| [1] Garcia-Gomez A, De Las Rivas J, Ocio EM, et al. Transcriptomic profile induced in bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells after interaction with multiple myeloma cells:implications in myeloma progression and myeloma bone disease. Oncotarget. 2014;5(18):8284-8305.[2] Bataille R, Harousseau JL.Multiple myeloma. N Eng J Med 1997;336(23):1657-1664. [3] Barillé-Nion S, Bataille R. New insights in myeloma induced osteolysis. Leuk Lymphoma. 2003;44(9): 1463-1467.[4] Noll JE, Williams SA, Tong CM,et al.Myeloma plasma cells alter the bone marrow microenvironment by stimulating the proliferation of mesenchymal stromal cells. Haematologica. 2014;99(1):163-171.[5] Xu X, Yang J, Tang Y, et al.In vitro migratory aberrancies of mesenchymal stem cells derived from mutiple myeloma patients only partially modulated by Bortezomib. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.2014;7(10):6705-6715. [6] Podar K,Richardson PG,Hideshima T,et al.The malignant clone and the bone-marrow environment. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol.2007;20(4):597-612.[7] Vidriales MB, Anderson KC. Adhesion of multiple myeloma cells to the bone marrow microenvironment: implications for future therapeutic strategies. Molecular Medicine Today. 1996; 2(10):425-431.[8] Witzig TE. The role of adhesion receptors in the pathogenesis of multiple myeloma. Hematology Oncology Clinics of North America.1999;13(6):1127-1143.[9] Grigorieva I, Thomas X, Epstein J,et al.The bone marrow stromal environment is a major factor in myeloma cell resistance to dexamethasone. Experimental Hematology. 1998;26(7):597-603.[10] Damiano JS, Cress AE, Hazlehurst LA,et al. Cell adhesion mediated drug resistance (CAM-DR): role of integrins and resistance to apoptosis in human myeloma cell lines. Blood. 1999;93(5):1658-1667.[11] Wang X, Zhang Z, Yao C. Survivin is upregulated in myeloma cell lines cocultured with mesenchymal stem cells. Leuk Res. 2010;34(10):1325-1329. [12] Skotnicki AB, Majka M. The Analysis of the Relationship between Multiple Myeloma Cells and Their Microenvironment. J Cancer.2015; 6(2):160-168.[13] Reagan, MR; Ghobrial, IM, et al. Multiple Myeloma Mesenchymal Stem Cells:Characterization, Origin, and Tumor-Promoting Effects.Clinical Cancer Research. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18(2):342-349. [14] Wang X, Zhang Z, Yao C. Angiogenic activity of mesenchymal stem cells in multiple myeloma. Cancer Invest.2011;29(1): 37-41.[15] Garayoa M, Garcia JL, Santamaria C, et al . Mesenchymal stem cells from multiple myeloma patients display distinct genomic profile as compared with those from normal donors. Leukemia. 2009;23(8):1515-1527.[16] Garderet L, Mazurier C, Chapel A,et al.Mesenchymal stem cell abnormalities in patients with multiple myeloma. Leuk- ymphoma.2007; 48(10):2032-2041. [17] Corre J, Mahtouk K, Attal M,et al.Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells are abnormal in multiple myeloma. Leukemia.2007; 21(5):1079-1088.[18] Maffini MV, Soto AM, Calabro JM, et al. The stroma as a crucial target in rat mammary gland carcinogenesis.J Cell Sci 2004;117(Pt 8):1495-1502. [19] Hideshima T, Mitsiades C, Tonon G, et al.Understanding multiple myeloma pathogenesis in the bone marrow to identify new therapeutic targets.Nat Rev Cancer.2007;7(8):585-98.[20] Mitsiades CS,Mitsiades NS,Munshi NC,et al.The role of the bone microenvironment in the pathophysiology and therapeutic management of multiple myeloma: interplay of growth factors, their receptors and stromal interactions. Eur J Cancer.2006; 42(11):1564-1573.[21] Podar K, Chauhan D, Anderson KC,et al. Bone marrow microenvironment and the identification of new targets for myeloma therapy. Leukemia .2009; 23(1):10-24[22] Basak GW, Srivastava AS, Malhotra R, et al. Multiple myeloma bone marrow niche. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2009; 10(3):345-6.[23] 夏雷,杨姣,陈诗婧,等.FCFR2,MMP1,CCL7在多发性骨髓瘤患者的骨髓微环境中的表达及其临床意义[J].江苏医药,2014; 40(12):1404-1406.[24] Bergfeld SA,DeClerck YA.Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells and the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Metastasis Rev.2010; 29(2):249-261.[25] Roccaro AM, Sacco A, Maiso P, et al.BM mesenchymal stromal cell-derived exosomes facilitate multiple myeloma progression.J Clin Invest.2013;123(4):1542-1555.[26] Nakajima S, Fujiwara T, Ohguchi H, et al.Induction of thymic stromal lymphopoietin in mesenchymal stem cells by interaction with myeloma cells.Leukemia & Lymphoma.2014; 55(11): 2605-2613.[27] Augello A, De Bari C.The regulation of differentiation in mesenchymal stem cells.Hum Gene Ther.2010;21(10): 1226-1238.[28] 杨姣,夏雷,雷芳,等.多次肿瘤坏死因子预处理骨髓间充质干细胞促进其成骨分化潜能[J].南京医科大学学报:自然科学版,2014, 34(3):275-280. [29] Pittenger MF. Mesenchymal stem cells from adult bone marrow. Methods Mol Biol. 2008; 449:27-44.[30] Giuliani N,Mangoni M,Rizzoli V,et al.Osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells in multiple myeloma: identification of potential therapeutic targets. Exp Hematol. 2009;37(8):879-886. [31] Arnulf B,Lecourt S,Soulier J, et al. Phenotypic and functional characterization of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells derived from patients with multiple myeloma. Leukemia.2007; 21(1):158-163. [32] Wallace SR,Oken MM,Lunetta KL, et al.Abnormalities of bone marrow mesenchymal cells in multiple myeloma patients. Cancer.2001; 91(7):1219-1230.[33] Li B, Fu J, Chen P,et al. Impairment in immunomodulatory function of mesenchymal stem cells from multiple myeloma patients. Arch Med Res. 2010;41(8):623-633.[34] Kawano M, Hirano T, Matsuda T, et al. Autocrine generation and requirement of BSF-2/IL-6 for human multiple myelomas. Nature. 1988;332(6159):83-85.[35] Schwab G,Siegall CB,Aarden LA,et al.Characterization of an interleukin-6-mediated autocrine growth loop in the human multiple myeloma cell line, U266. Blood.1991;77(3):587-593.[36] Klein B, Zhang XG, Jourdan M, et al. Paracrine rather than autocrine regulation of myeloma-cell growth and differentiation by interleukin-6.Blood. 1989;73(2):517-526.[37] Portier M, Rajzbaum G, Zhang XG, et al. In vivo interleukin 6 gene expression in the tumoral environment in multiple myeloma.Eur J Immunol.1991;21(7):1759-1762.[38] Xiong Y, Donovan KA, Kline MP, et al. Identification of two groups of smoldering multiple myeloma patients who are either high or low producers of interleukin-1. J Interferon Cytokine Res.2006;26(2):83-95.[39] Cozzolino F, Torcia M, Aldinucci D, et al. Production of interleukin-1 by bone marrow myeloma cells. Blood.1989; 74(1):380-387.[40] Torcia M, Lucibello M, Vannier E,et al. Modulation of osteoclast-activating factor activity of multiple myeloma bone marrow cells by different interleukin-1 inhibitors. Exp Hematol. 1996;24(8):868-874.[41] Ferreira E, Porter RM, Wehling N, et al.Inflammatory Cytokines Induce a Unique Mineralizing Phenotype in Mesenchymal Stem Cells Derived from Human Bone Marrow. The Journal Of Biological Chemistry.2013;288(41):29494- 29505.[42] Masui S,Nakatake Y,Toyooka Y,et al.Pluripotency governed by Sox2 via regulation of Oct3/4 expression in mouse embryonic stem cells.Nat Cell Biol.2007;9(6):625-635.[43] Nichols J,Zevnik B, Anastassiadis K, et al. Formation of pluripotent stem cells in the mammalian embryo depends on the POU transcription factor Oct4.Cell. 1998;95(3):379-391.[44] Rodda DJ, Chew JL, Lim LH,et al.Transcriptional regulation of Nanog by OCT4 and SOX2. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(26): 24731-24737.[45] Riekstina U, Cakstina I, Parfejevs V, et al. Embryonic stem cell marker expression pattern in human mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow, adipose tissue, heart and dermis. Stem Cell Rev.2009;5(4):378-386.[46] Takahashi K, Yamanaka S.Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors.Cell.2006;126(4):663-676.[47] Avilion AA, Nicolis SK, Pevny LH,et al.Multipotent cell lineages in early mouse development depend on SOX2 function. Genes Dev.2003;17(1):126-140.[48] Kallas A,Pook M,Trei A,et al.SOX2 Is Regulated Differently from NANOG and OCT4 in Human Embryonic Stem Cells during Early Differentiation Initiated with Sodium Butyrate. Stem Cells International.2014;2014:298163.[49] Peltier J,Conway A,Keung AJ,et al.Akt increases sox2 expression in adult hippocampal neural progenitor cells, but increased sox2 does not promote proliferation. Stem Cells Dev.2011; 20(7):1153-1161.[50] Spisek R,Kukreja A,Chen LC,et al.Frequent and specific immunity to the embryonal stem cell-associated antigen SOX2 in patients with monoclonal gammopathy. J Exp Med. 2007; 204(4):831-840.[51] Tanno T, Lim Y, Wang Q,et al.Growth differentiating factor 15 enhances the tumor-initiating and self-renewal potential of multiple myeloma cells.Blood.2014;123(5):725-733.[52] Baggiolini M.Chemokines and leukocyte traffic. Nature.1998; 392(6676):565-568.[53] Mackay C.Chemokines: immunology’s high impact factors. Nat Immunol .2001;2(2):95-101.[54] Wright N, de Lera TL, Garcia-Moruja C, et al. Transforming growth factor-betal down-regulates expression of chemokine stromal cell-derived factor-1: functional consequences in cell migration and adhesion.Blood.2003;102(6):1978-1984.[55] Colombo M, Mirandola L, Platonova N,et al. Notch-directed micro -environment reprogramming in myeloma: a single path to multiple outcomes. Leukemia.2013;27(5):1009-1018. [56] Möller C, Strömberg T, Juremalm M, et al. Expression and function of chemokine receptors in human multiple myeloma. Leukemia . 2003;17(1):203-210.[57] Oba Y,Lee JW,Ehrlich LA ,et al.MIP-1 alpha utilizes both CCR 1 and CCR 5 to induce osteoclast formation and increase adhesion of myeloma cells to marrow stromal cells Experimental Hematology.2005;33(3):272-278.[58] Vallet S, Raje N, Ishitsuka K, et al.MLN3897, a novel CCR1 inhibitor, impairs osteoclastogenesis and inhibits the interaction of multiple myeloma cells and osteoclasts. Blood. 2007;110(10):3744-3752. [59] Moreaux J, Hose D, Kassambara A,et al.Osteoclast-gene expression profiling reveals osteoclast-derived CCR2 chemokines promoting myeloma cell migration.Blood. 2011; 117(4):1280-1290. |
.jpg)
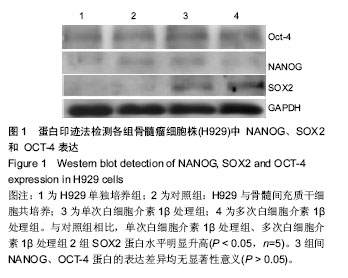
.jpg)
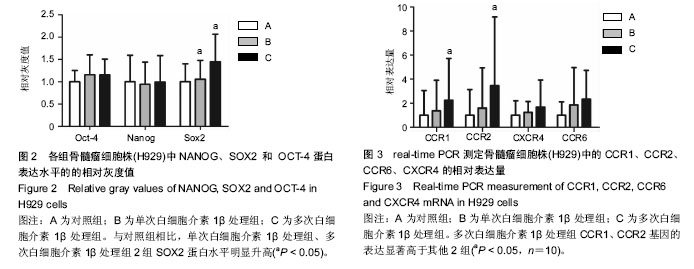
.jpg)