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces.2017;152:432-439. [38] Zhang YZ,Venugopal J,Huang ZM,et al.Characterization of the surface biocompatibility of the electrospun PCL-collagen nanofibers using fibroblasts.Biomacromolecules. 2005;6(5):2583.[39] Tan Z,Wang H,Gao X,et al.Composite vascular grafts with high cell infiltration by co-electrospinning.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2016;67:369-377. [40] Ping X,Min L,Chaoying Z,et al.Cytocompatibility of electrospun nanofiber tubular scaffolds for small diameter.Int J Biol Macromol. 2011;49:281-288.[41] Xiang P,Wang SS,He M,et al.The in vitro and in vivo biocompatibility evaluation of electrospun recombinant spider silk protein/PCL/gelatin for small caliber vascular tissue engineering scaffolds.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2018;163:19-28.[42] Fukunishi T,Best CA,Sugiura T,et al.Tissue-engineered small diameter arterial vascular grafts from cell-free nanofiber PCL/chitosan scaffolds in a sheep model.PloS One. 2016;11(7): e0158555.[43] Sankaran KK,Subramanian A,Krishnan UM,et al. Nanoarchitecture of scaffolds and endothelial cells in engineering small diameter vascular grafts.Biotechnol J. 2015;10(1):96-108.[44] Wilhelmi M,Jockenhoevel S,Mela P.Bioartificial fabrication of regenerating blood vessel substitutes: Requirements and current strategies.Biomed Tech (Berl).2014;59(3):185-195. [45] Benrashid E,McCoy CC,Youngwirth LM,et al.Tissue engineered vascular grafts: Origins, development, and current strategies for clinical application.Methods.2016;99:13-19.[46] Drews JD,Miyachi H,Shinoka T.Tissue-engineered vascular grafts for congenital cardiac disease: Clinical experience and current status.Trends Cardiovasc Med.2017;27(8):521-531.[47] Nieponice A,Soletti L,Guan J,et al.Development of a tissue-engineered vascular graft combining a biodegradable scaffold, muscle-derived stem cells and a rotational vacuum seeding technique. Biomaterials.2008;29(7):825-833.[48] Badhe RV,Bijukumar D,Chejara DR,et al.A composite chitosan- gelatin bio-layered, biomimetic macroporous scaffold for blood vessel tissue engineering.Carbohydr Polym. 2017;157:1215-1225. [49] Aper T,Wilhelmi M,Gebhardt C,et al.Novel method for the generation of tissue-engineered vascular grafts based on a highly compacted fibrin matrix.Acta Biomaterialia. 2016;29:21-32. [50] Augustine R,Dan P,Sosnik A,et al.Electrospun poly (vinylidene fluoride -trifluoroethylene)/zinc oxide nanocomposite tissue engineering scaffolds with enhanced cell adhesion and blood vessel formation. Nano Res. 2017;10(10):3358-3376. [51] Ahn H,Ju YM,Takahashi H,et al.Engineered small diameter vascular grafts by combining cell sheet engineering and electrospinning technology.Acta Biomaterialia.2015;16:14-22.[52] Yazdanpanah A,Tahmasbi M,Amoabediny G,et al.Fabrication and characterization of electrospun poly-L-lactide/gelatin graded tubular scaffolds: Toward a new design for performance enhancement in vascular tissue engineering. Prog Nat Sci Mater Int.2015;25(5):405-413. |