中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (52): 7872-7877.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.52.017
• 纳米生物材料 nanobiomaterials • 上一篇 下一篇
Fe3O4纳米粒子的组织相容性及组织分布研究
龚君佐1,屠重棋2,段 宏2,周绍兵3
- 1川北医学院,四川省南充市 637100;2四川大学华西医学中心骨科,四川省成都市 610041;3西南交通大学材料先进技术教育部重点实验室,四川省成都市 610031
Histocompatibility and distribution of ferroferric oxide nanoparticles
Gong Jun-zuo1, Tu Zhong-qi2, Duan Hong2, Zhou Shao-bing3
- 1North Sichuan Medical University, Nanchong 637100, Sichuan Province, China; 2Department of Orthopaedics, West China Center of Medical Sciences, Sichuan University, Chendu 610041, Sichun Province, China; 3Key Laboratory of Advanced Technologies of Materials of Southwest Jiaotong University, Ministry of Education, Chengdu 610031, Sichuan Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
Fe3O4纳米粒子:Fe3O4纳米粒子表面偶联亲水性材料(如聚乙二醇,聚氧乙烯,聚山梨酯80,西曲溴铵,泊洛沙姆,油酸钠等)进行修饰便于偶联化疗药物,同时可形成一层动态的亲水性物,以抵制血浆蛋白的结合。静脉注射后不易被单核巨噬细胞系统识别吞噬,可在血液循环系统中维持较长半衰期,使药物有选择性地渗入病灶,能够直接靶向于单核巨噬细胞系统之外的大多数肿瘤。
靶向:对特定目标(分子、细胞、个体等)采取的行动。如外源基因在宿主细胞基因组DNA预期位置上的定向插入;药物分子对效应靶组织或细胞的定向传送或作用。
背景:Fe3O4纳米粒子是目前研究较多的靶向性纳米药物递呈系统,它可与抗肿瘤药物结合在一起,在外界磁场作用下,运载抗肿瘤药物靶向性到达肿瘤部位发挥抗肿瘤作用,其亚微粒可以到达远离磁源数厘米的肿瘤部位。
目的:分析Fe3O4纳米粒子的组织相容性及在机体内的药物分布,及其在骨肉瘤化疗中作为药物载体的应用前景和存在问题。
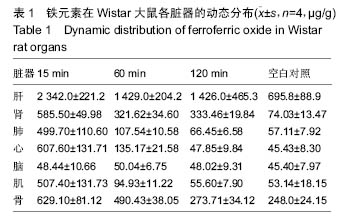
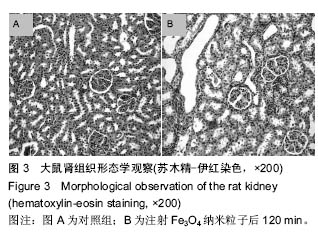
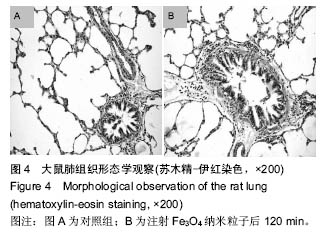
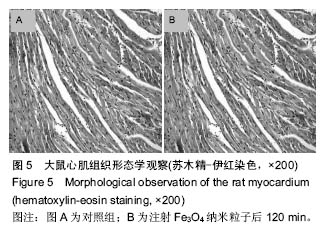
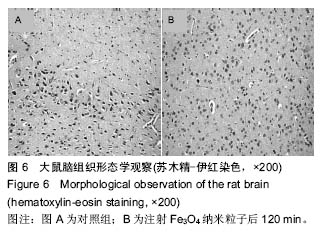
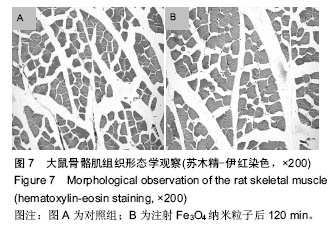
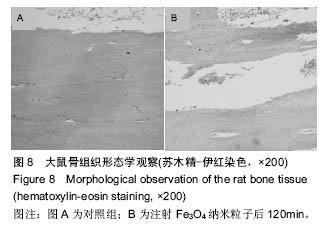
方法:使用Wistar大鼠,按10.0 mg/kg剂量,Fe3O4纳米粒子经鼠尾静脉推注后15,60,120 min处死,取各组织(肺、脑、心、肝脏、肾脏、后肢骨、骨骼肌),采用原子吸收光谱仪分析各组织单位质量的铁离子含量。将各时间点的各种组织作苏木精-伊红染色以观察组织形态变化。
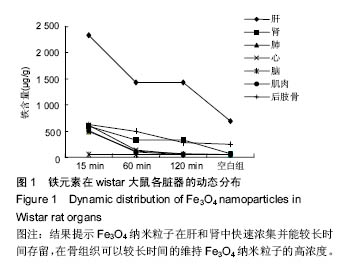
结果与结论:①在肝和肾组织Fe3O4纳米粒子浓度于15 min时达到峰值,给药后60 min和120 min检测到的肝和肾组织纳米粒子浓度虽呈下降趋势但仍然维持在较高水平,3个时间点Fe3O4纳米粒子浓度与对照组比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),提示Fe3O4纳米粒子在肝和肾中快速浓集并能较长时间存留;②在心、肺、骨骼肌和骨组织中Fe3O4纳米粒子浓度于15 min时达到峰值,但随后迅速下降。15 min时Fe3O4纳米粒子浓度与对照组比较差异有显著性意义 (P < 0.05),仅在骨组织代谢较慢,在60 min时与对照组比较差异仍有显著性意义 (P < 0.05),表明Fe3O4纳米粒子在这些血流灌注高的组织中虽能达到高浓度但存留时间短。唯有骨组织可以较长时间的维持Fe3O4纳米粒子的高浓度;③在脑组织中各时间点Fe3O4纳米粒子浓度与对照组比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),提示Wistar大鼠的血脑屏障可能对Fe3O4纳米粒子的穿透具有阻碍作用;④所有的组织通过苏木精-伊红染色后均未发现明显的改变;⑤结果表明,偶联油酸钠Fe3O4纳米粒子在机体组织中的分布受组织血流灌注和单核巨噬细胞系统的影响,且不能穿透血脑屏障。对各种组织均未发现有显著的影响。偶联油酸钠Fe3O4纳米粒子在肝、肾和骨组织内可以维持较长较高浓度,作为磁靶向热化疗载体治疗上述脏器的恶性肿瘤有重要的理论意义。
中图分类号:

.jpg)