中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (16): 2418-2424.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.16.019
• 纳米生物材料 nanobiomaterials • 上一篇 下一篇
纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66盖髓对造牙本质细胞及微血管的影响
佟玮玮,王健平,赵千宁,苏 丹,于彦衡
- 佳木斯大学附属口腔医院,黑龙江省佳木斯市 154002
Nano-hydroxyapatite/polyamide 66 as a direct pulp capping agent has effects on histological changes of odontoblasts and microvessels
Tong Wei-wei, Wang Jian-ping, Zhao Qian-ning, Su Dan, Yu Yan-heng
- Affiliated Stomatology Hospital of Jiamusi University, Jiamusi 154002, Heilongjiang Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
造牙本质细胞:是终末分化细胞,最后一次有丝分裂后期细胞发生极化,细胞骨架重排,分泌前期牙本质,同时牙本质特异蛋白,包括牙本质磷蛋白、牙本质唾蛋白及牙本质基质蛋白。修复牙本质形成过程中形成的新一代造牙本质样细胞与原发的成牙本质细胞是否具有相同的表型还不清楚,通过纤维连接蛋白植入牙髓后的观察,认为与原发的造牙本质细胞一致。目前造牙本质样细胞的评价标准还没有确定,但由于其能分泌极化的前期牙本质,所以虽然细胞并没有出现极化,但通常被认为是新的造牙本质细胞。
纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66复合物:是一种新型人体硬组织替代材料,已被实验证实有较好的生物相容性、生物活性和生物安全性。研究表明,纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66复合物具有用作根充材料的基本理化性能,对感染髓腔有抗菌性,对细胞无细胞毒性,但将其引入牙髓治疗方面用直接盖髓剂方面的研究还比较片面。
背景:前期研究表明,纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66复合物具有用作根充材料的基本理化性能,对感染髓腔有抗菌性,对细胞无细胞毒性,但将其作为直接盖髓剂的研究还比较片面。
目的:观察纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66复合物用作盖髓剂的组织学反应。
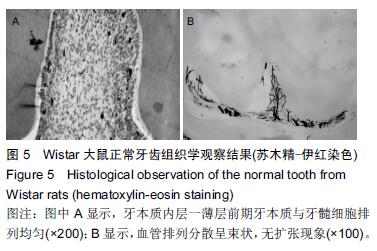
方法:取Wistar大鼠12只,在上下颌第一、二臼齿做Ⅰ类洞至露髓,随机分3组,分别采用纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66复合物、纳米羟基磷灰石、氢氧化钙盖髓,均以玻璃离子充填。充填后7,30 d处死动物,采用血管墨汁灌注法观察牙本质细胞和牙髓微血管组织学变化。
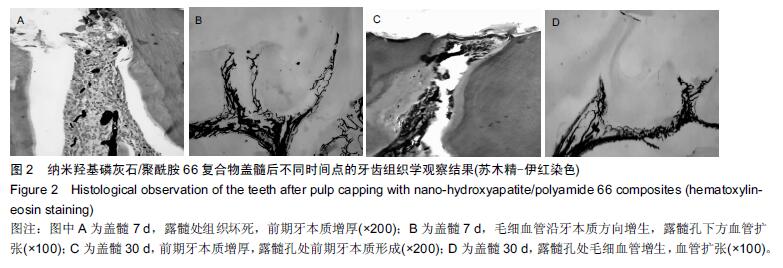
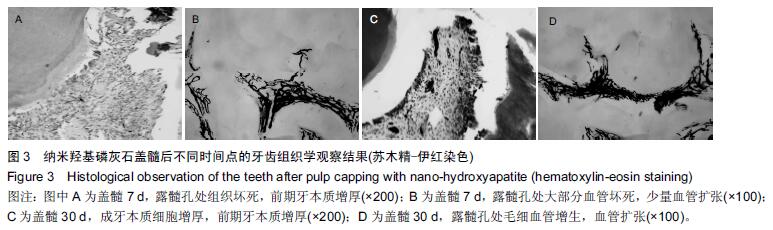
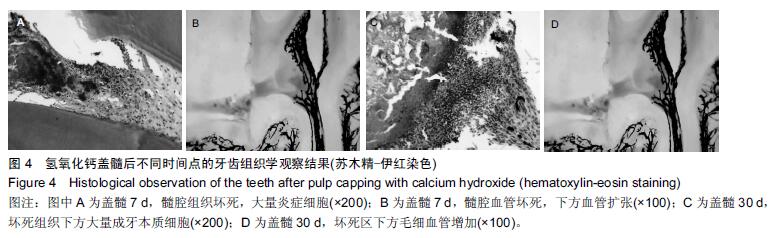
结果与结论:①充填后7 d:纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66复合物组牙髓纤维细胞增生,前期牙本质增厚,血管扩张明显;纳米羟基磷灰石组牙髓纤维细胞增生,前期牙本质无明显增厚,血管扩张;氢氧化钙组髓室大部牙髓组织坏死,下方牙髓纤维细胞增生明显,有一定炎症细胞浸润,血管坏死;②充填后30 d:纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66复合物组盖髓下方前期牙本质增厚明显,牙髓纤维细胞增生,成牙本质细胞增加,血管扩张;纳米羟基磷灰石组前期牙本质增厚,血管扩张明显;氢氧化钙组穿髓孔下牙髓表面坏死团块,牙髓交界处成牙本质细胞活跃牙本质壁上前期牙本质无明显增厚,坏死区下方血管密集;③结果表明:纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66复合物具有诱导牙髓细胞再生的作用。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程 ORCID: 0000-0001-5692-1333(佟玮玮)
.jpg)
.jpg)