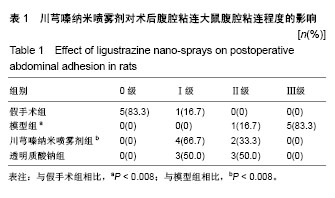
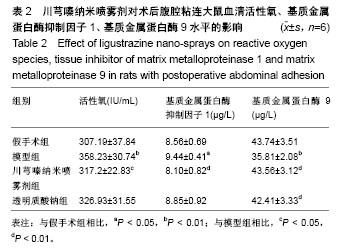
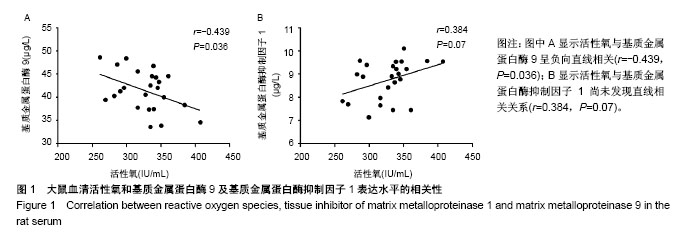
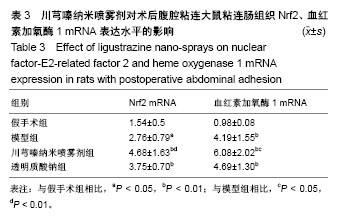
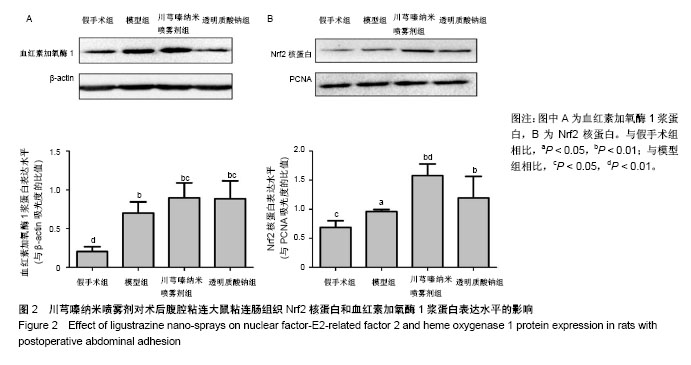
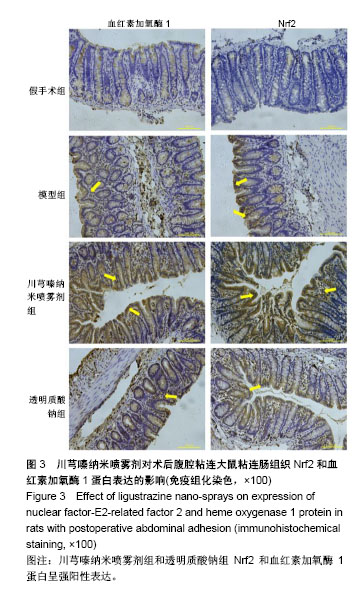
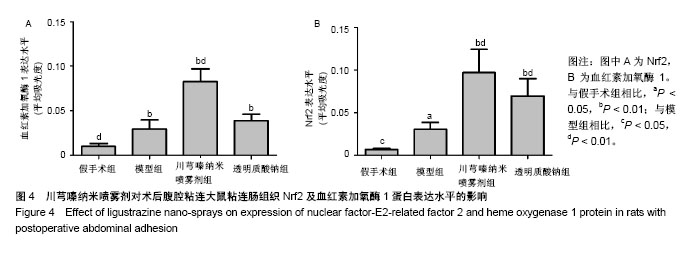
| [1] Ozerhan IH, Urkan M, Meral UM,et al. Comparison of the effects of Mitomycin-C and sodium hyaluronate/ carboxymethylcellulose [NH/CMC] (Seprafilm) on abdominal adhesions. Springerplus. 2016; 5(1):846. [2] Wei G, Chen X, Wang G, et al. Effect of Resveratrol on the Prevention of Intra-Abdominal Adhesion Formation in a Rat Model. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;39(1):33-46. [3] Jin X, Ren S, Macarak E, et al. Pathobiological mechanisms of peritoneal adhesions: The mesenchymal transition of rat peritoneal mesothelial cells induced by TGF-β1 and IL-6 requires activation of Erk1/2 and Smad2 linker region phosphorylation. Matrix Biol. 2016; 51:55-64. [4] Arslan E, Irkorucu O, Sozutek A, et al. The potential efficacy of Survanta (r) and Seprafilm (r) on preventing intra-abdominal adhesions in rats. Acta Cir Bras. 2016;31(6):389-395. [5] Ten Broek RPG, Stommel MWJ, Strik C, et al. Benefits and harms of adhesion barriers for abdominal surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. 2014;383(9911):48-59. [6] 颜帅,曾莉,李文林,等.从腹腔粘连论中医“结”病机学说[J]. 中医杂志, 2014,55(19):1641-1644.[7] 张昌林,倪小佳,李春花,等.川芎嗪的结构修饰及生物活性研究进展[J].中药新药与临床药理, 2017,28(4):549-556.[8] 姜宇懋,王丹巧.川芎嗪药理作用研究进展[J].中国现代中药, 2016,18(10): 1364-1370.[9] 杨雪梅.川芎嗪药理作用研究进展[J].中国生化药物杂志, 2010,31(3): 215-217.[10] 颜帅,李文林,曾莉.川芎嗪抗组织粘连研究进展[J].天然产物研究与开发, 2015,27(2):367-371.[11] 毛春芹,曾莉,陆兔林,等.川芎嗪纳米喷雾剂对大鼠腹腔粘连相关因子和纤溶系统影响的实验研究[J].中国药理学通报, 2012,28(1):118-123.[12] 王晓雯,陆兔林,卢金福,等.川芎嗪纳米制剂抗大鼠术后腹腔粘连实验研究[J]. 南京中医药大学学报, 2011,27(2):148-150.[13] 晏亦林,周莉玲.川芎嗪的研究概况[J].时珍国医国药, 2008,19(6): 1343-1345.[14] Awonuga AO, Belotte J, Abuanzeh S, et al. Advances in the Pathogenesis of Adhesion Development: The Role of Oxidative Stress. Reprod Sci. 2014;21(7):823-836. [15] 闫峰,赵咏梅,罗玉敏,等.大鼠局灶性脑缺血再灌注脑组织中活性氧自由基表达的时程变化[J].首都医科大学学报, 2015,36(5):694-698.[16] 周天域,吕鑫,陈雨桐,等.Nrf2的代谢调节作用与肿瘤的生长和增殖[J].中国细胞生物学学报, 2017,39(3):381-388.[17] Yan S, Yue YZ, Zeng L, et al. Effect of intra-abdominal administration of ligustrazine nanoparticles nano spray on postoperative peritoneal adhesion in rat model. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2015;41(12): 1942-1950.[18] 朱燕,李文林,曾莉,等.川芎嗪纳米喷雾剂对抗实验性腹腔粘连模型大鼠的最佳有效剂量[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(36):5799-5804.[19] Bayhan Z, Zeren S, Kocak FE, et al. Antiadhesive and anti-inflammatory effects of pirfenidone in postoperative intra-abdominal adhesion in an experimental rat model. J Surg Res. 2016;201(2):348-355.[20] 冉茂良,高环,尹杰,等.氧化应激与DNA损伤[J].动物营养学报, 2013, 25(10):2238-2245.[21] Ung L, Pattamatta U, Carnt N, et al. Oxidative stress and reactive oxygen species: a review of their role in ocular disease. Clin Sci (Lond). 2017;131(24):2865-2883.[22] Meng JX, Zhao MF. Reactive oxygen species and fibrosis in tissues and organs - review. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2012; 20(5):1284-1288.[23] Chen Q, Wang Q, Zhu J, et al. Reactive oxygen species: key regulators in vascular health and diseases. Br J Pharmacol. 2018; 175(8):1279-1292.[24] 刘瑞. ROS介导的以Nrf2为核心的抗氧化防御体系对肺纤维化的调控机制研究[D]. 西安:第四军医大学, 2008.[25] Kweider N, Wruck CJ, Rath W. New Insights into the Pathogenesis of Preeclampsia - The Role of Nrf2 Activators and their Potential Therapeutic Impact. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 2013;73(12): 1236-1240.[26] Liu W, Hu T, Zhou L, et al. Nrf2 protects against oxidative stress induced by SiO2 nanoparticles. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2017;12(19): 2303-2318.[27] Lau A, Tian W, Whitman SA, et al. The predicted molecular weight of Nrf2: it is what it is not. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013;18(1):91-93.[28] 申力军,辛绍杰,万志红. HO-1在肝肾疾病中的作用研究进展[J]. 现代生物医学进展, 2017,17(6):1172-1175.[29] 黄新宇,刘永林.白藜芦醇激活Nrf2/ARE信号通路降低心肌缺血再灌注损伤大鼠炎症和氧化应激[J].中华中医药学刊, 2017,35(6):1516-1520.[30] Gonzalez-Donquiles C, Alonso-Molero J, Fernandez-Villa T, et al. The NRF2 transcription factor plays a dual role in colorectal cancer: A systematic review. PLoS One. 2017;12(5):e0177549.[31] Sadeghi MR, Jeddi F, Soozangar N, et al. The role of Nrf2-Keap1 axis in colorectal cancer, progression, and chemoresistance. Tumour Biol. 2017;39(6):1010428317705510.[32] Menegon S, Columbano A, Giordano S. The Dual Roles of NRF2 in Cancer. Trends Mol Med. 2016;22(7):578-593.[33] 乔丽杰,王延让,张明.Nrf2/HO-1通路在氧化损伤保护机制中研究进展[J].中国职业医学, 2013,40(1):82-84. |
.jpg)
.jpg)