| [1] Yang SE, Ha CW, Jung M, et al. Mesenchymal stem/progenitor cells developed in cultures from UC blood.Cytotherapy. 2004;6(5):476-486.[2] Lee MW, Choi J, Yang MS, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells from cryopreserved human umbilical cord blood. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;320(1):273-278.[3] Wagner W, Wein F, Seckinger A, et al. Comparative characteristics of mesenchymal stem cells from human bone marrow, adipose tissue, and umbilical cord blood. Exp Hematol. 2005;33(11):1402-1416.[4] McGuckin CP, Forraz N, Allouard Q,et al. Umbilical cord blood stem cells can expand hematopoietic and neuroglial progenitors in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 2004;295(2):350-359.[5] Zeddou M, Briquet A, Relic B, et al. The umbilical cord matrix is a better source of mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) than the umbilical cord blood. Cell Biol Int. 2010;34(7):693-701.[6] Sun XC,Xu WR,Xu HX,et al. Jiangsu Daxue Xuebao. 2005; 15(5):369-372.孙晓春,许文荣,许化溪,等.不同来源的人间质干细胞分离与基本生物学特性研究[J]. 江苏大学学报,2005,15(5):369-372.[7] Perry SA, Spees JL, Prockop DJ. In vitro mesodermal differentiation of adherent CD133+ bone marrow stromal cells.Nonhematopoietic and Mesenchymal Stem Cells Meeting, 2003.[8] Tang TJ,Yang B,Yang HD,et al. Shiyong Yixue Zazhi. 2005;21 (21):2412-2414.汤天军,杨波,杨汉东,等.人脐带血间充质干细胞体外诱导分化为心肌细胞的实验研究[J].实用医学杂志,2005,21(21):2412- 2414.[9] Hong XY,Wang B,Du J,et al. Zhongguo Wuzhenxue Zazhi. 2005;15(17):3218-3220.洪小杨,王斌,杜江,等.人脐带血间充质干细胞体外分离培养研究[J].中国误诊学杂志,2005, 5(17):3218-3220.[10] Wang Y,Ji FQ,Sun HM,et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2006;10(29):50-52.王屹,季凤清,孙海梅,等.人脐血非造血干细胞的基本特性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2006,10(29):50-52.[11] Liu SF,Yan WH,Han XF,et al. Zhongguo Linchuang Kangfu. 2005;9(46):34-35.刘素芳,鄢文海,韩雪飞,等.人脐血间充质细胞体外分离培养方法及培养基特性[J].中国临床康复,2005,9(46):34-35.[12] Bieback K, Kern S, Klüter H, et al. Critical parameters for the isolation of mesenchymal stem cells from umbilical cord blood. Stem Cells. 2004;22(4):625-634.[13] Zhang T,Li M,Xu PR. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu. 2012;16(14) :2555-2558.张涛,李敏,徐佩茹.脐血间充质干细胞的适宜培养条件[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(14) :2555-2558.[14] Hou F, Huang JM, Zhang R, et al. An experimental study on the regulation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells through indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase signaling pathway by thymosin α1 for improving the immunosuppression mediated by T cell.Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2011;49(3): 181-185.[15] Yoo KH, Jang IK, Lee MW,et al. Comparison of immunomodulatory properties of mesenchymal stem cells derived from adult human tissues. Cell Immunol. 2009;259(2): 150-156. |
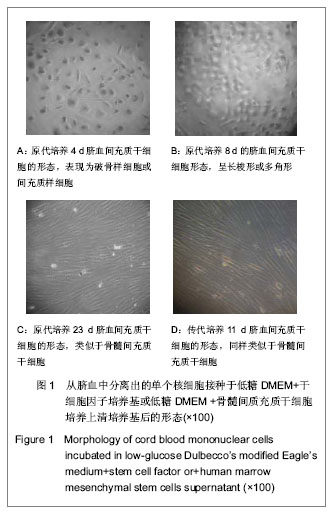
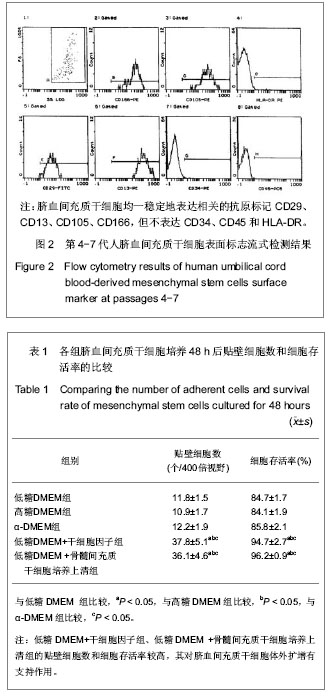
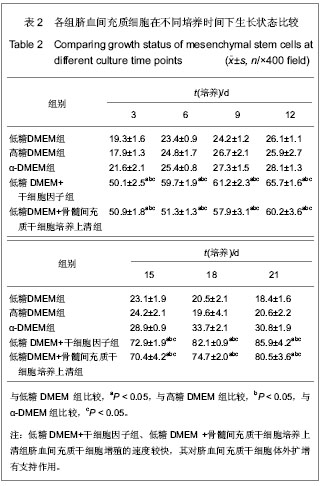
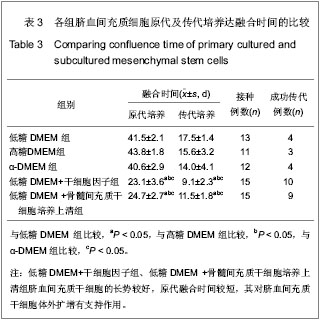
.jpg)