| [1] Oxland TR. A history of spine biomechanics. Der Unfallchirurg. 2015;118: 80-92.
[2] Weber EH. Anatomisch-physiologische undersuchung uber einige einrichtungen im mechamismus der menschlichen wirbelsaule. Arch Anatu Physiol. 1827: 240-271.
[3] Markolf KL. Deformation of the thoracolumbar intervertebral joint in response to external loads: a biomechanical study using autopsy material. Bone Joint Surg. 1972;54A: 511-533.
[4] Asazuma T, Stokes IF, Moreland MS. Intersegemental Spinal Flexibility with Lumbosacral Instrumentation An in Vitro Biomechanical Investigation. Spine. 1990;15(11): 1153-1158.
[5] 季伟,王向阳.人体脊柱运动测量方法研究进展[J].医用生物力学,2011, 26(1): 92-96.
[6] Guo LY, Yang CC, Yang CH, et al. The feasibility of using electromagnetic motion capture system to measure primary and coupled movements of cervical spine. J Med Biol Eng. 2011;31(4): 245-253.
[7] Pearcy M, Portek I, Shepherd J, et al. Three-Dimensional X-ray Analysis of Normal Movement in the Lumbar Spine. Spine. 1984;9(3): 294-297.
[8] Anderst W, Baillargeon E, Donaldson W, et al. Motion Path of the Instant Center of Rotation in the Cervical Spine During In Vivo Dynamic Flexion-Extension. Spine. 2013; 38(10): 594-601.
[9] 姜锦鹏,顾洪生,刘伟强,等.正常成人颈椎间盘相关参数测量及意义[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2013, 31(1): 32-36.
[10] 白文媛,顾洪生,廖振华,等.正常成人腰椎间盘相关参数的测量和意义[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2013, 31(5): 505-510.
[11] Sforza C, Grassi GP, Fragnito N, et al. Three-dimensional analysis of active head and cervical spine range of motion: effect of age in healthy male subjects. Clin Biomech. 2002;17: 611-614.
[12] Theobald PS, Jones MD, Williams JM. Do inertial sensors represent a viable method to reliably measure cervical spine range of motion. Man Ther. 2012;17: 86-92.
[13] Salem W, Lenders C, Mathieu J, et al. In vivo three-dimensional kinematics of the cervical spine during maximal axial rotation. Man Ther. 2013;18(4): 339-344.
[14] Panjabi MM, Goel V, Thomas O, et al. Human Lumbar Vertebrae Quantitative Three-Dimensional Anatomy. Spine. 1992;17(3): 299-306.
[15] 原芳,蒲婷,廖振华,等.Prestige LP和Discover人工颈椎间盘的生物力学有限元分析[J].北京生物医学工程,2014, 33(1): 13-20.
[16] Adams MA. Mechanical Properties of Aging Soft Tissues. Springer International Publishing, 2015: 7-35.
[17] Panjabi MM, Crisco JJ, Vasavada A, et al. Mechanical Properties of the Human Cervical Spine as Shown by Three-Dimensional Load-Displacement Curves. Spine. 2001;26(24): 2692-2700.
[18] Schultz AB, Andersson GB. Analysis of Loads on the Lumbar Spine. Spine. 1981;6(1): 76-82.
[19] Adams MA, McNally DS, Wagstaff J, et al. Abnormal stress concentrations in lumbar intervertebral discs following damage to the vertebral body: a cause of disc failure. Eur Spine J. 1993;1(4): 214-221.
[20] Panjabi MM, Abumi K, Duranceau J, et al. Biomechanical Evaluation of Spinal Fixation Devices: Ⅱ. Stability Provided by Eight Internal Fixation Devices. Spine. 1988; 13(10): 1135-1140.
[21] 薛清华,原芳,廖振华,等.表面应变法无损测量椎间盘压强[J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版),2014, 54(5): 690-694.
[22] Adams MA. Mechanical Testing of the Spine An Appraisal Methodology, Result, and Conclusions. Spine. 1995; 20(19): 2151-2156.
[23] Melnyk AD, Wen TL, Kingwell S, et al. Load transfer characteristics between posterior spinal implant and the lumbar spine under anterior shear loading: an in vitro investigation. Spine. 2012;37(18): E1126-1133.
[24] Adams MA,Hutton WC, Scott JR. The resistance to flexion of the lumbar intervertebral joint. Spine. 1980;5: 245-253.
[25] Han KS, Zander T, Rohlmann A, et al. An enhanced and validated generic thoraco-lumbar spine model for prediction of muscle forces. Med Eng Phys. 2012;34: 709-716.
[26] Bauman JA, Jaumard NV, Guarino BB, et al. Facet joint contact pressure is not significantly affected by ProDisc cervical disc arthroplasty in sagittal bending: a single-level cadaveric study. Spine. 2012;12(10):949-959.
[27] 房佐忠. 双节段人工颈椎间盘置换对邻近上位关节突关节影响的生物力学研究和临床观察[D].中南大学,2007.
[28] 徐波,张忠民,赵卫东,等. 颈椎人工椎间盘置换或前路融合内固定术后关节突间压力的改变[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2010, 20(5): 406-410.
[29] Brinckmann P, Biggemann M, Hilweg D. Fatigue fracture of human lumbar vertebrae. Clin Biomech. 1988;3(suppl 1):1-23.
[30] Adams MA, Dolan P. Intervertebral disc degeneration: evidence for two distinct phenotypes. J Anat. 2012;221(6): 497-506.
[31] Panjabi MM. Hybrid multidirectional test method to evaluate spinal adjacent-level effects. Clin Biomech. 2007; 22: 257-265.
[32] Ti-Sheng C, Ching-Wei C, Chien-Shuing W, et al. A New Multi-direction Tester for Evaluation of the Spinal Biomechanics. J Med Biol Eng. 2008;29(1): 7-13.
[33] Panjabi MM, Oxland TR, Kifune M, et al. Validity of the Three-Column Theory of Thoracolumbar Fractures. Spine. 1995;20(10): 1122-1127.
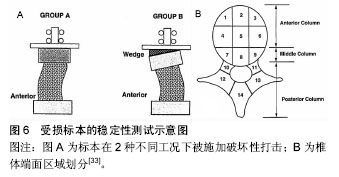
[34] Abumi K, Panjubi MM, Kramer KM, et al. Biomechanical Evaluation of Lumbar Spinal Stability After Graded Facetectomies. Spine. 1990; 15(11): 1142-1147.
[35] 蒲婷,吕聪伟,颜滨,等.人工颈椎间盘置换术与融合术的生物力学实验研究[J]. 医用生物力学,2014, 29(2):105-112.
[36] 刘伟强,吕聪伟,蒲婷,等.颈椎前路三节段融合与置换混合术的力学特性[J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 54(5): 685-689.
[37] Zigler JE, Delamarter R, Spivak J, et al. ProDisc-C and anterior cervical discectomy and fusion as surgical treatment for spine-level cervical symptomatic degenerative disc disease: five-year results of a food and drug administration study. Spine. 2013;38(3): 203-209.
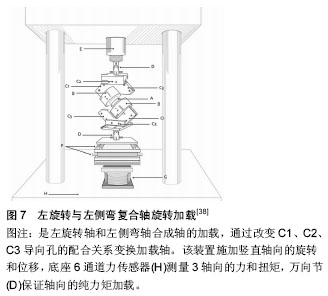
[38] Spenciner D, Greene D, Paiva J, et al. The multidirectional bending properties of the human lumbar intervertebral disc. Spine. 2006;4: 248-257. |
.jpg)
.jpg)