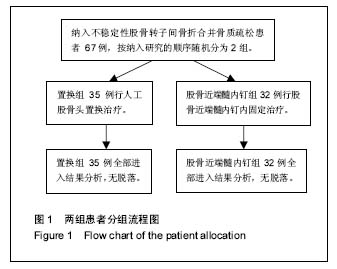
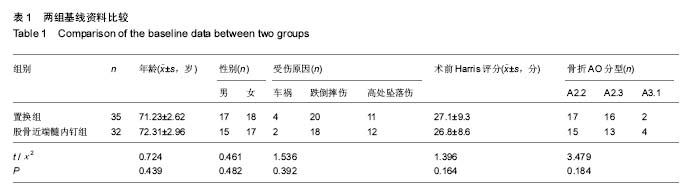
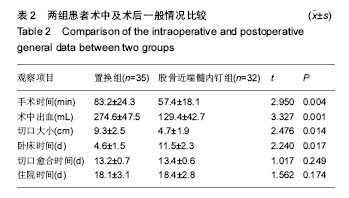
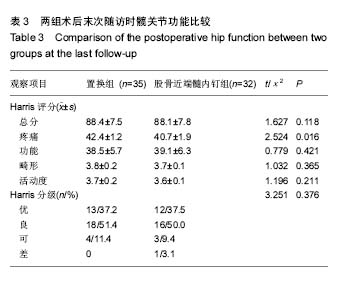
| [1] Kazemian GH, Manafi AR, Najafi F, et al. Treatment of intertrochanteric fractures in elderly highrisk patients: Dynamic hip screw vs. external fixation. Injury. 2014;45(3): 568-572.[2] 张伟强,祁宝昌,邓鹏飞,等.老年股骨粗隆间骨折治疗的临床进展[J].中国老年学杂志,2015,(1):266-268.[3] 吴利军.3种内固定手术治疗老年股骨粗隆间骨折的临床对照研究[J].重庆医学,2017,46(12):1681-1684.[4] Joshi D, Dhamangaonkar AC, Ramawat S, et al. Predictors of iatrogenic lateral wall fractures while treating intertrochanteric fracture femur with the dynamic hip screw system in Indian patients. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2015;25(4):677-682.[5] 曾敬茹,李思敏,杜春萍,等.住院骨质疏松病人健康行为现状与10年骨折风险的相关性研究[J].护理研究,2017,31(11): 1362-1364.[6] Bhattacharya A, Watts NB, Dwivedi A, et al. Combined Measures of Dynamic Bone Quality and Postural Balance-A Fracture Risk Assessment Approach in Osteoporosis. J Clin Densitom. 2015;17(3):418.[7] 张向阳,梁朝革,唐献忠,等.骨质疏松患者股骨头不同区域骨结构与生物力学分析[J].医用生物力学,2017,32(1):77-82.[8] 齐威,王林,胡宏伟,等. 股骨粗隆间骨折AO分型治疗分析[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2012, 27(12):1115-1116.[9] Bajpai J, Maheshwari R, Bajpai A, et al. Treatment options for unstable trochanteric fractures: Screw or helical proximal femoral nail. Chin J Traumatol. 2015;18(6):342-346.[10] 吴润福.PFNA联合骨水泥注入治疗老年不稳定性股骨骨折的疗效观察[J].临床医药文献电子杂志,2017,4(9):1595-1596.[11] 张明,李百通,姚猛,等.股骨转子间粉碎性骨折中小转子处理的临床治疗进展[J].创伤外科杂志,2017,19(4):315-318.[12] 丁坚,缪旭东,陈圣宝,等. 老年股骨粗隆间骨折患者围术期并发症的分析[J].上海医学, 2014,37(1):31-34.[13] 仇志韬,王文革,李仕臣,等. 股骨粗隆间骨折手术相关并发症分析[J]. 中国实用医刊,2013,40(3):41-42.[14] 张晓晴,蒋海燕.人性化护理干预对高龄股骨近端骨折患者预后效果的影响分析[J].中国民康医学,2016,28(8):112-113.[15] 顾小明,包洪卫,吴灿华,等.老年股骨粗隆间骨折不同内固定方法的疗效比较[J].实用临床医药杂志,2016,20(23):99-100.[16] 于学美,唐迎雪,王荣梅. 基于”治未病”理论防治骨折后骨量丢失[J]. 吉林中医药,2013,33(12):1207-1209.[17] 汪海滨,史法见.老年髋关节置换术后对侧再骨折的危险因素分析和预防[J].创伤外科杂志,2016,18(9):530-533[18] Xu Z, Zhang M, Yin J, et al. Redisplacement after reduction with intramedullary nails in surgery of intertrochanteric fracture: cause analysis and preventive measures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2015;135(6):751-758.[19] Wang XK, Ye JD, Gu FS, et al. Numerical simulation research to both the external fixation surgery scheme of intertrochanteric fracture and the healing process, and its clinical application. Biomed Mater Eng. 2014;24(1):625-632.[20] 张在谦,杜小平,高磊,等. 老年不稳定性股骨转子间骨折不同内固定方式的临床疗效分析[J]. 陕西医学杂志,2016,5:589-591.[21] 于延勇. 比较两种髓内钉置入修复骨质疏松性股骨转子间骨折的并发症发生率[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2015, 19(13): 2103-2107.[22] Sehmisch S, Rieckenberg J, Dresing K. [Stabilization of unstable intertrochanteric fractures with the proximal femoral nail]. Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2013;25(1):83-84.[23] 龚志强,徐晓峰,陈叶新,等.防旋型股骨近端髓内钉治疗老年骨质疏松性股骨粗隆间骨折效果分析[J].当代医学,2016,22(14): 25-26.[24] 赵正兴,林坚平,颜约军,等.防旋型股骨近端髓内钉治疗骨质疏松性粗隆间骨折40例临床疗效[J].昆明医科大学学报,2016,37(2): 119-122.[25] 杨志发, 刘展亮, 李晓彬,等. 人工关节置换与内固定治疗骨质疏松性不稳定股骨粗隆间骨折的对比分析[J]. 中国卫生产业, 2014(1):133-133.[26] Kim Y, Moon JK, Hwang KT, et al. Cementless bipolar hemiarthroplasty for unstable intertrochanteric fractures in octogenarians. Acta Orthopaedica Et Traumatologica Turcica. 2014;48(4):424-430.[27] 成世高,王万春,肖扬,等.骨水泥型人工股骨头置换治疗高龄不稳定型股骨转子间骨折[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(52): 8373-8378.[28] 张明. 动力髋螺钉与抗旋髓内钉治疗老年股骨粗隆间骨折的疗效对比分析[J]. 中国医药指南, 2015,13(9):134-135.[29] 董必成,李朝军,尹东武,等.股骨粗隆间骨折内固定失效原因分析[J].河北医药,2015,37(10):1510-1512[30] 任荣,李凌伟,郭启发,等.骨水泥型股骨柄人工股骨头置换治疗老年骨质疏松股骨颈骨折的可行性:随机对照临床试验方案[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(48):7261-7266.[31] 魏九定,付廷军,成中阳,等.动力髋螺钉置入固定股骨转子间骨折:失效原因分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(13):2096-2102.[32] Asif N, Ahmad S, Qureshi OA, et al. Unstable Intertrochanteric Fracture Fixation - Is Proximal Femoral Locked Compression Plate Better Than Dynamic Hip Screw. J Clin Diagn Res. 2016;10(1):9-13.[33] 庄禄昌,程兆明,冯康,等. 老年人股骨粗隆间骨折骨牵引治疗的临床分析[J]. 中国继续医学教育,2016,8(29):122-123.[34] ?ahin E, Songür M, Kalem M, et al. Traction table versus manual traction in the intramedullary nailing of unstable intertrochanteric fractures: A prospective randomized trial. Injury. 2016;47(7):1547-1554.[35] 张晓东,杨广忠. 高龄股骨粗隆间骨折的治疗进展[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2012,27(2):187-189.[36] 董佩龙,唐晓波,王健,等. 股骨近端防旋髓内钉与骨水泥柄人工股骨头置换治疗老年股骨粗隆间骨折的疗效分析[J]. 中华关节外科杂志电子版, 2016, 10(1):37-42.[37] Hsu C E, Huang K C, Lin T C, et al. Integrated risk scoring model for predicting dynamic hip screw treatment outcome of intertrochanteric fracture. Injury. 2016; 47(11):2501-2506.[38] 董佩龙,唐晓波,王健,等. 骨水泥柄人工股骨头置换与锁定钢板内固定治疗老年股骨粗隆间骨折效果分析[J]. 南通大学学报:医学版, 2016, 36(4):274-277.[39] Barwar N, Meena S, Aggarwal SK, et al. Dynamic hip screw with locking side plate: a viable treatment option for intertrochanteric fracture. Chin J Trauma. 2014;17(2):88-92.[40] Suh YS, Nho JH, Kim SM, et al. Clinical and Radiologic Outcomes among Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty, Compression Hip Screw and Proximal Femur Nail Antirotation in Treating Comminuted Intertrochanteric Fractures. South Asian J Exp Biol. 2015;27(1):103-107.[41] 王勇,周禹伯,赵伟. 人工股骨头置换术治疗不稳定型老年骨质疏松性股骨粗隆间骨折[J]. 中国骨科临床与基础研究杂志, 2014,6(4):227-232. [42] Tang P, Hu F, Shen J, et al. Proximal femoral nail antirotation versus hemiarthroplasty: a study for the treatment of intertrochanteric fractures. Injury. 2012;43(6):876-881. |
.jpg)
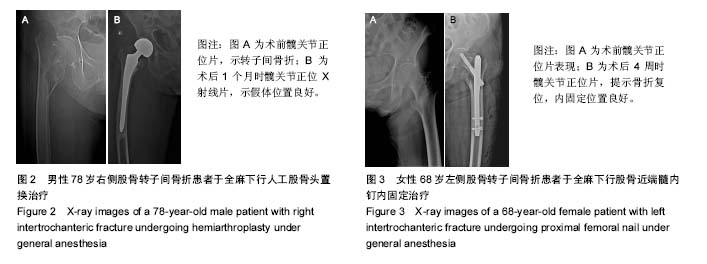
.jpg)