| [1] J PM,Angelo DL,Marc B,et al. Phase III trial comparing two dose levels of epirubicin combined with cyclophosphamide with cyclophosphamide, methotrexate, and fluorouracil in node-positive breast cancer.J Clin Oncol.2001;19(12): 3103-3110.[2] Le YL,Ho CT,Tsai FL. Inhibit multidrug resistance and induce apoptosis by using glycocholic acid and epirubicin. Eur J Pharm Sci .2008;35(1-2):52-67.[3] Leucuta SE,Achim M,Risca R,et al.Preparation and pharmaceutical/pharmacokinetic characterization of liposomes and nanoparticles loaded with epirubicin. STP Pharma Sci. 2003;13(5):291-297.[4] Temming K,Meyer DL,Zabinski R,et al. Evaluation of RGD-targeted albumin carriers for specific delivery of auristatin e to tumor blood vessels. Bioconj Chem .2006; 17(6): 1385-1394.[5] Guo W,Lee RJ.Receptor-targeted gene delivery viafolate-conjugated polyethylenimine.AAPS Pharm Sci.1999;1(4):20-26. doi: 10.1208/ps010419.[6] Ross JF, Chaudhuri PK, Ratnam M. Differential regulation of folate receptor isoforms in normal and malignant tissues in vivo and in established cell lines : physiologic and clinical implications.Cancer.1994;73(9):2432-2443.[7] Luten J,van Steenbergen MJ,Lok MC,et al.Degradable PEG-folate coated poly(DMAEA-co-BA)phosphazene-based polyplexes exhibit receptor-specific gene expression.Eur J Pharm Sci.2008;33(3):241-251.[8] Liang B,He ML,Xiao ZP,et al.Synthesis and characterization of folate-PEG-grafted-hyperbranched-PEI for tumor-targeted gene delivery.Biochem Biophys Res Commun.2008;367(4): 874-880.[9] Liu K,Wang K,Huang FS.Zhongguo Yaoye. 2005;14(2):46-48.刘凯,王昆,黄复生.前列腺素E1脂质体的制备及稳定性初步研究成果[J].中国药业,2005,14(2):46-48.[10] Lee RJ,Low PS.Delivery of liposomes into cultured KB cells via folate receptor-mediated endocytosis.J Biol Chem. 1994; 269(5):3198-204.[11] Weber C,Kreuter J,Langer K,et al.Desolvation process and surface characteristics of HSA-nanoparticles.Int J Pharm. 2000;196(2):197-200.[12] Zhang LK,Hou SX,Lu Y,et al.Zhongguo Yaoxue Zazhi. 2007;42(9):676-678.张良珂,侯世祥,卢懿,等.叶酸受体介导米托蒽醌白蛋白纳米粒的体内分布及药效学研究[J].中国药学杂志,2007,42(9):676-678.[13] Xiao SR,Tong CY,Liu XM,et al.Kexue Tongbao. 2006;51(10):1151-1155.肖苏尧,童春义,刘选明.等.肿瘤靶向性药物载体叶酸-淀粉纳米颗粒的研制与应用[J].科学通报,2006,51(10):1151-1155.[14] Guo LY,Yao JP,Sui LH.Gaodeng Xuexiao Huaxue Xuebao. 2009;30(3):474-477.郭莉媛,姚晶萍,隋丽华.白藜芦醇白蛋白纳米粒的制备及其抗卵巢癌细胞增殖作用的研究[J].高等学校化学学报,2009,30(3):474-477.[15] Yang Y.Jinri Yaoxue. 2009;19(6):57-60.杨莹.硫鸟嘌呤白蛋白纳米粒的制备[J].今日药学,2009,19(6):57-60.[16] Wu SL,Huang JG,Li G.Zhongguo Yiyuan Yaoxue Zazhi. 2009;29(7):l522-525.伍三兰,黄建耿,李高.氟尿嘧啶白蛋白磁亚微球的制备及释药特性[J].中国医院药学杂志,2009,29(7):522-525. |

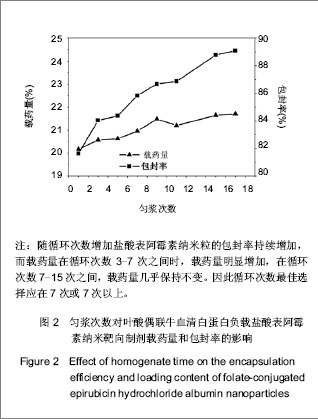
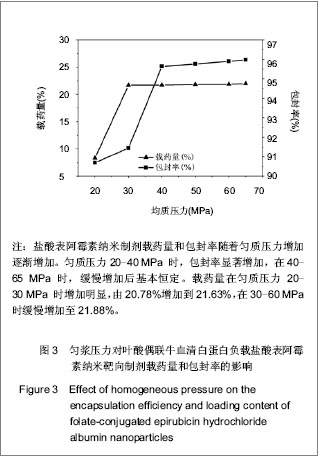

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)