| [1] Kobolak J, Dinnyes A, Memic A, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells: Identification, phenotypic characterization, biological properties and potential for regenerative medicine through biomaterial micro-engineering of their niche. Methods. 2015. in press.[2] 文亚男,郭明广,邓锦波.骨髓间充质干细胞研究进展[J].河南大学学报(自然科学版),2015,45(1):63-67.[3] Baker N, Boyette LB, Tuan RS. Characterization of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in aging. Bone. 2015;70:37-47. [4] Coelho MJ, Fernandes MH. Human bone cell cultures in biocompatibility testing. Part II: effect of ascorbic acid, beta-glycerophosphate and dexamethasone on osteoblastic differentiation. Biomaterials. 2000;21(11): 1095-1102.[5] Wang X, Wang Y, Gou W, et al. Role of mesenchymal stem cells in bone regeneration and fracture repair: a review. Int Orthop. 2013;37(12):2491-2498. [6] 蒋晓帆,丁然然,姜汉国,等.Notch信号与心脏干细胞关系的研究进展[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2014,36(6): 818-825.[7] Zhou PY, Peng GH, Xu H, et al. c-Kit? cells isolated from human fetal retinas represent a new population of retinal progenitor cells. J Cell Sci. 2015;128(11): 2169-2178.[8] Barile L, Cerisoli F, Frati G, et al. Bone marrow-derived cells can acquire cardiac stem cells properties in damaged heart. J Cell Mol Med. 2011;15(1):63-71.[9] Ding R, Jiang X, Ha Y, et al. Activation of Notch1 signalling promotes multi-lineage differentiation of c-Kit(POS)/NKX2.5(POS) bone marrow stem cells: implication in stem cell translational medicine. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;6:91.[10] Khan M, Mohsin S, Khan S, et al. Lin-c-kit(+) BM-derived stem cells repair Infarcted Heart. J Stem Cells Regen Med. 2010;6(1):15-25.[11] Kubo H, Berretta RM, Jaleel N, et al. c-Kit+ bone marrow stem cells differentiate into functional cardiac myocytes. Clin Transl Sci. 2009;2(1):26-32.[12] 栗扬阳,赵庆华.不同因子影响骨髓间充质干细胞的多向分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(23):4299-4305.[13] Chen BY, Wang X, Chen LW, et al. Molecular targeting regulation of proliferation and differentiation of the bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells or mesenchymal stromal cells. Curr Drug Targets. 2012; 13(4):561-571.[14] Alketbi A, Attoub S. Notch Signaling in Cancer: Rationale and Strategies for Targeting. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2015;15(5):364-374.[15] Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Matsuno K, Fortini ME. Notch signaling. Science. 1995;268(5208):225-232.[16] Weinmaster G. The ins and outs of notch signaling. Mol Cell Neurosci. 1997;9(2):91-102.[17] Tu X, Chen J, Lim J, et al. Physiological notch signaling maintains bone homeostasis via RBPjk and Hey upstream of NFATc1. PLoS Genet. 2012;8(3): e1002577.[18] Ng P, Parks RJ, Cummings DT, et al. A high-efficiency Cre/loxP-based system for construction of adenoviral vectors. Hum Gene Ther. 1999;10(16):2667-2672.[19] Li X, Zhang Y, Qi G. Evaluation of isolation methods and culture conditions for rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Cytotechnology. 2013; 65(3):323-334.[20] 何志义,原丽英,陈晏,等.大鼠骨髓基质细胞的体外分离?培养和鉴定的实验研究[J].中国医科大学学报,2004, 33(5):395-396.[21] Ikebe C, Suzuki K. Mesenchymal stem cells for regenerative therapy: optimization of cell preparation protocols. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:951512.[22] 陈欢意,牛平,赵帅,等.改良贴壁培养法简单的骨髓基质干细胞分离纯化法[J].解剖科学进展,2007,13(2):190.[23] van der Spoel TI, Jansen of Lorkeers SJ, Agostoni P, et al. Human relevance of pre-clinical studies in stem cell therapy: systematic review and meta-analysis of large animal models of ischaemic heart disease. Cardiovasc Res. 2011;91(4):649-658.[24] Kim J, Shapiro L, Flynn A. The clinical application of mesenchymal stem cells and cardiac stem cells as a therapy for cardiovascular disease. Pharmacol Ther. 2015;151:8-15.[25] Telukuntla KS, Suncion VY, Schulman IH, et al. The advancing field of cell-based therapy: insights and lessons from clinical trials. J Am Heart Assoc. 2013; 2(5):e000338.[26] Smits AM, van Vliet P, Hassink RJ, et al. The role of stem cells in cardiac regeneration. J Cell Mol Med. 2005;9(1):25-36.[27] He JQ, Vu DM, Hunt G, et al. Human cardiac stem cells isolated from atrial appendages stably express c-kit. PLoS One. 2011;6(11):e27719.[28] 孙丽莉,谭玉珍,王海杰,等.骨髓间充质干细胞的克隆培养及其向心肌细胞的诱导分化[J].复旦学报(医学版), 2003, 30(6):519-523.[29] 薛静,彭江,张莉,等.绿色荧光蛋白和Nel1型蛋白基因共表达腺病毒载体的构建及体外转染大鼠BMSCs的初步实验研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2010,24(5):606-612.[30] Zhang Z, Yan R, Zhang Q, et al. Hes1, a Notch signaling downstream target, regulates adult hippocampal neurogenesis following traumatic brain injury. Brain Res. 2014;1583:65-78.[31] Ross DA, Rao PK, Kadesch T. Dual roles for the Notch target gene Hes-1 in the differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 2004;24(8):3505-3513.[32] Su F, Zhang W, Liu J. Membrane estrogen receptor alpha is an important modulator of bone marrow C-Kit+ cells mediated cardiac repair after myocardial infarction. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8(5):4284-4295. |
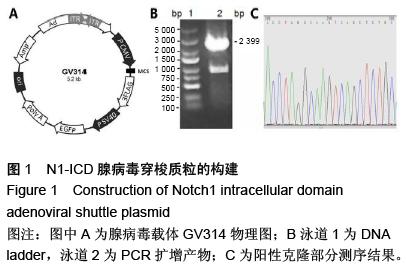
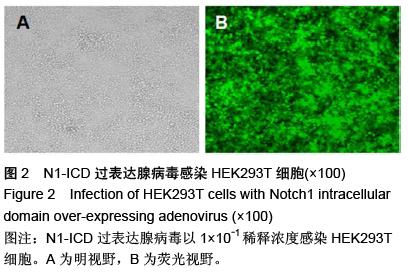
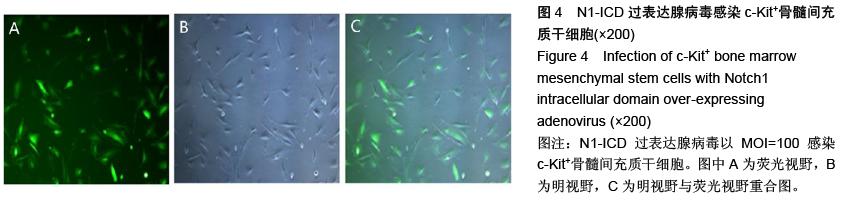
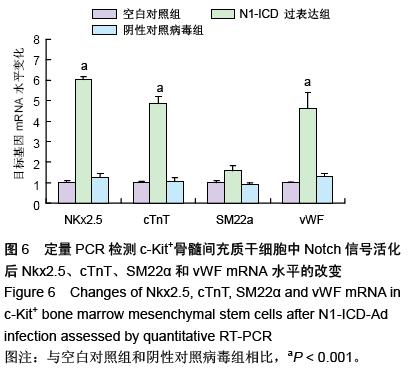
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)