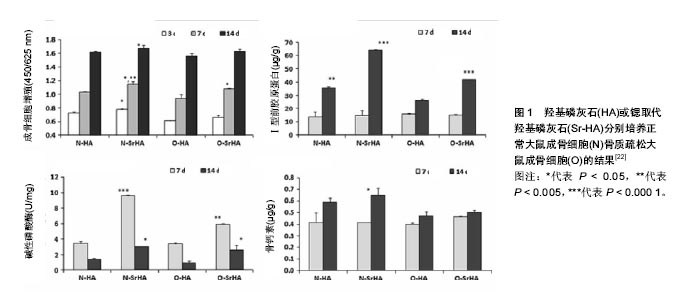
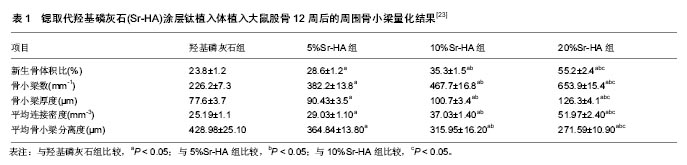
| [1]Vestermark MT.Strontium in the bone-implant interface.Dan Med Bull.2011;58(5):B4286.[2]McElderry JD,Zhu P, Mroue KH,et al.Crystallinity and compositional changes in carbonated apatites: Evidence from 31P solid-state NMR, Raman, and AFM analysis.J Solid State Chem.2013;206(1):192-198.[3]Heslop DD,Bi Y,Baig AA,et al.A comparative study of the metastable equilibrium solubility behavior of high-crystallinity and low-crystallinity carbonated apatites using pH and solution strontium as independent variables.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2005;289(1):14-25.[4]Laurencin D,Almora-Barrios N,de Leeuw NH,et al.Magnesium incorporation into hydroxyapatite. Biomaterials. 2011;32(7): 1826-1837.[5]Xu L,Jiang L,Xiong C,et al.Effect of different synthesis conditions on the microstructure, crystallinity and solubility of Mg-substituted hydroxyapatite nanopowder.Adv Powder Technol. 2014;25(3): 1142-1146.[6]Cox SC,Jamshidi P,Grover LM,et al.Preparation and characterisation of nanophase Sr, Mg, and Zn substituted hydroxyapatite by aqueous precipitation. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2014;35(35):106-114.[7]Abert J,Bergmann C,Fischer H.Wet chemical synthesis of strontium-substituted hydroxyapatite and its influence on the mechanical and biological properties.Ceram Int. 2014;40(7): 9195-9203.[8]Fu DL,Jiang QH,He FM,et al.Fluorescence microscopic analysis of bone osseointegration of strontium-substituted hydroxyapatite implants.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B.2012;13(5):364-371.[9]Pors Nielsen S.The biological role of strontium.Bone 2004;35(3): 583-588.[10]Boivin G,Deloffre P,Perrat B,et al.Strontium distribution and interactions with bone mineral in monkey iliac bone after strontium salt (S 12911) administration.J Bone Miner Res.1996;11(9): 1302-1311.[11]Brennan TC,Rybchyn MS,Green W,et al.Osteoblasts play key roles in the mechanisms of action of strontium ranelate.Br J Pharmacol.2009;157(7):1291-1300.[12]Fromigué O,Haÿ E,Barbara A,et al.Calcium sensing receptor-dependent and receptor-independent activation of osteoblast replication and survival by strontium ranelate.J Cell Mol Med.2009;13(8b):2189-2199.[13]Caverzasio J.Strontium ranelate promotes osteoblastic cell replication through at least two different mechanisms. Bone. 2008;42(6):1131-1136.[14]Atkins GJ,Welldon KJ,Halbout P,et al.Strontium ranelate treatment of human primary osteoblasts promotes an osteocyte-like phenotype while eliciting an osteoprotegerin response.Osteoporos Int. 2009;20(4):653-664.[15]Yamaguchi T.The calcium-sensing receptor in bone.J Bone Miner Metab.2008;26(4):301-311.[16]Teitelbaum SL.Bone Resorption by Osteoclasts. Science. 2000; 289(5484):1504-1508.[17]Bonnelye E,Chabadel A,Saltel F,et al.Dual effect of strontium ranelate: stimulation of osteoblast differentiation and inhibition of osteoclast formation and resorption in vitro.Bone. 2008;42(1): 129-138.[18]Buehler J,Chappuis P,Saffar JL,et al.Strontium ranelate inhibits bone resorption while maintaining bone formation in alveolar bone in monkeys (Macaca fascicularis).Bone.2001;29(2):176-179.[19]Canalis E,Hott M,Deloffre P,et al.The divalent strontium salt S12911 enhances bone cell replication and bone formation in vitro.Bone.1996;18(6):517-523.[20]Takahashi N,Sasaki T,Tsouderos Y,et al.S 12911-2 inhibits osteoclastic bone resorption in vitro. J Bone Miner Res. 2003; 18(6):1082-1087.[21]Li ZY,Lam WM,Yang C,et al.Chemical composition, crystal size and lattice structural changes after incorporation of strontium into biomimetic apatite.Biomaterials.2007;28(7):1452-1460.[22]Boanini E,Torricelli P,Fini M,et al.Osteopenic bone cell response to strontium-substituted hydroxyapatite.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2011;22(9):2079-2088.[23]Tao ZS,Bai BL,He XW,et al.A comparative study of strontium-substituted hydroxyapatite coating on implant's osseointegration for osteopenic rats.Med Biol Eng Comput. 2016;54(12):1959-1968.[24]Frasnelli M,Cristofaro F,Sglavo VM,et al.Synthesis and characterization of strontium-substituted hydroxyapatite nanoparticles for bone regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2017;71:653-662.[25]Khajuria DK,Vasireddi R,Trebbin M,et al.Novel therapeutic intervention for osteoporosis prepared with strontium hydroxyapatite and zoledronic acid: In vitro and pharmacodynamic evaluation. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2017;71:698-708.[26]Krishnan V,Bhatia A,Varma H.Development, characterization and comparison of two strontium doped nano hydroxyapatite molecules for enamel repair/regeneration.Dent Mater. 2016;32(5): 646-659.[27]Ni GX,Shu B,Huang G,et al.The effect of strontium incorporation into hydroxyapatites on their physical and biological properties.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2012;100(2):562-568.[28]Zhang W,Shen Y,Pan H,et al.Effects of strontium in modified biomaterials.Acta Biomaterialia. 2011;7(2):800-808.[29]Jiang F,Wang DP,Ye S,et al.Strontium-substituted, luminescent and mesoporous hydroxyapatite microspheres for sustained drug release.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2014;25(2):391-400.[30]Capuccini C,Torricelli P,Boanini E,et al.Interaction of Sr-doped hydroxyapatite nanocrystals with osteoclast and osteoblast-like cells.J Biomed Mater Res A.2009;89(3):594-600.[31]Kaygili O,Keser S,Kom M,et al.Strontium substituted hydroxyapatites: Synthesis and determination of their structural properties, in vitro and in vivo performance.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2015;55:538-546.[32]Vahabzadeh S,Roy M,Bandyopadhyay A,et al.Phase stability and biological property evaluation of plasma sprayed hydroxyapatite coatings for orthopedic and dental applications.Acta Biomaterialia. 2015;17:47-55.[33]Fielding GA,Roy M,Bandyopadhyay A,et al. Antibacterial and biological characteristics of silver containing and strontium doped plasma sprayed hydroxyapatite coatings.Acta Biomaterialia. 2012;8(8):3144-52.[34]Yang H,Lin M,Xu Y,et al.Osteogenesis of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on strontium-substituted nano-hydroxyapatite coated roughened titanium surfaces.Int J Clin Exp Med.2015;8(1):257-264.[35]Chung CJ,Long HY.Systematic strontium substitution in hydroxyapatite coatings on titanium via micro-arc treatment and their osteoblast/osteoclast responses.Acta biomaterialia. 2011; 7(11):4081-4087.[36]Sariibrahimoglu K,Yang W,Leeuwenburgh SC,et al.Development of porous polyurethane/strontium-substituted hydroxyapatite composites for bone regeneration.J Biomed Mater Res A.2015; 103(6):1930-1939.[37]Zhou J,Li B,Lu S,et al.Regulation of osteoblast proliferation and differentiation by interrod spacing of Sr-HA nanorods on microporous titania coatings. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2013; 5(11):5358-5365.[38]Yang F,Yang D,Tu J,et al.Strontium enhances osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells and in vivo bone formation by activating Wnt/catenin signaling.Stem Cells. 2011; 29(6):981-991.[39]Fonseca JE.Rebalancing bone turnover in favour of formation with strontium ranelate: implications for bone strength. Rheumatology. 2008;47(Suppl 4):iv17-19.[40]Steeve KT,Marc P,Sandrine T,et al.IL-6, RANKL, TNF-alpha/IL-1: interrelations in bone resorption pathophysiology.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev.2004;15(1):49-60.[41]Garbani M,Xia W,Rhyner C,et al. Allergen-loaded strontium-doped hydroxyapatite spheres improve allergen-specific immunotherapy in mice.Allergy. 2017;72(4): 570-578.[42]Li H,Jiang F,Ye S,et al.Bioactive apatite incorporated alginate microspheres with sustained drug-delivery for bone regeneration application.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2016;62:779-786. |
.jpg)
.jpg)