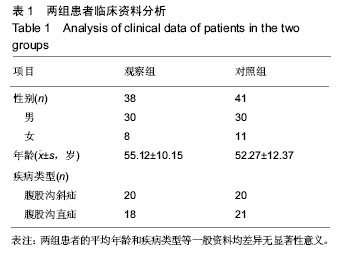
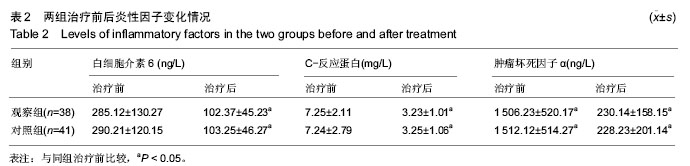
| [1] 刘永强,姚学仁,钱小刚,等.疝环充填式无张力疝修补术106例治疗体会[J].实用临床医药杂志,2008,12(9):68-69.[2] 章阳,姚玉民,张伟,等.平片式修补与疝环充填式修补在腹股沟疝无张力疝修补术中的选择探讨[J].中华疝和腹壁外科杂志(电子版),2010,4(2):125-128. [3] 丁钋,刘兴强,回建峰,等.疝环充填式无张力疝修补术的临床应用(附136例临床报告)[J].实用临床医药杂志, 2005, 9(5):126-127. [4] 刘志力,王建,何跃军,等.巴德材料疝环充填式无张力疝修补术治疗腹股沟疝268例临床体会[J].南京医科大学学报(自然科学版),2007,27(9):1059-1060. [5] Sajid MS, Ladwa N, Colucci G, et al. Diagnostic laparoscopy through deep inguinal ring: a literature-based review on the forgotten approach to visualize the abdominal cavity during emergency and elective groin hernia repair. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2013;23(3):251-254. [6] 杨涛,范警华.无张力疝环充填式修补术治疗腹股沟疝的临床体会[J].中国医疗前沿,2009,4(14):36-36. [7] 阿力木江•阿布都热衣木,马木提江•阿巴拜克热,艾武等.生物补片修补术治疗腹股沟疝疗效观察[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版),2013,(8):3593-3595. [8] 赵为元,杨庭华,丁贤章,等.巴德材料疝环充填式无张力疝修补术治疗腹股沟疝56例临床体会[J].临床军医杂志, 2006,34(1):56-58. [9] 骆聪.巴德疝环充填式无张力疝修补术治疗腹股沟疝[J].医学理论与实践,2005,18(2):171-172. [10] Tokunaga Y, Tokuka A, Ohsumi K, et al. Sigmoid colon diverticulosis adherent to mesh plug migration after open inguinal hernia repair. Cur Surg. 2001;58(5):493-494. [11] Gong K, Zhang NW, Lu YP. Comparison of the open tension-free mesh-plug,transabdominal preperitoneal (TAPP), and totally extraperitoneal (TEP) laparoscopic techniques for primary unilateral inguinal hernia repair: a prospective randomized controlled trial. Surg Endosc. 2011;25(1):234-239.[12] Xu H, Chen M, Xu Q, et al. Application of tension-free hernioplasty with hernia meshes of different materials and the postoperative effects on the reproductive function of male rats. Mol Med Rep. 2014;9(5):1968-1974. [13] 吴福宁,刘胜利,尹福君,等.疝环充填式无张力疝修补术(附203例报告)[J].天津医药,2001,29(6):369-370. [14] 杜晓辉,郑伟,李沛雨,等.疝环充填式疝修补术在腹股沟疝中的应用[J].解放军医学杂志,2001,26(12):931. [15] Mazaki T, Mado K, Masuda H, et al. A randomized trial of antibiotic prophylaxis for the prevention of surgical site infection after open mesh-plug hernia repair. Am J Surg. 2014;207(4):476-484. [16] Gonzalez Ojeda A, Anaya Prado R, Fuentes Orozco C, et al. Combined transurethral prostatectomy and mesh-based tension-free inguinal hernia repair. Hernia. 2003;7(3):141-145. [17] Al-Momani H, Stephenson BM. Comparison of mesh-plug and Lichtenstein for inguinal hernia repair: A meta- analysis of randomized controlled trials. Hernia. 2013; 17(1):151. [18] 布建中,班东杰,杜秉权,等.疝环充填式无张力疝修补术治疗腹股沟疝的应用体会[J].天津医药, 2003,31(4):243-244.[19] 黄永泰,黄文伟,黄伟超,等.疝环充填式无张力疝修补术治疗腹股沟疝的临床体会[J].中国现代医生, 2012,50(22): 138-139. [20] Lee DH, Koo KC, Lee SH, et al. A simple procedure to prevent postoperative inguinal hernia after robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: a plugging method of the internal inguinal floor for patients with patent processus vaginalis. J Urol. 2014;191(2):468-472. [21] 王力锋.巴德补片在无张力疝修补术中的应用138例分析[J].中国误诊学杂志,2011,11(6):1424-1425. [22] Gianetta E, Civalleri D, Serventi A, et al. Anterior tension-free repair under local anesthesia of abdominal wall hernias in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis patients. Hernia. 2004;8(4):354-357. [23] Gomez GG. Mesh prosthesis versus triangular flap from the anterior sheath of the abdominal rectus muscle in primary inguinal hernia repair. J Invest Surg. 2003;16(1): 45-50. [24] 袁远程,曾秀芳,吴天明,等.疝环充填式无张力疝修补术在绞窄性腹股沟疝中的应用探讨[J].医药产业资讯, 2005, 2(12):17-18. [25] 赵方有.应用疝环充填式无张力疝修补术治疗复发疝30例治疗分析[J].中国保健营养(上旬刊), 2013,23(7): 3595-3595. [26] 李贵忠,杨苏锦,胡玉蓉,等.补片填充式无张力疝修补术治疗腹股沟疝16例分析[J].中国医药导报, 2008,5(20):189-190. [27] Sarli L, Villa F, Marchesi F, et al. Hernioplasty and simultaneous laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a prospective randomized study of open tension-free versus laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair. Surgery. 2001;129(5):530-536. [28] Jiang DZ, Qiu M, Zheng XM, et al. Comparative study of open tension-free and laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair in hernioplasty and simultaneous laparoscopic cholecystectomy. J Med Colleges PLA. 2006;21(2): 129-132. [29] Gong K, Zhang N, Lu Y, et al. Comparison of the open tension-free mesh-plug, transabdominal preperitoneal (TAPP), and totally extraperitoneal (TEP) laparoscopic techniques for primary unilateral inguinal hernia repair: a prospective randomized controlled trial. Surg Endosc. 2011;25(1):234-239. [30] Bringman S, Ramel S, Heikkinen TJ, et al. Tension-free inguinal hernia repair: TEP versus mesh-plug versus Lichtenstein: a prospective randomized controlled trial. Ann Surg. 2003;237(1):142-147. [31] 冯伟.巴德疝环充填式无张力疝修补术治疗老年腹股沟疝119例临床分析[J].吉林医学,2013,34(33):6911.[32] Hirabayashi T, Sakoda A, Kawano A, et al. Ventrally dislocated attachment of the ovarian suspensory ligament, a risk factor for tubal occlusion as a postoperative complication of inguinal hernia repair: efficacy of laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair for preventing tubal damage. Pediatr Surg Int. 2012; 28(11): 1089-1094. [33] Sanders DL, Samarakoon DH, Ganshirt SW, et al. A two-centre blinded randomised control study comparing the Lichtenstein patch, Perfix plug and ProLoop plug in the repair of primary inguinal hernia. Hernia. 2009;13(5):499-503. [34] 黄培贵,吴国忠,刘华安,等.疝环充填式无张力修补术在腹股沟疝中的应用分析(附126例报告)[J].医药产业资讯, 2005,2(8):48-49. [35] Khoury N. A randomized prospective controlled trial of laparoscopic extraperitoneal hernia repair and mesh-plug hernioplasty: a study of 315 cases. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 1998;8(6):367-372. [36] Pikoulis E, Tsigris C, Diamantis T, et al. Laparoscopic preperitoneal mesh repair or tension-free mesh plug technique? A prospective study of 471 patients with 543 inguinal hernias. Eur J Surg. 2002;168(11): 587-591. [37] 胡刚.疝环充填式无张力疝修补术治疗老年男性腹股沟疝[J].内蒙古中医药,2011,30(7):30-31.[38] Prieto Diaz Chavez E, Medina Chavez JL, Anaya Prado R, et al. A cost-effectiveness analysis of tension-free versus shouldice inguinal hernia repair: a randomized double-blind clinical trial. Hernia. 2009; 13(3):233-238. [39] 马宁钢.疝环充填式无张力腹股沟疝修补术41例临床体会[J].吉林医学,2011,32(28):5991-5992.[40] 林舜国,池畔,林梃,等.涤纶补片与巴德网塞网片在腹股沟疝无张力疝修补术中的应用[J].福建医科大学学报, 2001, 35(1):70-71. |
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)