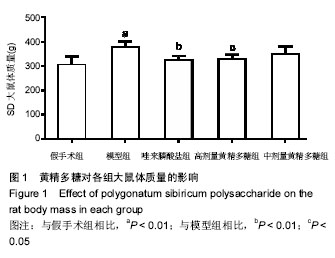
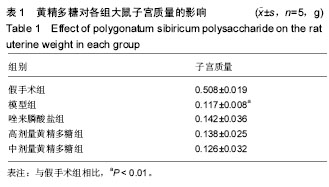
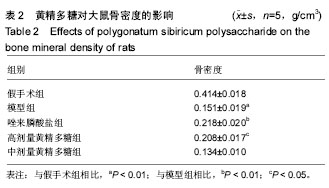
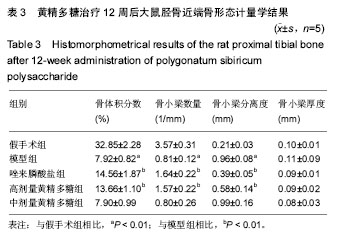
| [1] Klibanski A,Campbell LA,Bassford T,et al.Osteoporosis prevention,diagnosis,and therapy.JAMA.2001;285(6):8595.[2] Cosman F, de Beur SJ, LeBoff MS, et al.Clinician's Guide to Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int. 2014;25(10):2359-2381.[3] 原发性骨质疏松症诊治指南(2011年).中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志[J]. 2011,4(1):2-17.[4] Compston J, Bowring C, Cooper A, et al.Diagnosis and management of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women and older men in the UK: National Osteoporosis Guideline Group (NOGG) update 2013. Maturitas.2013;75(4): 392-396.[5] Cummings SR, San Martin J, McClung MR,et al.Denosumab for Prevention of Fractures in Postmenopausal Women with Osteoporosis.N Engl J Med. 2009;361(8):756-765.[6] Burge R, Dawson-Hughes B, Solomon DH, et al.Incidence and economic burden of osteoporosis-related fractures in the United States, 2005-2025. J Bone Miner Res. 2007;22(3): 465-475.[7] Yang JX, Wu S, Huang XL,et al.Hypolipidemic Activity and Antiatherosclerotic Effect of Polysaccharide of Polygonatum sibiricum in Rabbit Model and Related Cellular Mechanisms. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.2015;2015:391065.[8] Wang Y, Qin S, Pen G, et al.Potential ocular protection and dynamic observation of Polygonatum sibiricum polysaccharide against streptozocin-induced diabetic rats' model. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2017;242(1):92-101.[9] Zhang H, Cao Y, Chen L, et al.A polysaccharide from Polygonatum sibiricum attenuates amyloid-beta-induced neurotoxicity in PC12 cells. Carbohydr Polym. 2015;117: 879-886.[10] 农梦妮,曾高峰,宗少晖,等.黄精多糖调控骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化[J].中国组织工程研究, 2016,20(15): 2133-2139.[11] 曾高峰,张志勇,鲁力,等. 黄精多糖干预骨质疏松性骨折大鼠白细胞介素1和白细胞介素6的表达[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012, 16(2): 220-222.[12] Du L, Nong MN, Zhao JM, et al.Polygonatum sibiricum polysaccharide inhibits osteoporosis by promoting osteoblast formation and blocking osteoclastogenesis through Wnt/beta-catenin signalling pathway. Sci Rep. 2016;6:32261.[13] Kanis JA, McCloskey EV, Johansson H,et al.European guidance for the diagnosis and management of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. Osteoporos Int.2013;24(1):23-57. [14] Watts NB, Diab DL. Long-Term Use of Bisphosphonates in Osteoporosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010;95(4): 1555-1565.[15] Black DM, Delmas PD, Eastell R, et al.Once-yearly zoledronic acid for treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis. N Engl J Med.2007;356(18):1809-1822.[16] Tsai JN, Uihlein AV, Lee H, et al.Teriparatide and denosumab, alone or combined, in women with postmenopausal osteoporosis: the DATA study randomised trial. Lancet. 2013; 382(9886): 50-56.[17] Maraka S, Kennel KA. Bisphosphonates for the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis. BMJ.2015;351: h3783.[18] McClung M, Harris ST, Miller PD, et al.Bisphosphonate Therapy for Osteoporosis: Benefits, Risks, and Drug Holiday. Am J Med. 2013;126(1):13-20.[19] Black DM, Rosen CJ. Clinical Practice. Postmenopausal Osteoporosis. N Engl J Med, 2016;374(3):254-262.[20] Dang ZC, van Bezooijen RL, Karperien M,et al.Exposure of KS483 cells to estrogen enhances osteogenesis and inhibits adipogenesis. J Bone Miner Res. 2002;17(3):394-405.[21] Kanis JA.Diagnosis of osteoporosis and assessment of fracture risk. Lancet. 2002;359(9321):1929-1936.[22] Devareddy L , Khalil DA , Smith BJ ,et al.Soy moderately improves microstructural properties without affecting bone mass in an ovariectomized rat model of osteoporosis. Bone. 2006;38(5): 686-693.[23] Blume SW, Curtis JR.Medical costs of osteoporosis in the elderly Medicare population. Osteoporosis International.2011; 22(6):1835-1844.[24] Vasikaran S, Eastell R, Bruyère O,et al.Markers of bone turnover for the prediction of fracture risk and monitoring of osteoporosis treatment: a need for international reference standards. Osteoporosis International.2011;22(2):391-420.[25] Liu Q, Wang T, Zhou L,et al. Nitidine chloride prevents OVX-induced bone loss via suppressing NFATc1-mediated osteoclast differentiation. Sci Rep.2016;6: 36662.[26] Abdallah BM, Jafari A, Zaher W, et al.,Skeletal (stromal) stem cells: an update on intracellular signaling pathways controlling osteoblast differentiation. Bone. 2015; 70: 28-36.[27] Sethu SN, Namashivayam S, Devendran S, et al. Nanoceramics on osteoblast proliferation and differentiation in bone tissue engineering. Int J Biol Macromol. 2017;98:67-74[28] Glynn ER, Londono AS, Zinn SA, et al.Culture conditions for equine bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and expression of key transcription factors during their differentiation into osteoblasts. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2013;4(1):40.[29] 阙文君,冯正平.骨转换生化标志物的研究进展[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志, 2014,20(5): 575-579.[30] Vimalraj S, Arumugam B, Miranda PJ,et al.Runx2: Structure, function, and phosphorylation in osteoblast differentiation. Int J Biol Macromol.2015;78:202-208.[31] Song CY, Peng B, Shen JY,et al. Research on regulation mechanism of osteoclast differentiation. Zhongguo Gu Shang, 2015;28(6):580-584. |
.jpg)
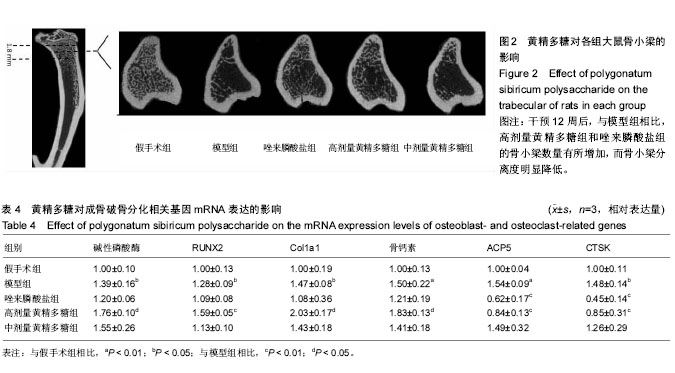
.jpg)