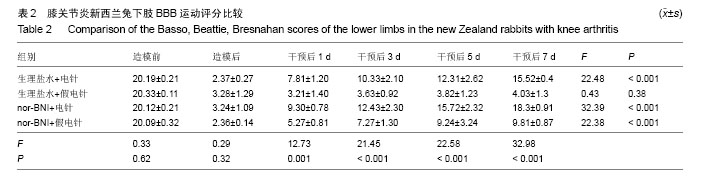
| [1] Zhao ZQ.Neural mechanism underlying acupuncture analgesia. Progress in Neurobiology.2008;85:355-375.[2] Han JS, Ho YS. Global trends and performances of acupuncture research. Neurosci Biobehav Rev.2011;35(3):680-687.[3] Sun Y,Gan TJ,Dubose JW,et al.Acupuncture and related techniques for postoperative pain: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials.Br J Anaesth.2008;101(2):151-160.[4] Sim CK,Xu PC, Pua HL,et al.Effects of electroacupuncture on intraoperative and postoperative analgesic requirement. Acupunct Med.2002;20(2-3):56-65.[5] Lin JG,Lo MW,Wen YR,et al.The effect of high and low frequency electroacupuncture in pain after lower abdominal surgery. Pain.2002;99(3):509-514.[6] 林文注,王佩.实验针灸学[M].上海:上海科学技术出版社, 1999: 288-289.[7] 陈向荣,游思维,金大地,BBB评分评估脊髓损伤大鼠后肢运动功能的探讨[J]中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2014,14(9):547-549.[8] 韩冠英 凌沛学 王凤山,等,不同浓度木瓜蛋白酶建立兔膝骨关节炎模型的比较研究[J],中国骨伤,2012(5)5:424-429[9] Berman BM, Lao L, Langenberg P et al. Effectiveness of acupuncture as adjunctive therapy in osteoarthritis of the knee: a randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med.2004; 141(12): 901-910.[10] Jubb RW, Tukmachi ES, Jones PW et al. A blinded randomised trial of acupuncture (manual and electroacupuncture) compared with a non-penetrating sham for the symptoms of osteoarthritis of the knee. Acupunct Med.2008; 26(2):69-78.[11] Molsberger AF, Schneider T, Gotthardt H et al. German Randomized Acupuncture Trial for chronic shoulder pain (GRASP)-a pragmatic, controlled, patient-blinded, multi-centre trial in an outpatient care environment. Pain.2010; 151(1): 146-154.[12] Linde K, Allais G, Brinkhaus B, et al. Acupuncture for migraine prophylaxis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.2009; (1): CD001218.[13] Ernst E, Pittler MH. The effectiveness of acupuncture in treating acute dental pain: a systematic review.Br Dent J.1998; 184(9): 443-447.[14] Manheimer E,Cheng K,Linde K,et al.Acupuncture for peripheral joint osteoarthritis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.2010; (1):CD001977.[15] Madsen MV,Gtzsche PC,Hróbjartsson A.Acupuncture treatment for pain: systematic review of randomised clinical trials with acupuncture, placebo acupuncture, and no acupuncture groups. BMJ.2009;338: a3115.[16] Manheimer E, White A, Berman B et al. Meta-analysis: acupuncture for low back pain. Ann Intern Med.2005; 142(8): 651-663.[17] Trinh KV, Phillips SD, Ho E et al. Acupuncture for the alleviation of lateral epicondyle pain: a systematic review. Rheumatology (Oxford).2004; 43(9): 1085-1090.[18] Ernst E, Lee MS, Choi TY. Acupuncture: does it alleviate pain and are there serious risks? A review of reviews. Pain.2011; 152(4):755-764.[19] Henke C. Response to the article of Ernst et al. Acupuncture: does it alleviate pain and are there serious risks? A review of reviews. Pain 2011;152:755-64]. Pain.2011;152(9): 2183-2184;[20] McNamee KE, Alzabin S, Hughes JP,et al. IL-17 induces hyperalgesia via TNF-dependent neutrophil infiltration. Pain.2011;152(8):1838-1845.[21] Kleinschnitz C, Hofstetter HH, Meuth SG,et al.T cell infiltration after chronic constriction injury of mouse sciatic nerve is associated with interleukin-17 expression.Exp Neurol.2006; 200(2):480- 485.[22] Noma N, Khan J, Chen IF,et al. Interleukin-17 levels in rat models of nerve damage and neuropathic pain.Neurosci Lett. 2011;493(3):86-91.[23] Kim CF,Moalem-Taylor G.Interleukin-17 contributes to neuroinflammation and neuropathic pain following peripheral nerve injury in mice.J Pain.2011;12(3):370-383.[24] Pinto LG, Cunha TM, Vieira SM,et al. IL-17 mediates articular hypernociception in antigen-induced arthritis in mice.Pain. 2010;148(2):247-256. |
.jpg)

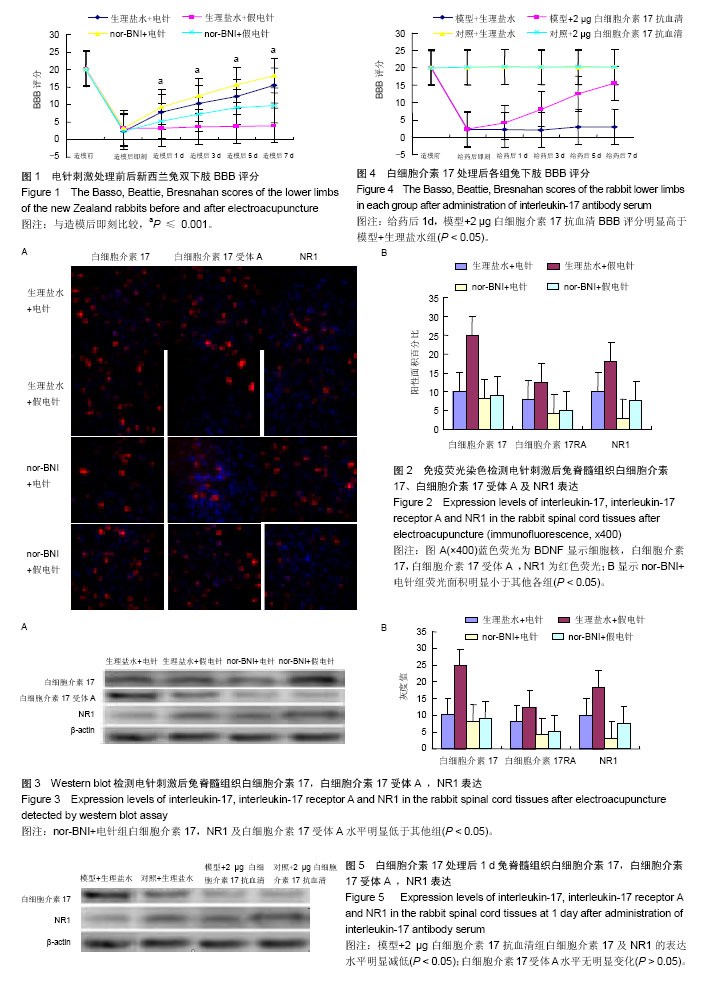
.jpg)