| [1] Diehl AM, Rai R. Review: regulation of liver regeneration by pro-inflammatory cytokines. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1996; 11(5):466-470.[2] Banas A, Teratani T, Yamamoto Y, et al. Rapid hepatic fate specification of adipose-derived stem cells and their therapeutic potential for liver failure. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;24(1):70-77.[3] Yu Y, Yao AH, Chen N, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells over-expressing hepatocyte growth factor improve small-for-size liver grafts regeneration. Mol Ther. 2007;15(7): 1382-1389.[4] Pournasr B, Mohamadnejad M, Bagheri M, et al. In vitro differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into hepatocyte-like cells. Arch Iran Med. 2011;14(4): 244-249.[5] Oyagi S, Hirose M, Kojima M, et al. Therapeutic effect of transplanting HGF-treated bone marrow mesenchymal cells into CCl4-injured rats. J Hepatol. 2006;44(4):742-748.[6] Si-Tayeb K, Noto FK, Nagaoka M, et al. Highly efficient generation of human hepatocyte-like cells from induced pluripotent stem cells. Hepatology. 2010;51(1):297-305.[7] Yu LM, Luo N, Li QL, et al. EPCAM-positive normal hepatic progenitor cells transformation into liver stem cells and HBx-mediated effects on stability in adult mouse. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2015;23(11):854-859.[8] Giri S, Acikgöz A, Bader A. Isolation and Expansion of Hepatic Stem-like Cells from a Healthy Rat Liver and their Efficient Hepatic Differentiation of under Well-defined Vivo Hepatic like Microenvironment in a Multiwell Bioreactor. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2015;5(2):107-122.[9] Habeeb MA, Vishwakarma SK, Bardia A, et al. Hepatic stem cells: A viable approach for the treatment of liver cirrhosis. World J Stem Cells. 2015;7(5):859-865.[10] Khan AA, Shaik MV, Parveen N, et al. Human fetal liver-derived stem cell transplantation as supportive modality in the management of end-stage decompensated liver cirrhosis. Cell Transplant. 2010; 19(4):409-418.[11] 吴波,张博,李伟光,等.TGF-β1基因修饰的肝干细胞诱导大鼠移植肝脏免疫耐受的实验研究[J].胃肠病学和肝病学杂志, 2014, 23(4):425-427.[12] 韩博,徐三荣,张进,等.同基因与异基因胚胎肝干细胞移植治疗小鼠肝硬化[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,16(36):6474-6480.[13] 张锡峰,胡代曦,芦永良,等. Wnt3a过表达对小鼠胚胎肝干细胞凋亡的抑制作用[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志, 2013,29(12): 1277-1280.[14] 黄增辉,曾珊,欧阳淼,等.肝素联合肝干细胞经脾移植治疗SD大鼠急性肝损伤[J].中南大学学报:医学版,2011,36(5):411-416.[15] Ito M, Nagata H, Miyakawa S, et al. Review of hepatocyte transplantation. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2009;16(2): 97-100.[16] Carpentier B, Gautier A, Legallais C. Artificial and bioartificial liver devices: present and future. Gut. 2009;58(12): 1690-1702.[17] 刘勇,冯东福,陈二涛,等.绿色荧光蛋白转基因胚胎大鼠神经干细胞生物学特性研究[J].实用医学杂志,2008,24(5):709-712.[18] Gai H, Nguyen DM, Moon YJ, et al. Generation of murine hepatic lineage cells from induced pluripotent stem cells. Differentiation. 2010;79(3):171-181.[19] Gouon-Evans V, Boussemart L, Gadue P, et al. BMP-4 is required for hepatic specification of mouse embryonic stem cell-derived definitive endoderm. Nat Biotechnol. 2006;24(11): 1402-1411.[20] Polisetti N, Chaitanya VG, Babu PP, et al. Isolation, characterization and differentiation potential of rat bone marrow stromal cells. Neurol India. 2010;58(2):201-208.[21] Sakaida I. Autologous bone marrow cell infusion therapy for liver cirrhosis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;23(9): 1349-1353.[22] 周晓飞,王茜,褚建新,等. Retrorsine对小鼠肝损伤后肝细胞增殖的影响[J].第二军医大学学报,2006,27(1):31-35.[23] Mohamadnejad M, Alimoghaddam K, Mohyeddin-Bonab M, et al. Phase 1 trial of autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis. Arch Iran Med. 2007;10(4):459-466.[24] Giuliani AL, Wiener E, Lee MJ, et al. Changes in murine bone marrow macrophages and erythroid burst-forming cells following the intravenous injection of liposome-encapsulated dichloromethylene diphosphonate (Cl2MDP). Eur J Haematol. 2001;66(4):221-229.[25] Bauer D, Schmitz A, Van Rooijen N, et al. Conjunctival macrophage-mediated influence of the local and systemic immune response after corneal herpes simplex virus-1 infection. Immunology. 2002;107(1):118-128.[26] Tsai PC, Fu TW, Chen YM, et al. The therapeutic potential of human umbilical mesenchymal stem cells from Wharton's jelly in the treatment of rat liver fibrosis. Liver Transpl. 2009; 15(5):484-495.[27] Levicar N, Pai M, Habib NA, et al. Long-term clinical results of autologous infusion of mobilized adult bone marrow derived CD34+ cells in patients with chronic liver disease. Cell Prolif. 2008;41 Suppl 1:115-125.[28] 李劲,张健,刘光泽,等. D-氨基半乳糖与脂多糖对小鼠肝脏损伤后再生修复的影响[J].南方医科大学学报,2012,32(1):50-54. |
.jpg)
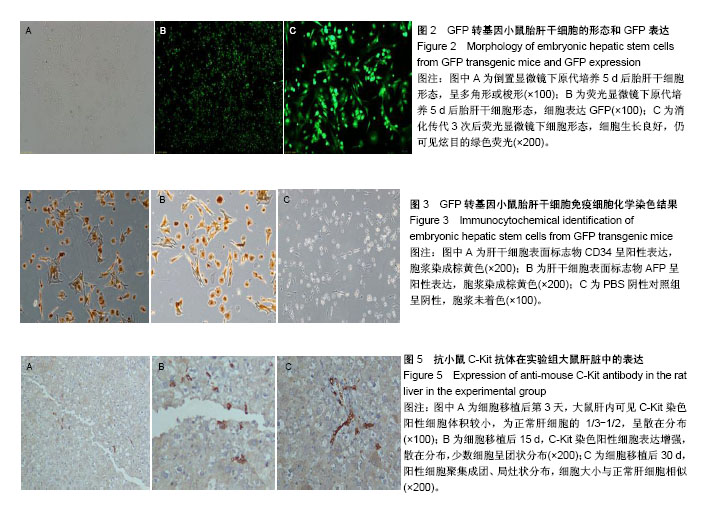
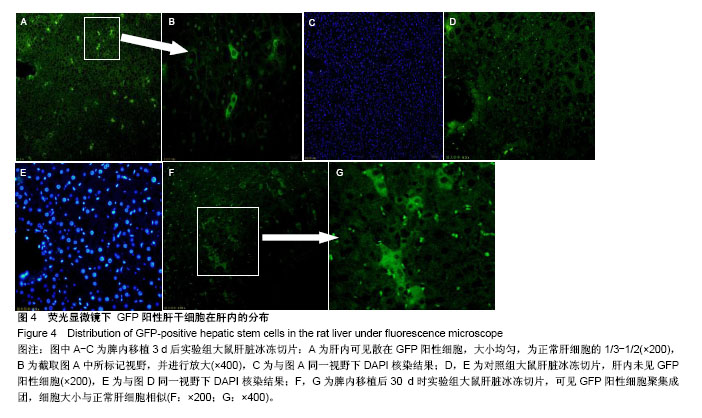
.jpg)
.jpg)