| [1] Jackson WM, Nesti LJ, Tuan RS. Concise review: clinical translation of wound healing therapies based on mesenchymal stem cells. Stem cells translational medicine.2012;1(1):44-50.
[2] Friedenstein A, Piatetzky-Shapiro I, Petrakova K. Osteogenesis in transplants of bone marrow cells. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1966;16(3):381-190.
[3] Kalladka D, Muir KW. Brain repair: cell therapy in stroke. Stem cells and cloning: advances and applications. 2014;7:31.
[4] Knight MN, Hankenson KD. Mesenchymal stem cells in bone regeneration. Advances in wound care. 2013; 2(6):306-316.
[5] Friedenstein A, Chailakhyan R, Gerasimov U. Bone marrow osteogenic stem cells: in vitro cultivation and transplantation in diffusion chambers. Cell proliferation. 1987;20(3):263-272.
[6] Zhang X, Jiao C,Zhao S.Role of mesenchymal stem cells in immunological rejection of organ transplantation. Stem Cell Reviews and Reports. 2009;5(4):402-409.
[7] Rodda SJ, McMahon AP. Distinct roles for Hedgehog and canonical Wnt signaling in specification, differentiation and maintenance of osteoblast progenitors. Development. 2006;133(16):3231-3244.
[8] Bartel DP.MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. cell. 2004;116(2):281-297.
[9] Ambros V.The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. 2004;431(7006):350-355.
[10] Berezikov E,Guryev V,van de Belt J,et al.Phylogenetic shadowing and computational identification of human microRNA genes.cell.2005;120(1):21-24.
[11] Lewis BP,Burge CB,Bartel DP.Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets.cell. 2005; 120(1):15-20.
[12] Wang Q, Cai J, Cai X, et al. miR-346 regulates osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells by targeting the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. PLoS One.2013;8(9): e72266.
[13] Zhang JF, Fu WM, He ML, et al.MiRNA-20a promotes osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells by co-regulating BMP signaling.RNA biology. 2011;8(5):829-838.
[14] Li Z, Hassan MQ, Jafferji M, et al. Biological functions of miR-29b contribute to positive regulation of osteoblast differentiation. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(23): 15676-15684.
[15] Kim EJ,Kang IH,Lee JW,et al.MiR-433 mediates ERRγ-suppressed osteoblast differentiation via direct targeting to Runx2 mRNA in C3H10T1/2 cells. Life sciences. 2013;92(10):562-568.
[16] Gao J,Yang T,Han J,et al. MicroRNA expression during osteogenic differentiation of human multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells from bone marrow.J Cell Biochem. 2011;112(7):1844-1856.
[17] Nakao A,Afrakhte M,Morn A,et al.Identification of Smad7, a TGFβ-inducible antagonist of TGF-β signalling. Nature.1997;389(6651):631-635.
[18] Yan X,Chen Y.Smad7: not only a regulator, but also a cross-talk mediator of TGF-beta signalling. Biochem J.2011;434:1-10.
[19] Chen G,Deng C,Li YP.TGF-β and BMP signaling in osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. International journal of biological sciences. 2012;8(2): 272.
[20] Watabe T,Miyazono K.Roles of TGF-β family signaling in stem cell renewal and differentiation. Cell research. 2009;19(1):103-15.
[21] Pagani F,Francucci C, Moro L. Markers of bone turnover: biochemical and clinical perspectives. Journal of endocrinological investigation. 2004;28 (10 Suppl):8-13.
[22] 王帅,周一鸣,范公忍,等.骨髓间充质干细胞移植后在肝损伤大鼠体内的分布及其治疗作用[J].中国体视学与图像分析,2014(2):187-195.
[23] 刘雅娟,郭丽,张桂英,等.不同数量骨髓间充质干细胞静脉移植治疗老年糖尿病大鼠的疗效[J].中国老年学杂志, 2014,34(19):80.
[24] Jia J, Tian Q, Ling S,et al.miR-145 suppresses osteogenic differentiation by targeting Sp7. FEBS letters.2013;587(18):3027-3031.
[25] Cai C, Chen QB, Han ZD, et al. miR-195 inhibits tumor progression by targeting RPS6KB1 in human prostate cancer. Clinical Cancer Research. 2015;21(21): 4922-4934.
[26] Soon PS,Tacon LJ,Gill AJ,et al.miR-195 and miR-483-5p identified as predictors of poor prognosis in adrenocortical cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15(24): 7684-7692.
[27] Li D, Zhao Y, Liu C, et al.Analysis of MiR-195 and MiR-497 expression, regulation and role in breast cancer. Clinical Cancer Research. 2011;17(7): 1722-1730.
[28] Wang X,Wang J,Ma H,et al.Downregulation of miR-195 correlates with lymph node metastasis and poor prognosis in colorectal cancer.Medical Oncology. 2012;29(2):919-927.
[29] Bhattacharya A,Schmitz U,Wolkenhauer O,et al. Regulation of cell cycle checkpoint kinase WEE1 by miR-195 in malignant melanoma.Oncogene. 2013; 32(26):3175-3183.
[30] Yang X,Yu J,Yin J,et al.MiR-195 regulates cell apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting LATS2. Die Pharmazie-An International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2012;67(7): 645-651.
[31] Wei W,Zhang WY, Bai JB, et al. The NF-?B modulated miR-195/497 inhibit myoblast proliferation by targeting Igf1r/Insr and cyclin genes.J Cell Sci.2015:jcs. 174235.
[32] Sato T, Yamamoto T, Sehara-Fujisawa A. miR-195/497 induce postnatal quiescence of skeletal muscle stem cells. Nat Commun. 2014;5:4597. |
.jpg)
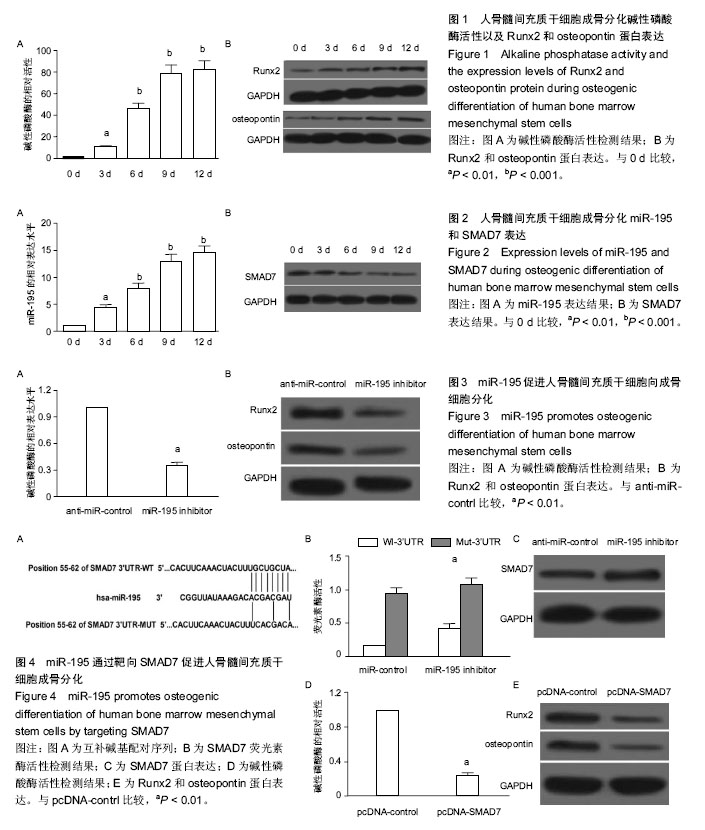
.jpg)