中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (19): 3077-3084.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0261
• 骨与关节综述 bone and joint review • 上一篇 下一篇
人工关节置换后假体周围感染诊断的新进展
胡雪峰,左 强,蔚 磊
- 包头医学院第一附属医院骨科,内蒙古自治区包头市 014010
-
出版日期:2018-07-08发布日期:2018-07-08 -
通讯作者:蔚磊,硕士,主任医师,包头医学院第一附属医院骨科,内蒙古自治区包头市 014010 -
作者简介:胡雪峰,男,1985年生,内蒙古自治区包头市人,汉族,2013年广西医科大学毕业,硕士,主治医师,主要从事骨与关节方面的研究。
Advances in diagnosis of periprosthetic infection after arthroplasty
Hu Xue-feng, Zuo Qiang, Wei Lei
- Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Baotou Medical College, Baotou 014010, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China
-
Online:2018-07-08Published:2018-07-08 -
Contact:Wei Lei, Master, Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Baotou Medical College, Baotou 014010, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Hu Xue-feng, Master, Attending physician, Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Baotou Medical College, Baotou 014010, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
中图分类号:
引用本文
胡雪峰,左 强,蔚 磊. 人工关节置换后假体周围感染诊断的新进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2018, 22(19): 3077-3084.
Hu Xue-feng, Zuo Qiang, Wei Lei. Advances in diagnosis of periprosthetic infection after arthroplasty[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(19): 3077-3084.
2.1 直接证据
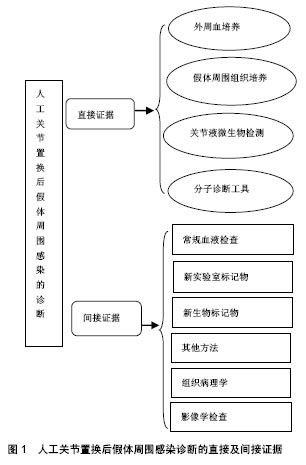
2.1.2 假体周围组织培养 假体周围组织培养对于假体周围感染的诊断是一项十分有价值的诊断方法。但是,在低毒力微生物存在的情况下,这一方法则表现出较低的敏感性和较大的波动性。有研究发现假体置换术后感染的微生物常常通过形成生物膜定植于假体表面,而且假体周围组织内的细菌长期保持静止状态,以抵御机体免疫系统的攻击,抵制抗生素对细菌的作用,从而限制了常规细菌培养技术的使用。常规假体周围组织取样进行培养往往不能取到假体表面的微生物。Peel等[3]应用贝叶斯潜伏类建模接种组织到血培养瓶中进行培养,与常规琼脂和肉汤培养物的灵敏度相比提高47%, 准确度达92%,而且培养时间短。Tunney等[4]在诊断假体周围感染时首次应用超声裂解液培养法,之后众多学者进行超声裂解液培养,证实相较传统方法其敏感性和特异性高,肯定了超声裂解液培养对于诊断假体周围感染的意义,也进一步证明了这一方法的可靠性。超声比传统组织培养更敏感,特异性更高,特别是对于以前服用抗生素的患者[5]。假体周围组织培养的取材关键是需要外科翻修手术来获取,这就限制了其使用,无法在术前诊断中发挥其作用。目前植入物超声处理,因为检测费用和临床易用性限制了该技术的使用,但是,未来可能极大地改变和拓宽临床微生物检测的手段。

| [1] Parvizi J,Zmistowski B,Berbari EF, et al. New definition for periprosthetic joint infection: from the Workgroup of theMusculoskeletal Infection Society. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011; 469(11): 2992-2994.[2] 袁俊,冯建民. 人工关节置换术后假体周围感染的病原学诊断研究进展[J].中华关节外科杂志:电子版,2016,10(4):432-435.[3] Peel TN,Dylla BL,Hughes JG,et al.Improved diagnosis ofprosthetic joint infection by culturing periprosthetic tissuespecimens in blood culture bottles. MBio. 2016;7(1):e01776-15. [4] Tunney MM,Patrick S,Gorman SP,et al. Improved detection ofinfection in hip replacements. A currently underestimated problem. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1998; 80(4): 568-572.[5] Rak M, Kav?I? M, Trebše R, et al. Detection of bacteria with molecular methods in prosthetic joint infection: sonication fluid better than periprosthetic tissue. Acta Orthop. 2016;87(4):339-345. [6] Cross MC, Kransdorf MJ, Chivers FS, et al. Utility of percutaneous joint aspiration and synovial biopsy in identifying culture-positive infected hip arthroplasty. Skeletal Radiol. 2014;43: 165-168.[7] Fink B, Gebhard A, Fuerst M, et al. High diagnostic value of synovial biopsy in periprosthetic joint infection of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471: 956-964.[8] 张宁,赵翔,周鑫叠,等.关节液与组织培养在髋膝关节置换术后感染诊断价值的Meta分析[J]. 中华关节外科杂志:电子版,2014,8(1):72-76.[9] Durmaz G, Us T, Aydinli A, et al. Optimum detection times for bacteria and yeast species with the BACTEC 9120 aerobic blood culture system: evaluation for a 5-year period in a Turkish university hospital. J Clin Microbiol. 2003;41(2):819-821.[10] Font-Vizcarra L, García S, Martínez-Pastor JC, et al. Blood culture flasks for culturing synovial fluid in prosthetic joint infections. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468(8):2238-2243.[11] Geller JA, MacCallum KP, Murtaugh TS, et al. Prospective Comparison of Blood Culture Bottles and Conventional Swabs for Microbial Identification of Suspected Periprosthetic Joint Infection.J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(8):1779-1783.[12] Squire MW,Della Valle CJ,Parvizi J. Preoperative diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infection: role of aspiration. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011; 196(4): 875-879.[13] Bémer P,Plouzeau C,Tande D,et al. Evaluation of 16S rRNAgene PCR sensitivity and specificity for diagnosis of prosthetic joint infection: a prospective multicenter cross- sectional study. J Clin Microbiol. 2014; 52(10): 3583-3589.[14] Ghebremedhin B, Layer F, König W,et al. Genetic classification and distinguishing of Staphylococcus species based on different partial gap, 16S rRNA, hsp60, rpoB,sodA, and tuf gene sequences. J Clin Microbiol. 2008;46(3):1019-1025.[15] Greenwood-Quaintance KE,Uhl JR,Hanssen AD,et al. Diagnosis of Prosthetic Joint Infection by Use of PCR-Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry. J Clin Microbiology. 2014; 52(2):642-649.[16] Prieto-Borja L, Rodriguez-Sevilla G, Auñon A, et al. Evaluation of a commercial multiplex PCR (Unyvero i60®) designed for the diagnosis of bone and joint infections using prosthetic-joint sonication. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2016,pii: S0213-005X(16)30287-7. [17] Hischebeth GT, Randau TM, Buhr JK, et al. Unyvero i60 implant and tissue infection (ITI) multiplex PCR system in diagnosing periprosthetic joint infection. J Microbiol Methods. 2016;121:27-32.[18] Lourtet-Hascoëtt J, Bicart-See A, Félicé MP,et al. Is Xpert MRSA/SA SSTI real-time PCR a reliable tool for fast detection of methicillin- resistant coagulase-negative staphylococci in periprosthetic joint infections? Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2015;83(1):59-62.[19] Larsen LH, Lange J, Xu Y, et al. Optimizing culture methods for diagnosis of prosthetic joint infections: a summary of modifications and improvements reported since 1995. J Med Microbiol. 2012;61(Pt 3): 309-316.[20] Bizzini A, Greub G. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry, a revolution in clinical microbial identification. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2010;16(11):1614-1619.[21] Peel TN, Cole NC, Dylla BL,et al. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time of flight mass spectrometry and diagnostic testing forprosthetic joint infection in the clinical microbiology laboratory. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2015;81(3):163-168.[22] Melendez DP, UhI JR, Greenwood-Quaintance KE, et al. Detection of prosthetic joint infection by use of PCR-electrospray ionization mass spectrometry applied tosynovial fluid. J Clin Microbiol. 2014,52(6): 2202-2205. [23] Nistico L, Hall-Stoodley L, Stoodley P. Imaging bacteria and biofilms on hardware and periprosthetic tissue in orthopedic infections. Methods Mol Biol. 2014;1147:105-126.[24] Hogdall D, Hvolris JJ, Christensen L. Improved detection methods for infected hip joint prostheses. APMIS.2010;118(11):815-823.[25] Trampuz A, Steinhuber A, Wittwer M, et al. Rapid diagnosis of experimental meningitis by bacterial heat production in cerebrospinal fluid. BMC Infect Dis. 2007;7:116.[26] Corvec S, Portillo ME, Pasticci BM,et al. Epidemiology and new developments in the diagnosis of prosthetic joint infection. Int J Artif Organs. 2012;35(10):923-934.[27] Parvizi J, Della Valle CJ. AAOS clinical practice guideline: Diagnosis and treatment of periprosthetic joint infections of the hip and knee. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2010;18:771-772.[28] Saltzman MD, Marecek GS, Edwards SL, et al. Infection after shoulder surgery. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2011;19:208-218.[29] Parvizi J, Adeli B, Zmistowski B, et al. Management of periprosthetic joint infection: the current knowledge: AAOS exhibit selection.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94(14):e104. [30] Chen A, Fei J, Deirmengian C. Diagnosis ofperiprosthetic infection: novel developments. J Knee Surg. 2014; 27(4): 259-265.[31] Randau TM, Friedrich MJ, Wimmer MD, et al. Interleukin-6 in serum and in synovial fluid enhances the differentiation between periprosthetic joint infection and aseptic loosening. PLoS One. 2014; 9(2):e89045.[32] Elgeidi A, Elganainy AE, Abou Elkhier N,et al. Interleukin-6 and other inflammatory markers in diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infection. Int Orthop. 2014;38(12):2591-2595.[33] Matsen Ko L, Parvizi J.Diagnosis of Periprosthetic Infection: Novel Developments. Orthop Clin North Am. 2016;47(1):1-9.[34] Frangiamore SJ, Saleh A, Grosso MJ,et al. Neer Award 2015: Analysis of cytokine profiles inthe diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infections of theshoulder. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2016. pii: S1058-2746(16)30244-0. [35] Grosso MJ, Frangiamore SJ, Saleh A,et al. Poor utility of seruminterleukin-6 levels to predict indolent periprosthetic shoulderinfections. J Shoulder Elbow Surg .2014;23(9):1277-1281.[36] Ahmad SS, Shaker A, Saffarini M,et al. Accuracy of diagnostictests for prosthetic joint infection: a systematic review. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016;24(10):3064-3074. [37] Galliera E, Drago L, Vassena C, et al. Toll-Like Receptor 2 in Serum: a Potential Diagnostic Marker of Prosthetic Joint Infection? J Clin Microbiol. 2014; 52(2): 620-623.[38] Pajarinen J, Jamsen E, Konttinen YT, et al. Innate Immune Reactions in Septic and Aseptic Osteolysis Around Hip Implants. J Long Term Eff Med Implants. 2014; 24(4): 283-296.[39] Deirmengian C, Kardos K, Kilmartin P,et al. Diagnosing Periprosthetic Joint Infection Has the Era of the Biomarker Arrived?.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472:3254-3262.[40] Bonanzinga T, Zahar A, Dütsch M, et al. How Reliable Is the Alpha-defensin Immunoassay Test for Diagnosing Periprosthetic Joint Infection? A Prospective Study.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016. [Epub ahead of print][41] Wyatt MC, Beswick AD, Kunutsor SK,et al. The Alpha-Defensin Immunoassay and Leukocyte Esterase Colorimetric Strip Test for the Diagnosis of Periprosthetic Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2016;98(12):992-1000. [42] Deirmengian C, Kardos K, Kilmartin P, et al. The alpha-defensin test for periprosthetic joint infection outperforms the leukocyte esterase test strip.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015;473(1):198-203. [43] Deirmengian C, Kardos K, Kilmartin P, et al. Combined measurement of synovial fluid α-Defensin and C-reactive protein levels: highly accurate fordiagnosing periprosthetic joint infection. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014;96(17):1439-1445. [44] Bingham J, Clarke H, Spangehl M,et al. The alpha defensin-1 biomarker assay can be used to evaluate the potentially infected total jointarthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472(12):4006-4009. [45] Deirmengian C, Kardos K, Kilmartin P, et al. The Alpha-defensin Test for Periprosthetic Joint Infection Responds to a Wide Spectrum of Organisms. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015;473(7):2229-2235. [46] Shahi A, Parvizi J, Kazarian GS,et al. The Alpha-defensin Test for Periprosthetic Joint Infections Is Not Affected by Prior Antibiotic Administration.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016;474(7):1610-1615.[47] Parvizi J, Jacovides C, Antoci V, et al. Diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infection: the utility of a simple yet unappreciated enzyme.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93(24):2242-2248.[48] Colvin OC, Kransdorf MJ, Roberts CC, et al.Leukocyte esterase analysis in the diagnosis of joint infection: can we make a diagnosis using a simpleurine dipstick? Skeletal Radiol. 2015;44(5):673-677.[49] Wetters NG, Berend KR, Lombardi AV,et al. Leukocyte esterase reagent strips for the rapid diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infection.J Arthroplasty. 2012;27(8 Suppl):8-11.[50] Shafafy R, McClatchie W, Chettiar K,et al.Use of leucocyte esterase reagent strips in the diagnosis or exclusion of prosthetic jointinfection. Bone Joint J. 2015;97-B(9):1232-1236.[51] Friedrich MJ, Randau TM, Wimmer MD, et al. Lipopolysaccharide- binding protein: a valuable biomarker inthe differentiation between periprosthetic jointinfection and aseptic loosening?Int Orthop. 2014; 38(10):2201-2207.[52] Galliera E, Drago L, Marazzi MG, et al. Soluble urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor (suPAR) as new biomarker of the prosthetic jointinfection: correlation with inflammatory cytokines. Clin Chim Acta. 2015;441:23-28.[53] Morawietz L, Schröder JH, Dynybil C,et al. Proposal for a histopathological consensus classification of the periprosthetic interface membrane. J Clin Pathol. 2006;59:591-597. doi: 10.1136/jcp.2005.027458. [54] Janz V, Wassilew GI, Hasart O,et al. Evaluation of sonicate fluid cultures in comparison to histological analysis of theperiprosthetic membrane for the detection of periprosthetic joint infection. Int Orthop. 2013;37(5):931-936.[55] Claassen L, Ettinger S, Pastor MF,et al. The value of arthroscopic neosynovium biopsies to diagnose periprosthetic knee joint low-grade infection. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2016;136(12):1753-1759. [56] Kwiecien G, George J, Klika AK,et al. Intraoperative Frozen Section Histology: Matched for Musculoskeletal Infection Society Criteria. J Arthroplasty. 2016. pii: S0883-5403(16)30286-8. [57] Zimmerli W, Trampuz A, Ochsner PE. Prosthetic-joint infections. N Engl J Med. 2004;351(16):1645-1654.[58] George J, Kwiecien G, Klika AK,et al.Are Frozen Sections and MSIS Criteria Reliable at the Time of Reimplantation of Two-stageRevision Arthroplasty?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016;474(7):1619-1626. [59] Tang X, Wang Q, Wang H,et al. [Comparison and estimation of different diagnostic methods in detecting the presence of periprosthetic joint infection]. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2016;54(4):251-257.[60] Banke IJ, Stade N, Prodinger PM,et al.[Synovial biomarkers for differential diagnosis of painful arthroplasty].Orthopade. 2015;44(12): 936-938, 940-941. [61] Gravius S, Randau TM, Casadonte R,et al. Investigation of neutrophilic peptides in periprosthetic tissue by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionisationtime-of-flight imaging mass spectrometry. Int Orthop. 2015;39(3):559-567.[62] Kölbel B, Wienert S, Dimitriadis J, et al. [CD15 focus score for diagnostics of periprosthetic joint infections : Neutrophilic granulocytesquantification mode andthe development of morphometric software (CD15 quantifier)]. Z Rheumatol. 2015;74(7):622-630.[63] Osmon DR, Berbari EF, Berendt AR, et al; Infectious Diseases Society of America. Executive summary: diagnosis and management of prosthetic joint infection: clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2013; 56(1): 1-10.[64] Brause BD. Infection with Prostheses in Bones and Joints.In: Mandell GL, Bennett JE, Dolin R, (eds). Mandell,Douglas and Bennett’s principles and practice of infectious diseases, 7th edition (vol 1). Philadelphia: Elsevier Inc; 2010: 1469-1474.[65] Sendi P, Zimmerli W. Diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infections in clinical practice. Int J Artif Organs. 2012;35(10): 913-922.[66] Gemmel F, Van den Wyngaert H, Love C,et al. Prosthetic joint infections: radionuclide state-of-the-art imaging. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2012; 39(5): 892-909.[67] Trevail C, Ravindranath-Reddy P, Sulkin T,et al. An evaluation of the role of nuclear medicine imaging in the diagnosis of periprostheticinfections of the hip. Clin Radiol. 2016;71(3):211-219. [68] Ouyang Z, Li H, Liu X, et al.Prosthesis infection: diagnosis after total joint arthroplasty with three-phase bonescintigraphy. Ann Nucl Med. 2014;28(10):994-1003.[69] Glaudemans AW, de Vries EF, Vermeulen LE, et al. A large retrospective single centre study to define best acquisition protocols and interpretation criteria for white blood cell scintigraphy with99mTc-HMPAO-labelled leukocytes in musculoskeletal infections. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2013;40: 1760.[70] Erba PA, Glaudemans AW, Veltman NC, et al. Image acquisition and interpretation criteria for99mTc-HMPAO-labelled white blood cell scintigraphy: results of a multicenter study. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2014; 41: 615.[71] Pakos EE, Trikalinos TA, Fotopoulos AD, et al. Prosthesis infection: diagnosis after total joint arthroplasty with antigranulocytescintigraphy with 99mTc-labeled monoclonal antibodies-a meta-analysis. Radiology. 2007; 242 (1): 101-108.[72] Al Mohajer M, Darouiche RO. Darouiche.The expanding horizon of prosthetic joint infections. J Appl Biomater Funct Mater. 2014;12(1): 1-12.[73] Filippi L, Schillaci O. Usefulness of hybrid SPECT/CT in 99mTc-HMPAO-labeled leukocyte scintigraphy for bone and joint infections. J Nucl Med. 2006; 47(12):1908-1913.[74] Zhuang H, Yang H, Alavi A. Critical role of 18F-labeled fluorodeoxyglucose PET in the management of patients with arthroplasty. Radiol Clin North Am. 2007; 45(4):711-718, vii.[75] Del Arco A, Bertrand ML. The diagnosis of periprosthetic infection. Open Orthop J. 2013;7:178-183. |
| [1] | 林清凡, 解一新, 陈婉清, 叶振忠, 陈幼芳. 人胎盘源间充质干细胞条件培养液可上调缺氧状态下BeWo细胞活力和紧密连接因子的表达[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [2] | 张 宇, 田少奇, 曾国波, 胡 川. 初次下肢全关节置换后发生心肌梗死的危险因素[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [3] | 韦 玮, 李 剑, 黄林海, 兰敏东, 卢显威, 黄绍东. 全膝或全髋关节置换后老年人首次活动时跌倒恐惧的影响因素[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [4] | 王金军, 邓增发, 刘 康, 何智勇, 余新平, 梁建基, 李 晨, 郭洲洋. 全膝关节置换静脉滴注氨甲环酸联合含氨甲环酸鸡尾酒局部应用的止血效果及安全性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [5] | 肖国庆, 刘选泽, 严钰皓, 钟喜红. 后交叉韧带替代型假体全膝关节置换术后屈曲受限的影响因素[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1362-1367. |
| [6] | 黄泽晓, 杨 妹, 林诗炜, 何和与. 血清n-3多不饱和脂肪酸水平与全膝关节置换早期股四头肌肌力变化的相关性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1375-1380. |
| [7] | 张 冲, 刘志昂, 姚帅辉, 高军胜, 姜 岩, 张 陆. 局部应用氨甲环酸减少老年股骨颈骨折全髋关节置换后引流的安全和有效性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [8] | 袁家威, 张海涛, 揭 珂, 曹厚然, 曾意荣. 基于网络药理学研究桃红四物汤治疗假体周围感染的潜在靶点和机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1428-1433. |
| [9] | 张秀梅, 翟运开, 赵 杰, 赵 萌. 类器官模型国内外数据库近10年文献研究热点分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [10] | 焦 慧, 张一宁, 宋雨晴, 林 宇, 王秀丽. 乳腺癌类器官研究进展及临床应用前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1122-1128. |
| [11] | 曾燕华, 郝延磊. 许旺细胞体外培养及纯化的系统性综述[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [12] | 王 丰, 周立宇, 赛吉拉夫, 齐士斌, 马艳霞, 韦善文. CaMKⅡ-Smad1促进外周神经的轴突再生[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1064-1068. |
| [13] | 袁 俊, 杨家福. 局部氨甲环酸浸润在非骨水泥全膝关节置换过程中止血效果的评价[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(6): 873-877. |
| [14] | 李 琰, 王 佩, 邓东焕, 严 伟, 李 磊, 姜红江. 电针干预全膝关节置换后疼痛的Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(6): 957-963. |
| [15] | 赵中溢, 李勇阵, 陈 峰, 季爱玉. 同期双侧全膝关节置换和单髁置换治疗创伤性关节炎的比较[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(6): 854-859. |
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
1.1 资料来源 由第一作者检索1998年1月至2016年12月PubMed数据(http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ PubMed) 及CNKI中国期刊全文数据库(http://www. cnki.net/),以“arthroplasty,periprosthetic joint infection,diagnosis,culture,synovial biopsy,microbial identification,inflammatory markers,histology,markers,Alpha-Defensin,PCR,imaging”为英文检索词,“关节置换,假体周围感染,诊断,血培养,组织培养,关节滑膜组织,微生物检测,炎症标志物,组织病理学,生物标记物,聚合酶链反应,影像学”为中文检索词,检索摘要内同时包含上述检索词的文献,文献包括研究原著、综述、述评、经验交流、病例报告及荟萃分析,总计英文文献103篇,中文文献30篇。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
.jpg)