中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (47): 7021-7026.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.47.004
• 纳米生物材料 nanobiomaterials • 上一篇 下一篇
聚乙二醇修饰载血管紧张素转化酶RNA壳聚糖纳米粒治疗高血压
王 勇1,张亚光2
- 1河南省人民医院高血压科,河南省郑州市 450000;2河南医学高等专科学校,河南省郑州市 451191
Polyethylene glycol-modified chitosan nanoparticles loaded with angiotensin converting enzyme-shRNA for hypertension
Wang Yong1, Zhang Ya-guang2
- 1Department of Hypertension, Henan Provincial People’s Hospital, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China; 2Henan Medical College, Zhengzhou 451191, Henan Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
基因载体:开发基因药物的一个重要环节在于基因递送载体的研制。理想的基因载体应具备以下性能:结构稳定,能保护基因不被破坏,可选择性的导向靶细胞,能将基因运送到细胞腔内并使其高效的转染和表达,对机体无免疫原性和无毒性,并能被临床接受。
壳聚糖:是从甲壳类生物的贝壳中提取出来的一种可生物降解的多糖,具有良好的生物相容性,作为药物载体得到广泛应用。
背景:临床治疗原发性高血压的传统降压药物一般半衰期较短,且治疗效果不佳。壳聚糖可以作为基因载体,将目标基因载入机体起到靶向治疗作用。聚乙二醇与DNA结合形成纳米粒后,可以起到表面保护效果,稳定纳米粒,使其在体内保持长循环。
目的:探讨聚乙二醇修饰的载血管紧张素转化酶RNA壳聚糖纳米粒注射到自发性高血压模型大鼠体内后,对模型大鼠的降压疗效以及对心脏组织的影响。
方法:实验共分为5组,取32只自发性高血压大鼠随机分为4组,为模型组、壳聚糖组、实验组、阳性药物组,每组8只;取8只正常大鼠,不作处理作为对照组。分组后分别于实验第1,10天进行给药2次,其中模型组和对照组尾静脉注射等量的生理盐水,壳聚糖组尾静脉注射1 mg/kg壳聚糖,实验组尾静脉注射1 mg/kg的聚乙二醇修饰载血管紧张素转化酶RNA壳聚糖纳米粒,阳性药物组灌胃 0.5 mg/kg盐酸贝那普利。
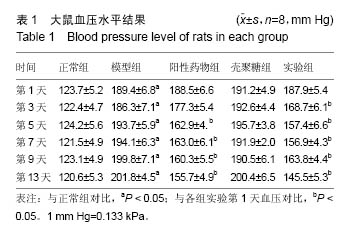
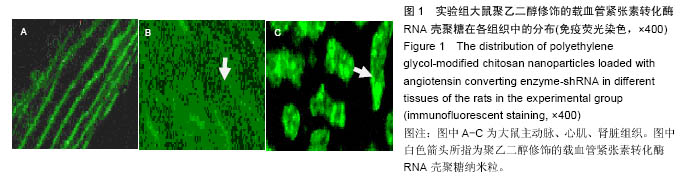
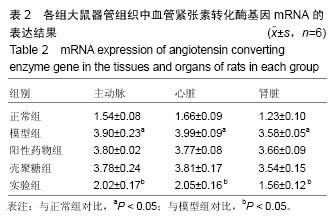
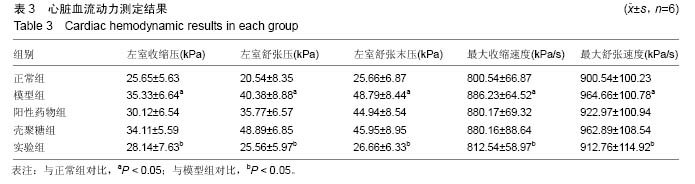
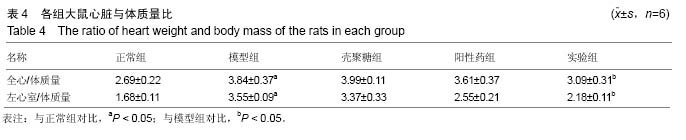
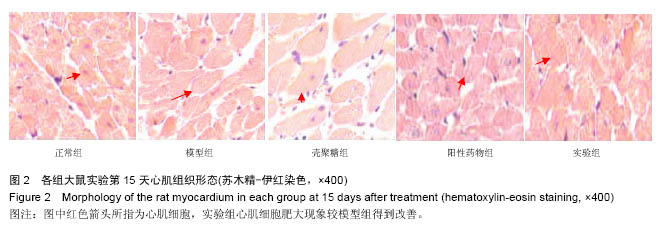
结果与结论:①血压水平:大鼠注射修饰的壳聚糖纳米粒后第3天,与第1天比血压显著下降(P < 0.05);②组织学变化:实验组主动脉、肾脏及心脏组织切片显示均有绿色荧光表达,和血管紧张素转换酶的体内分布基本一致;③RT-PCR检测及左室功能检测:注射后第3天,与模型组相比,实验组各组织器管中血管紧张素转换酶mRNA表达水平及心肌肥厚相关指标减少(P < 0.05)、心肌细胞肥大现象均有显著的减轻(P < 0.05);④结果证实,聚乙二醇修饰的载血管紧张素转化酶RNA壳聚糖纳米粒可以降低高血压模型大鼠的血压值和修复受损心脏,其作用机制可能与血管紧张素转移酶有关。
中图分类号:
.jpg)